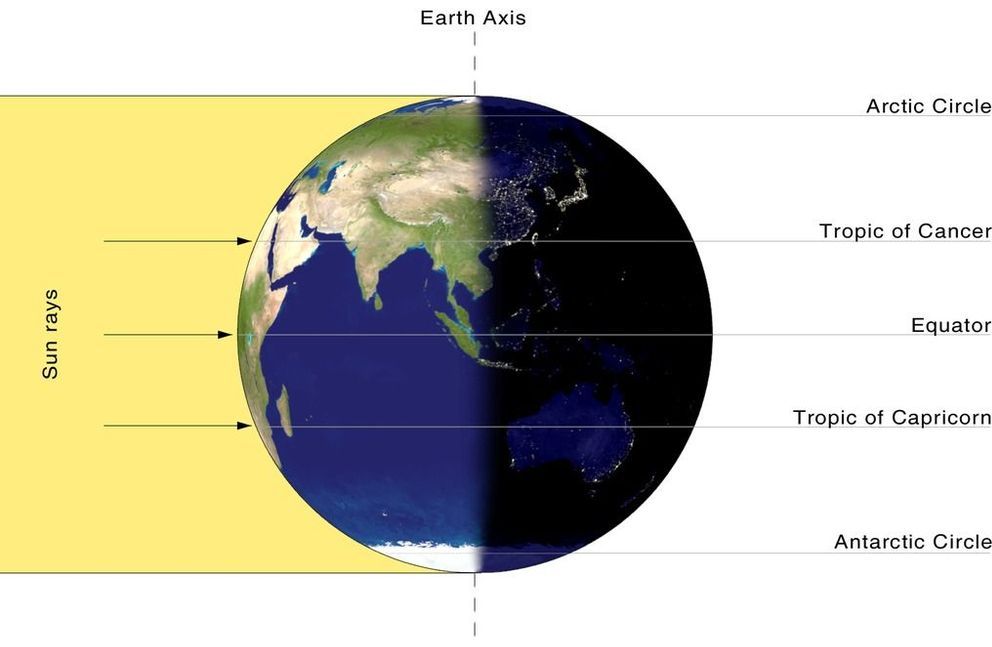
No one has seen an equinox this early since the 19th century: March 19 everywhere in the USA. And you’d better get used to it.
Let’s say it was possible to buy your health by the day. How much would you be willing to pay for each year of perfect health? What if you could buy years of health for your loved ones, too? At what price point would you draw the line?
This sort of difficult calculus, on a much larger and chronologically longer scale, underpins many decisions we make in medicine — not just decisions that we make as patients, but also the decisions that are made for us by employers, health insurance funders and policymakers. We don’t have the resources to pursue every possible treatment, to research every possible breakthrough, so how do we allocate the resources available? It turns out that there is an entire field of healthcare economics devoted to understanding the costs and benefits of conventional medicine, and to navigating the trade-offs between more expense and better healthcare.
Determining the costs and benefits of new areas like genomic medicine is especially tricky, because we have so much less experience in these areas, and even experts cannot yet fully agree on the spectrum of harms and benefits.
Researchers from AgeX Therapeutics and other organizations have proved the feasibility of reprogramming banked cells derived from a supercentenarian. Their discovery portends exciting new possibilities for aging research.
What is cellular reprogramming?
Cellular reprogramming is the process of reverting mature, specialized cells into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which can develop into any cell type found in the human body. Cellular reprogramming technology was pioneered in 2006 by Drs. Takahashi and Yamanaka, who achieved this impressive result by overexpressing just four genes, Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc (OSKM), which became collectively known as the Yamanaka factors. For this breakthrough, Yamanaka was awarded the Nobel Prize in 2012. Fun fact: Yamanaka called these cells iPSCs – with a small “i” – as a nod to the iPod and similarly named devices.
What do you think?
In science fiction stories, research can accidentally create superintelligent animal species. As the ability to alter animals’ brains grows, some say we should be wary of fiction becoming reality.
University of Exeter team make senescent cells look younger and begin to divide while exhibiting longer telomeres to reduce cellular aging.
Circa 2016 o.o
The federal government just proposed new rules that would allow researchers to grow human-animal hybrids for research, so long as they can’t think, feel, or breed.
The news did not sit well with Chinese scientists, who are still recovering from the CRISPR baby scandal. “It makes you wonder, if their reason for choosing to do this in a Chinese laboratory is because of our high-tech experimental setups, or because of loopholes in our laws?” lamented one anonymous commentator on China’s popular social media app, WeChat.
