MIT’s latest brain scan study reveals how overusing AI might be shrinking your memory, focus, and originality.


MIT’s latest brain scan study reveals how overusing AI might be shrinking your memory, focus, and originality.

The quantum physics community is buzzing with excitement after researchers at Rice University finally observed a phenomenon that had eluded scientists for over 70 years. This breakthrough, recently published in Science Advances is known as the superradiant phase transition (SRPT), represents a significant milestone in quantum mechanics and opens extraordinary possibilities for future technological applications.
In 1954, physicist Robert H. Dicke proposed an intriguing theory suggesting that under specific conditions, large groups of excited atoms could emit light in perfect synchronization rather than independently. This collective behavior, termed superradiance, was predicted to potentially create an entirely new phase of matter through a complete phase transition.
For over seven decades, this theoretical concept remained largely confined to equations and speculation. The primary obstacle was the infamous “no-go theorem,” which seemingly prohibited such transitions in conventional light-based systems. This theoretical barrier frustrated generations of quantum physicists attempting to observe this elusive phenomenon.

A force that couples electrons and neutrons could be an addition to the Standard Model, and a new study places an upper limit on this hypothetical force’s strength.

For decades, scientists have been searching for the universe’s elusive “missing matter,” and now they say they finally found it.
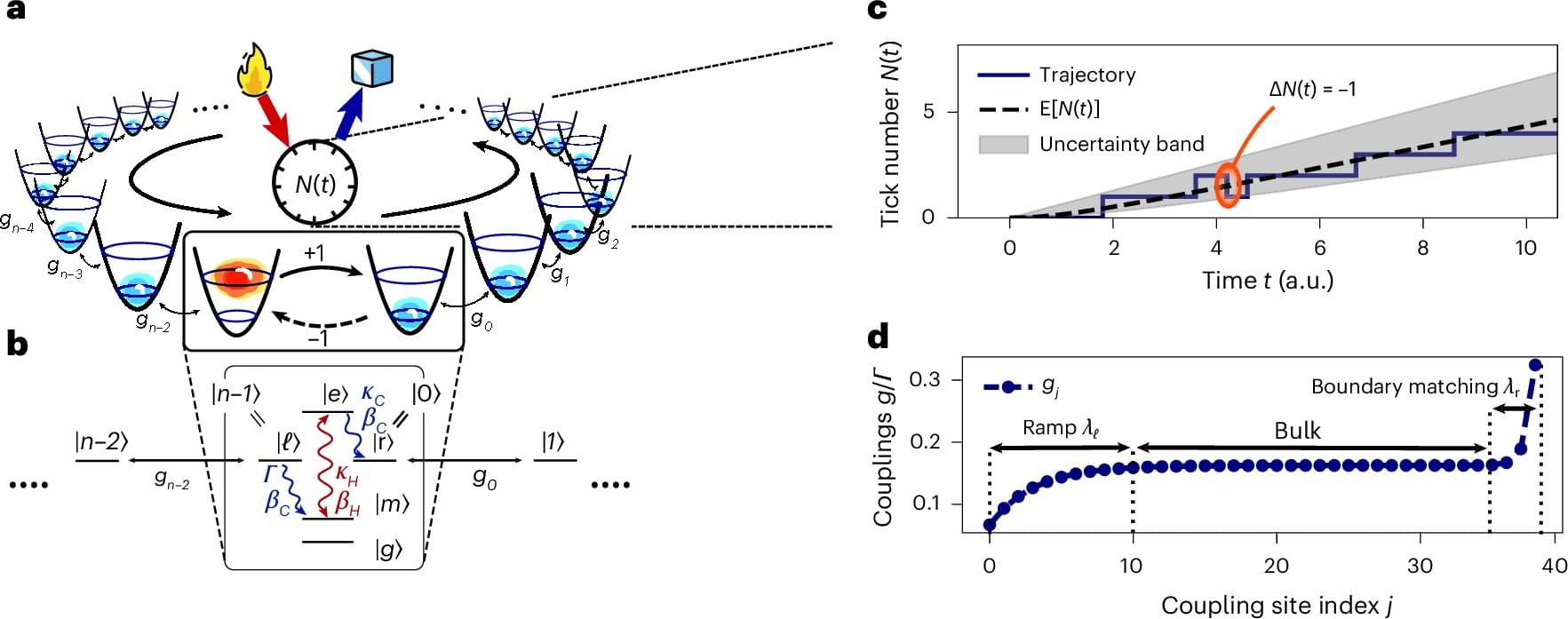
Over the past decades, physicists have been trying to develop increasingly sophisticated and precise clocks to reliably measure the duration of physical processes that unfold over very short periods of time, helping to validate various theoretical predictions. These include so-called quantum clocks, timekeeping systems that leverage the principles of quantum mechanics to measure time with extremely high precision.

