A new report says that chips made by TSMC Arizona are being sent back to Taiwan for packaging, fulfilling demand coming from the AI markets.


Together, Spirit and Opportunity represented the Mars Exploration Rover Mission (MER)—itself part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program.
The twin missions’ main scientific objective was to search for a range of rocks and soil types and then look for clues for past water activity on Mars. Each rover, about the size of a golf cart and seven times heavier (408 pounds or 185 kilograms) than the Sojourner rover on Mars, was targeted to opposite sides of the planet in locales that were suspected of having been affected by liquid water in the past.
The plan was for the rovers to move from place to place and to perform on-site geological investigations and take photographs with mast-mounted cameras (about five feet or 1.5 meters off the ground) providing 360-degree stereoscopic views of the terrain.
To manufacture the human pancreatic islets, the research team had to fine-tune the settings of the 3D printer.
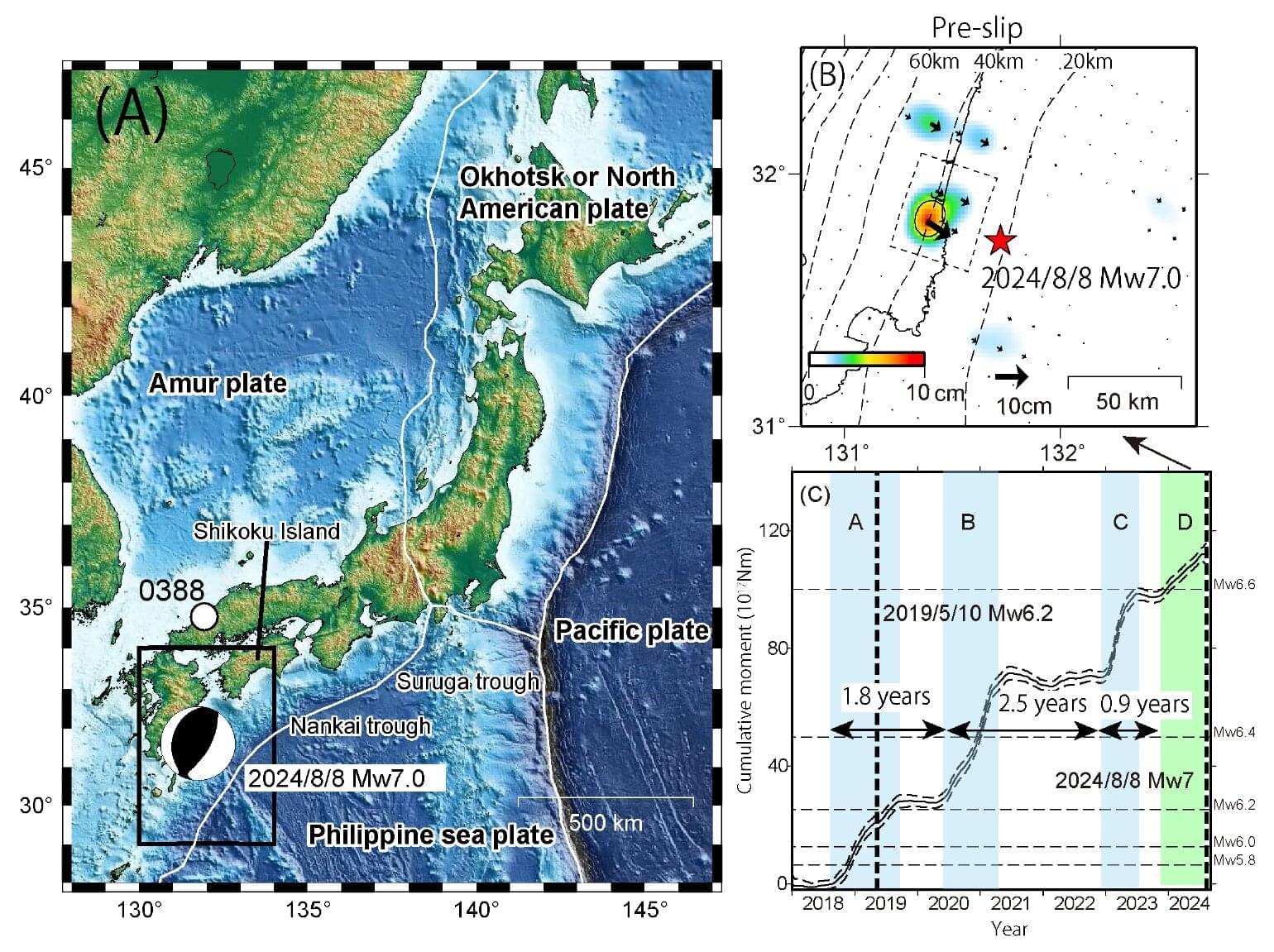
Scientists for the first time have detected a slow slip earthquake in motion during the act of releasing tectonic pressure on a major fault zone at the bottom of the ocean.
