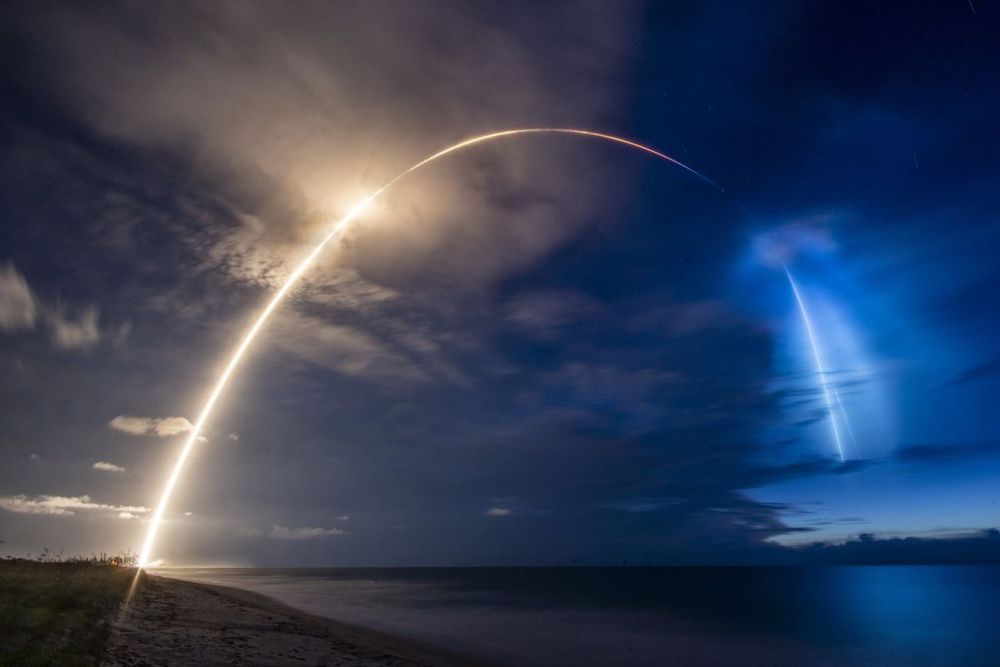
SpaceX successfully launched its first Starlink rideshare mission into orbit today (June 13), lofting 58 Starlink internet satellites along with three Earth-observation satellites before nailing a rocket landing at sea.


The human brain operates on roughly 20 watts of power (a third of a 60-watt light bulb) in a space the size of, well, a human head. The biggest machine learning algorithms use closer to a nuclear power plant’s worth of electricity and racks of chips to learn.
That’s not to slander machine learning, but nature may have a tip or two to improve the situation. Luckily, there’s a branch of computer chip design heeding that call. By mimicking the brain, super-efficient neuromorphic chips aim to take AI off the cloud and put it in your pocket.
The latest such chip is smaller than a piece of confetti and has tens of thousands of artificial synapses made out of memristors—chip components that can mimic their natural counterparts in the brain.
Every second of every day, countless biochemical reactions take place in our bodies’ cells. The organization of this complex system is the result of billions of years of evolution, fine-tuning our functions since the first primordial organisms.
One such vital reaction is “methylation,” where a methyl group —a carbon atom linked to three hydrogen atoms—attaches itself to a target molecule. Methylation is involved in the regulation of everything from DNA to proteins, and it is so vital that it can be found in all living organisms.
In a recent paper published in Communications Biology, a team of researchers lead by Jean-Michel Fustin and Hitoshi Okamura from Kyoto University’s Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences has uncovered an intimate connection between methylation and the body’s circadian rhythms: a link that exists even in organisms that don’t traditionally “sleep,” such as bacteria.
