Researchers at Albany Medical College in New York have discovered that a specific type of immune cell accumulates in older brains, and that activating these cells improves the memory of aged mice. The study, which will be published on February 5, 2020, in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), suggests that targeting these cells might reduce age-related cognitive decline and combat aging-associated neurodegenerative disease in humans.
The brain is highly susceptible to aging, with cognitive functions, such as learning and memory, gradually declining as we get older. Much of the body’s immune system also deteriorates with age, resulting in increased susceptibility to infection and higher levels of inflammation. In their new JEM study, however, a team of researchers led by Qi Yang and Kristen L. Zuloaga at Albany Medical College reveal that aging-related changes in a class of immune cell known as group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) could allow doctors to combat the effects of aging on the brain.
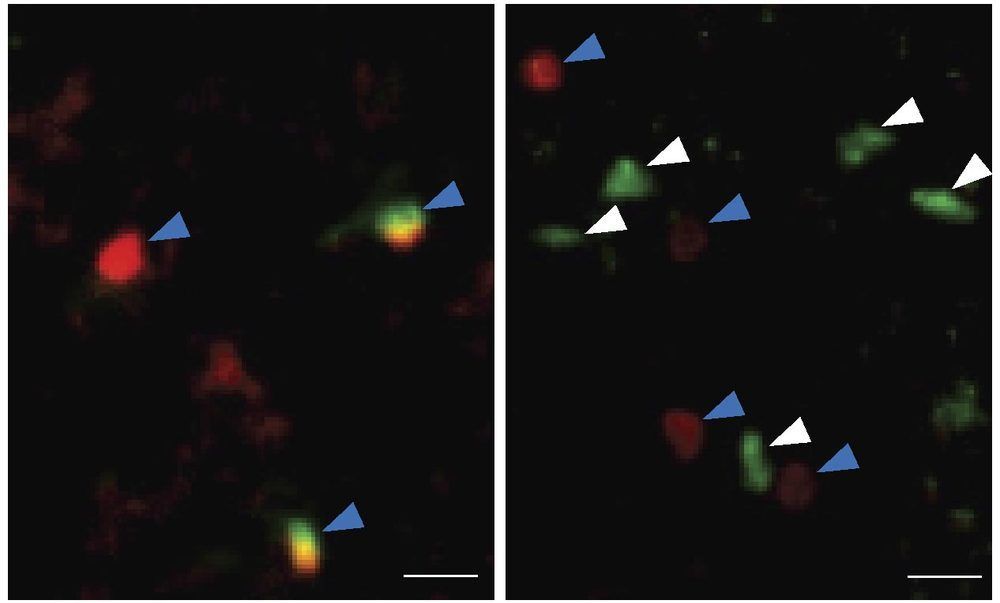
ILC2s reside in specific tissues of the body and help to repair them when they are damaged. Recently, for example, ILC2s in the spinal cord were shown to promote healing after spinal cord injury. “However, whether ILC2s also reside in other parts of the central nervous system, and how they respond to aging, was unknown,” Yang says.