The slow earthquake was recorded spreading along the tsunami-generating portion of the fault off the coast of Japan, behaving like a tectonic shock absorber. Researchers from The University of Texas at Austin described the event as the slow unzipping of the fault line between two of the Earth’s tectonic plates.
Their results were published in Science.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/
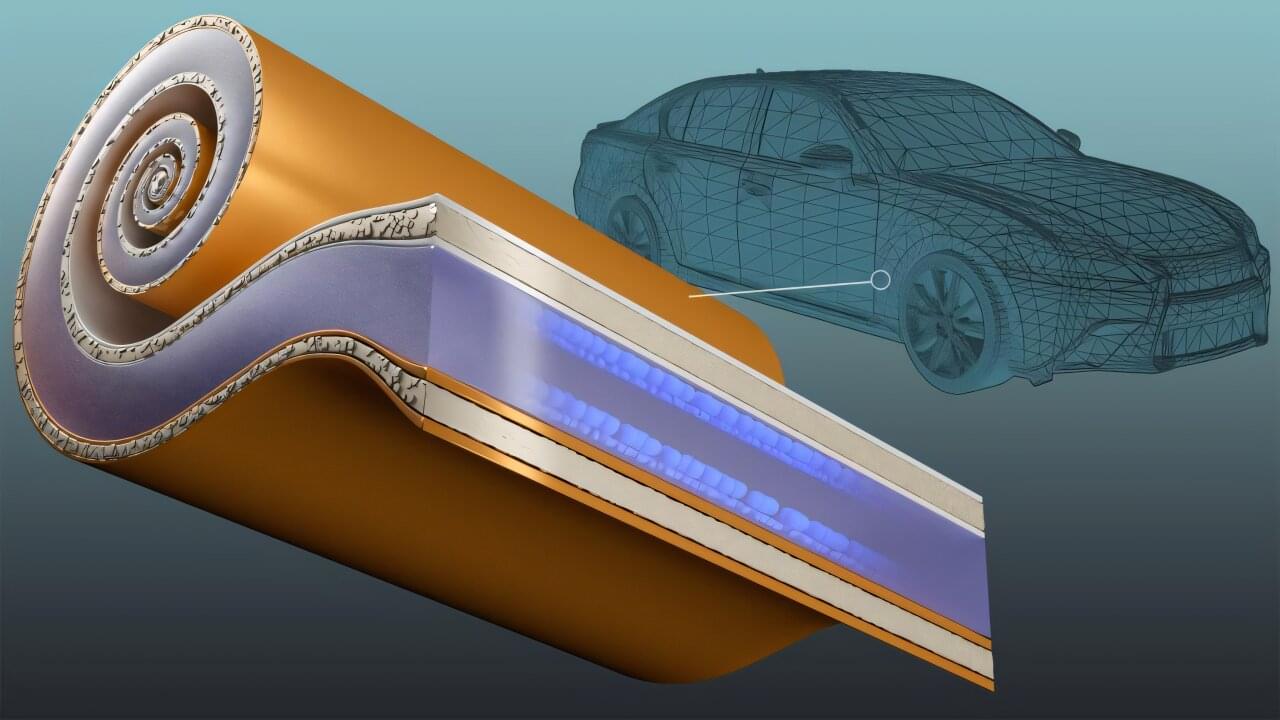
Strengthening the competitiveness of the American transportation industry relies on developing domestically produced electric vehicle batteries that enable rapid charging and long-range performance. The energy density needed to extend driving distance can, however, come at the expense of charging rates and battery life.