Their frustration is understandable. Earlier in April, a team from southern China came under international fire for sticking extra copies of human “intelligence-related” genes into macaque monkeys. And despite efforts to revamp its reputation in biomedical research ethics, China does have slacker rules in primate research compared to Western countries.
If you’re feeling icked out, you’re not alone. The morality and ethics of growing human-animal hybrids are far from clear. But creepiness aside, scientists do have two reasons for wading into these uncomfortable waters.
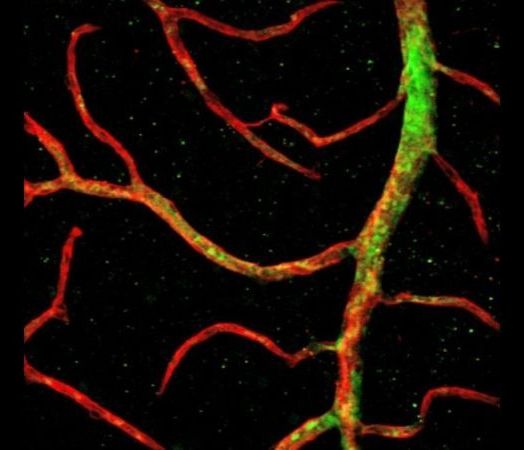
Human vascular progenitor cells (green), made from Zambidis’ lab-grown naive stem cells, engraft into blood vessels (red) in a mouse retina. Credit: Elias Zambidis, Johns Hopkins Medicine.
O„.o.
So much emphasis has been placed on human genome editing that other types of genetic editing are falling through the cracks.
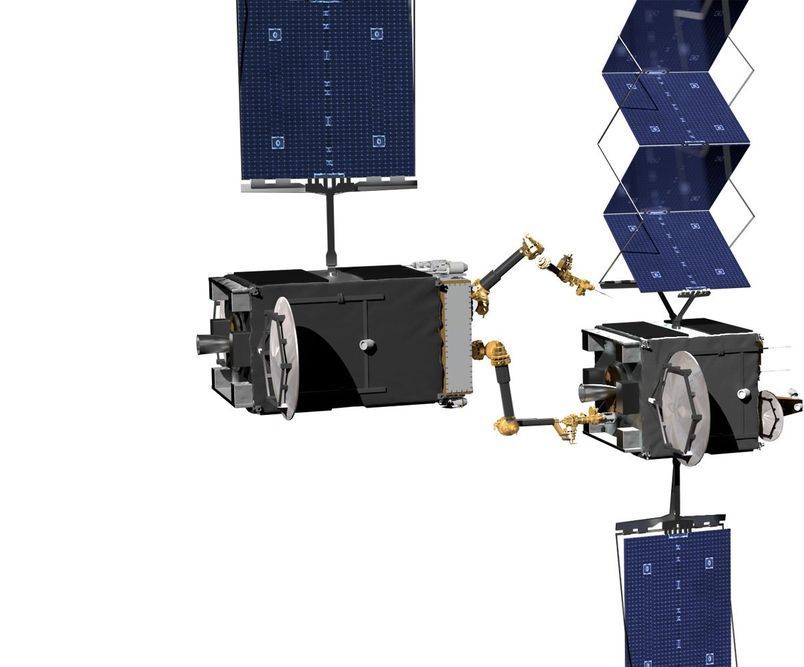
DARPA has entered into a partnership with Northrop Grumman subsidiary Space Logistics LLC to develop robotic technologies for servicing and extending the service lives of orbital satellites. Based on the Mission Extension Vehicle-1 (MEV-1), which recently docked with a communication satellite in geosynchronous orbit, the technology will be used by the agency’s Robotic Servicing of Geosynchronous Satellites (RSGS) program to develop a dexterous robotic servicer that would be operated by private companies.
Founded in 2016, the RSGS program completed a Payload Critical Design Review in 2019 and is developing key technologies in the run up to the first space launch scheduled for 2023. As part of this effort, DARPA says it is funding the US Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) to bring together components like the robotic manipulator arms, a variety of interchangeable tools, cameras, sensors, software, and avionics into a functioning robotic payload.
Meanwhile, Space Logistics will provide the spacecraft bus based on the MEV and integrate the robotic payload, as well as providing launch and orbital operation services. Once the spacecraft has been checked out and demonstrated its capabilities, the technology will be marketed to commercial and government organizations.