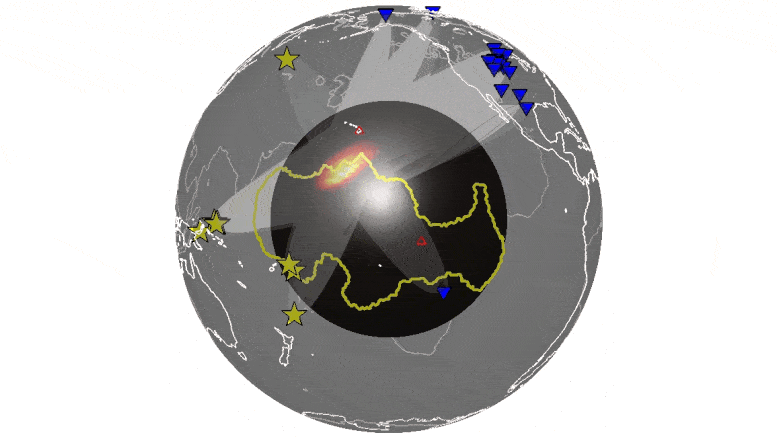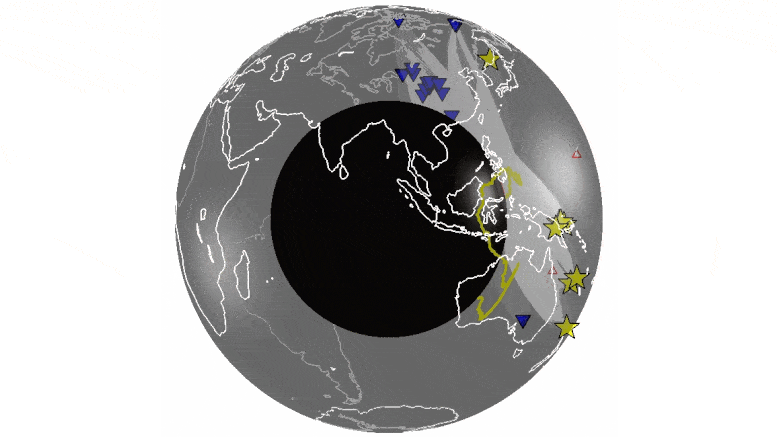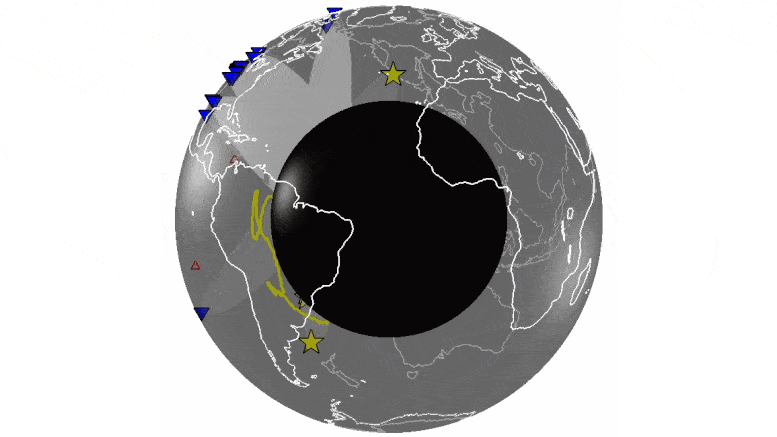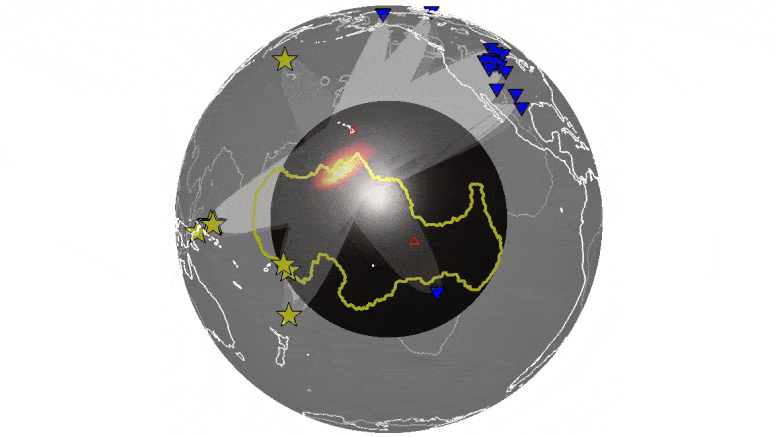
University of Maryland researchers conduct first simultaneous analysis of hundreds of earthquakes to identify echoes from features deep inside Earth.
University of Maryland geophysicists analyzed thousands of recordings of seismic waves, sound waves traveling through the Earth, to identify echoes from the boundary between Earth’s molten core and the solid mantle layer above it. The echoes revealed more widespread, heterogenous structures—areas of unusually dense, hot rock—at the core-mantle boundary than previously known.
Scientists are unsure of the composition of these structures, and previous studies have provided only a limited view of them. Better understanding their shape and extent can help reveal the geologic processes happening deep inside Earth. This knowledge may provide clues to the workings of plate tectonics and the evolution of our planet.
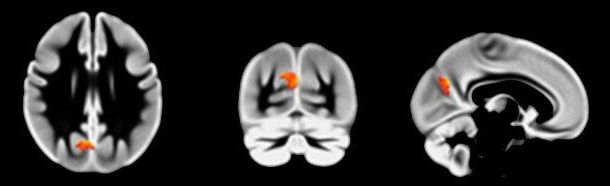
Being a late-riser suggests you could have more grey matter in your brain, a study from Brunel University London has shown.
A new survey of thousands of MRI scans revealed that people with a preference for waking up in the late hours of one morning, and going to bed in the early hours of the next, are likely to have a higher volume of grey matter in their precuneus, a key area of the brain associated with social behaviour.
Previous studies have shown that lower volumes of grey matter are associated with how empathetic or cooperative a person is, traits that scientists have also previously found correlate with being an early bird, suggesting such personality traits could be underpinned by a physical signature.