By integrating a new type of current collector, which is a key battery component, researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have demonstrated how to manufacture a battery with both superior energy density and a lasting ability to handle extreme fast charging. This enables restoring at least 80% of battery energy in 10 minutes. By using less metal, particularly high-demand copper, the technology also relieves strain on U.S. supply chains.
“This provides a significant savings on near-critical materials, because much less copper and aluminum are needed,” said lead researcher Georgios Polyzos. “At the same time, this will greatly enhance the energy density achievable with a 10-minute charge.”


Until recently, practical attempts rarely pushed beyond proof-of-concept.
Now researchers have used the teleportation trick to forge a working logic gate between two separate quantum chips sitting about six feet apart, hinting at a future where clusters of modest processors act as one mighty computer.
A qubit is valuable because it can be zero and one at the same moment, yet that superposition collapses if the qubit feels a nudge from the outside world.

As humans, we rely on all sorts of stimuli to navigate in the world, including our senses: sight, sound, touch, taste, smell. Until now, AI devices have been solely reliant on a single sense—visual impressions. Brand-new research from Duke University goes beyond reliance only on visual perception. It’s called WildFusion, combining vision with touch and vibration.
The four-legged robot used by the research team includes microphones and tactile sensors in addition to the standard cameras commonly found in state-of-the-art robots. The WildFusion robot can use sound to assess the quality of a surface (dry leaves, wet sand) as well as pressure and resistance to calibrate its balance and stability. All of this data is gathered and combined or fused, into a single data representation that improves over time with experience. The research team plans enhance the robot’s capabilities by enabling it to gauge things like heat and humidity.
As the types of data used to interact with the environment become richer and more integrated, AI moves inexorably closer to true AGI.
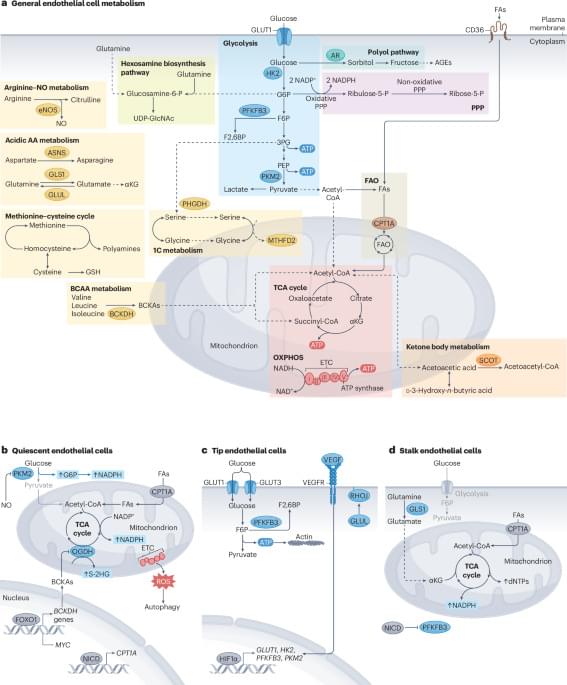
In this Review, the authors describe the metabolic programmes that control endothelial cell function in the cardiovascular system, discuss the role of endothelial cell metabolism in different cardiovascular diseases, and highlight the therapeutic potential and challenges of targeting endothelial cell metabolism to treat cardiovascular diseases.