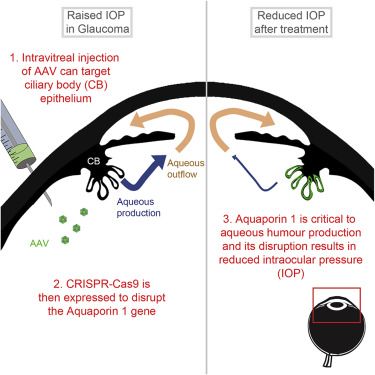
3 minutes for glaucoma eye surgery.
Cataract and glaucoma are eye diseases that progress by aging. Both are severe diseases that can cause blindness, but in Japan, unique treatment methods and causes are being investigated. For cataracts, the world is paying attention to a Japanese doctor who has devised an innovative surgical method which is in just over 3 minutes. And distinctive research is progressing at Japanese universities as to what kind of ingredients can delay the progression of glaucoma. How can we save people from blindness? Explore with us the forefront of Japanese ophthalmic medical care.