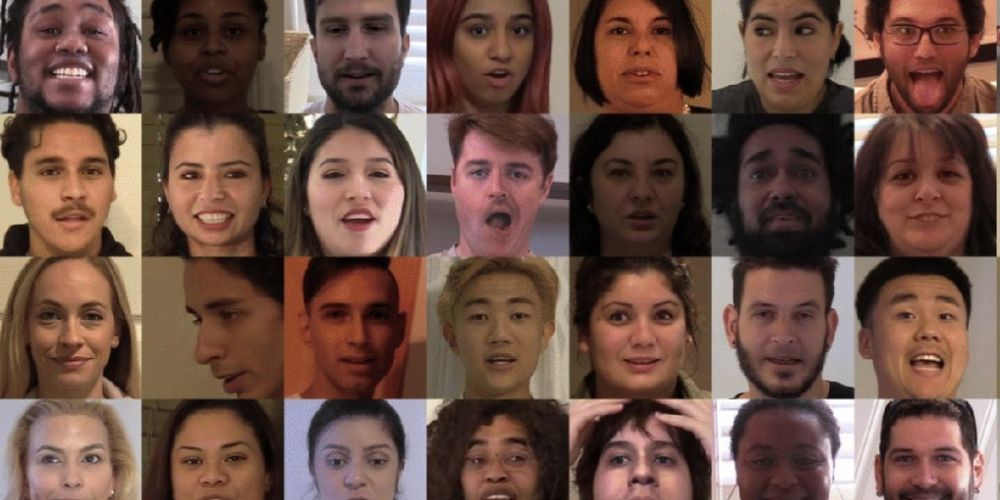

Deepfakes have struck a nerve with the public and researchers alike. There is something uniquely disturbing about these AI-generated images of people appearing to say or do something they didn’t.
With tools for making deepfakes now widely available and relatively easy to use, many also worry that they will be used to spread dangerous misinformation. Politicians can have other people’s words put into their mouths or made to participate in situations they did not take part in, for example.
That’s the fear, at least. To a human eye, the truth is that deepfakes are still relatively easy to spot. And according to a report from cybersecurity firm DeepTrace Labs in October 2019, still the most comprehensive to date, they have not been used in any disinformation campaign. Yet the same report also found that the number of deepfakes posted online was growing quickly, with around 15,000 appearing in the previous seven months. That number will be far larger now.

Accelerating progress in neuroscience is helping us understand the big picture—how animals behave and which brain areas are involved in bringing about these behaviors—and also the small picture—how molecules, neurons, and synapses interact. But there is a huge gap of knowledge between these two scales, from the whole brain down to the neuron.
A team led by Christos Papadimitriou, the Donovan Family Professor of Computer Science at Columbia Engineering, proposes a new computational system to expand the understanding of the brain at an intermediate level, between neurons and cognitive phenomena such as language. The group, which includes computer scientists from Georgia Institute of Technology and a neuroscientist from the Graz University of Technology, has developed a brain architecture that is based on neuronal assemblies, and they demonstrate its use in the syntactic processing in the production of language; their model, published online June 9 in PNAS, is consistent with recent experimental results.
“For me, understanding the brain has always been a computational problem,” says Papadimitriou, who became fascinated by the brain five years ago. “Because if it isn’t, I don’t know where to start.”
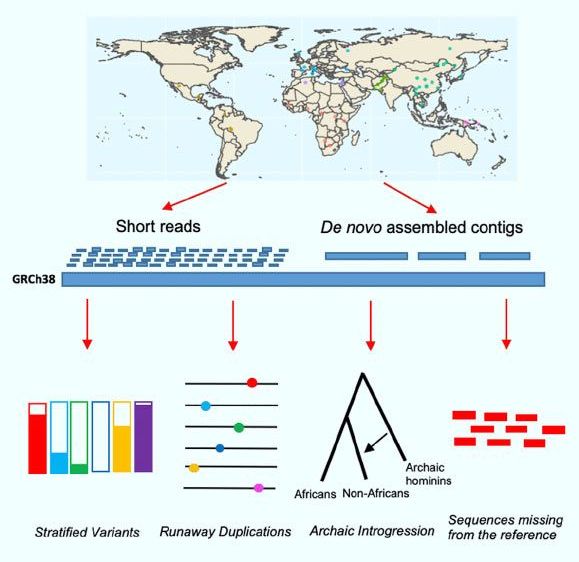
A team of scientists from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the Francis Crick Institute, and EMBL-EBI has created a comprehensive structural variation atlas for a geographically diverse set of human genomes and recovered sequences missing from the human reference sequence. Among the 126,018 structural variations discovered by the team were medically-important genes in Oceanian populations that were inherited from Denisovans, a sister group to Neanderthals.
The world’s largest atom smasher has “given birth” to a set of four ultraheavy particles — called top quarks.
The formation of these chubby-but-tiny quadruplets, at the Large Hadron Collider in Geneva, Switzerland, has long been predicted by the Standard Model, the prevailing physics theory that governs subatomic interactions. But new physics theories suggest they could be created much more often than the Standard Model predicts. Finding more of such foursomes is the first step in testing those theories. The new findings were announced at the LHCP 2020 Conference.
