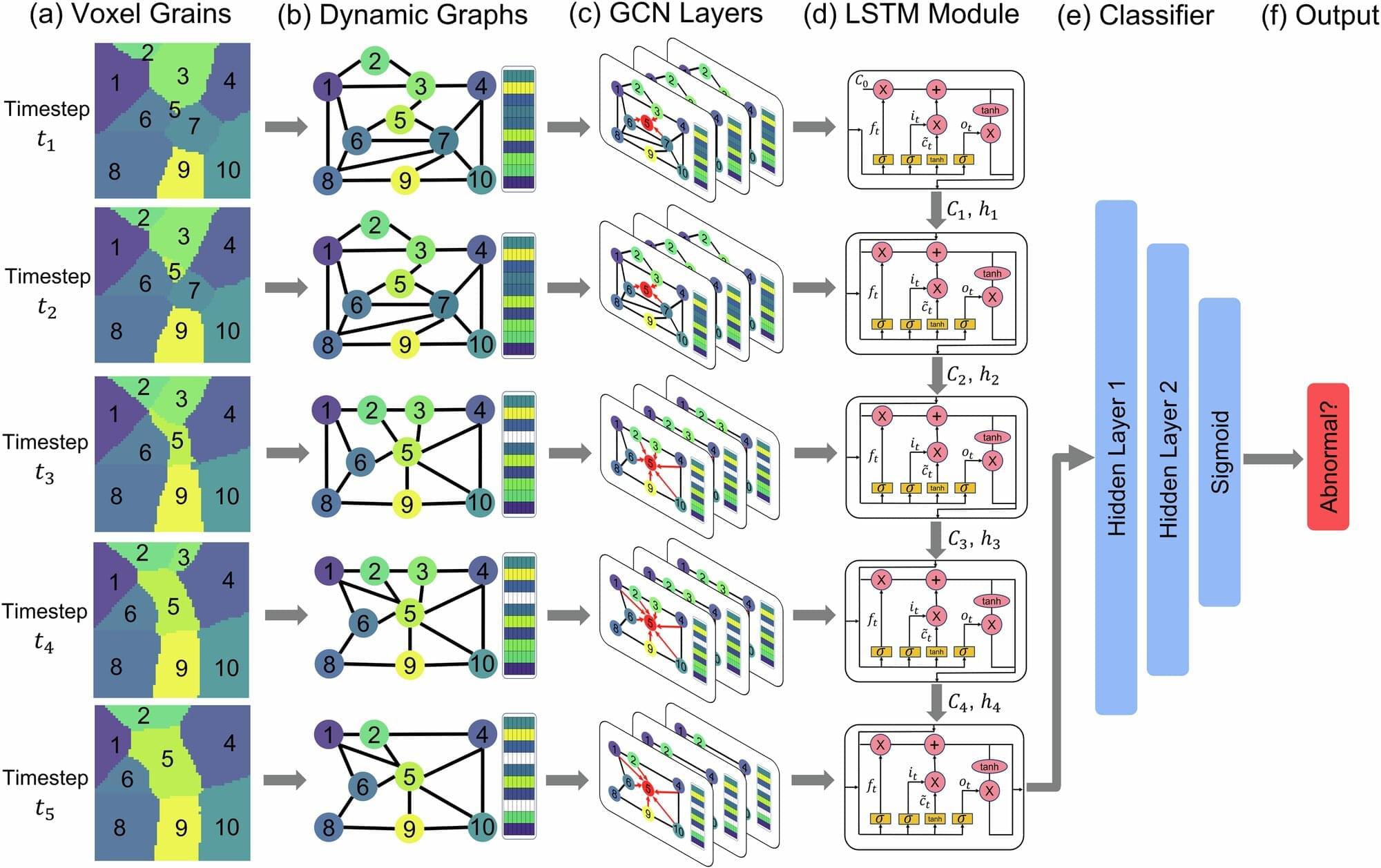
A team of Lehigh University researchers has successfully predicted abnormal grain growth in simulated polycrystalline materials for the first time—a development that could lead to the creation of stronger, more reliable materials for high-stress environments, such as combustion engines. A paper describing their novel machine learning method was recently published in Nature Computational Materials.
“Using simulations, we were not only able to predict abnormal grain growth, but we were able to predict it far in advance of when that growth happens,” says Brian Y. Chen, an associate professor of computer science and engineering in Lehigh’s P.C. Rossin College of Engineering and Applied Science and a co-author of the study. “In 86% of the cases we observed, we were able to predict within the first 20% of the lifetime of that material whether a particular grain will become abnormal or not.”
When metals and ceramics are exposed to continuous heat—like the temperatures generated by rocket or airplane engines, for example—they can fail. Such materials are made of crystals, or grains, and when they’re heated, atoms can move, causing the crystals to grow or shrink. When a few grains grow abnormally large relative to their neighbors, the resulting change can alter the material’s properties. A material that previously had some flexibility, for instance, may become brittle.