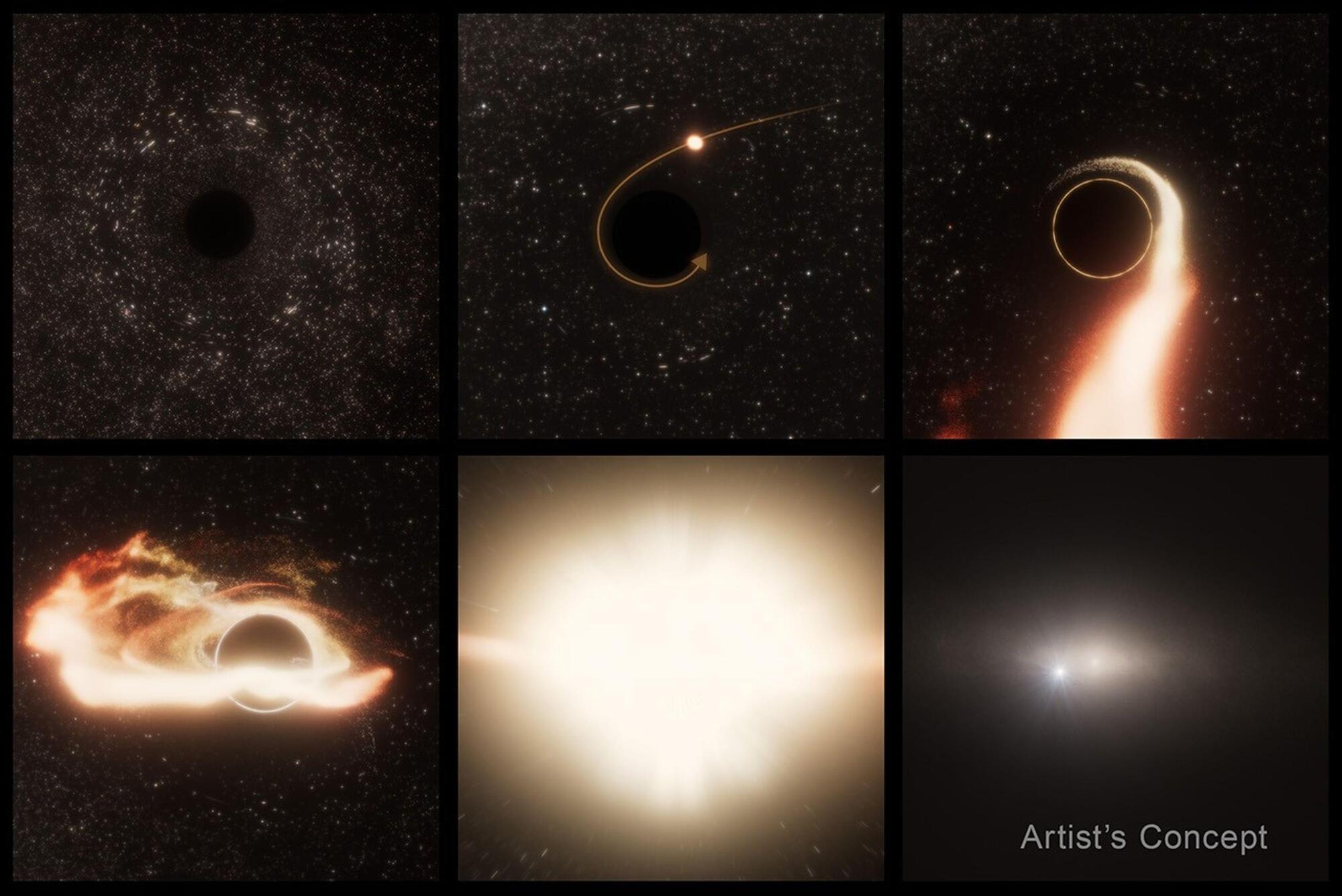
Like a scene out of a sci-fi movie, astronomers using NASA telescopes have found “Space Jaws.” Lurking 600 million light-years away, within the inky black depths between stars, there is an invisible monster gulping down any wayward star that plummets toward it. The sneaky black hole betrayed its presence in a newly identified tidal disruption event (TDE) where a hapless star was ripped apart and swallowed in a spectacular burst of radiation.
These disruption events are powerful probes of black hole physics, revealing the conditions necessary for launching jets and winds when a black hole is in the midst of consuming a star, and are seen as bright objects by telescopes.
The new TDE, called AT2024tvd, allowed astronomers to pinpoint a wandering supermassive black hole using NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, with similar supporting observations from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and the NRAO Very Large Array telescope that also showed that the black hole is offset from the center of the galaxy.