A new study led by researchers at the Universities of Oxford, Cambridge and Manchester has achieved a major advance in quantum materials, developing a method to precisely engineer single quantum defects in diamond—an essential step toward scalable quantum technologies. The results have been published in the journal Nature Communications.

Researchers have released genetic and behavioral data from over 1,500 children and adolescents with autism who were hospitalized in psychiatric units across the U.S.
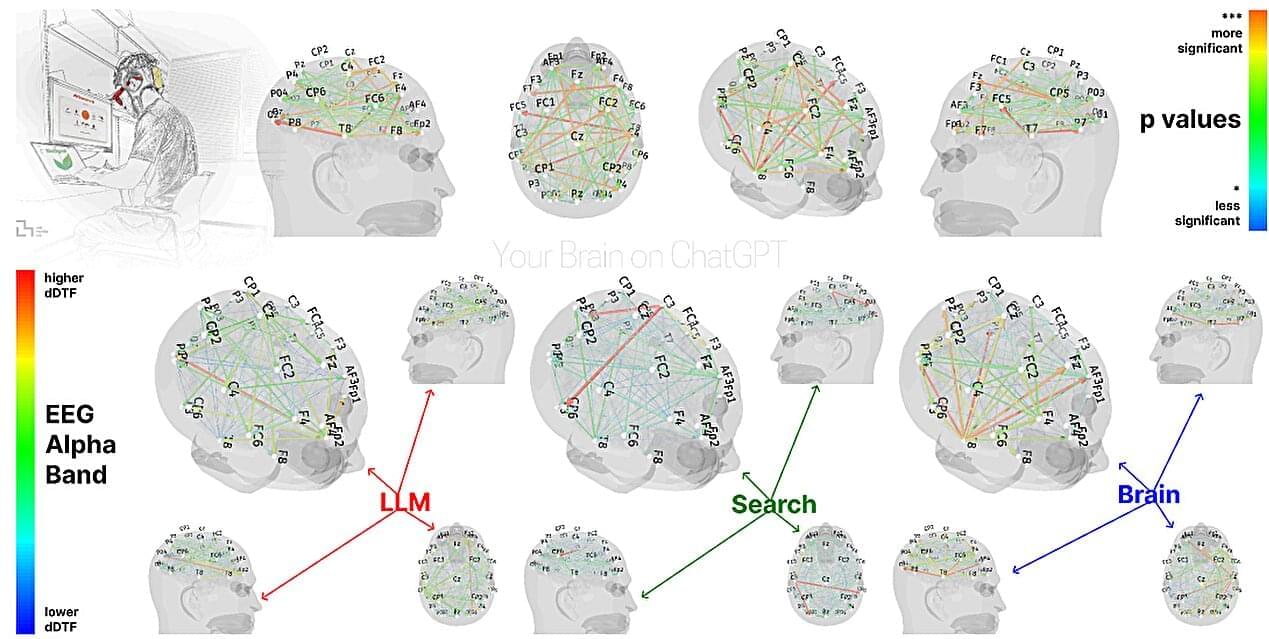
A team of neurologists and AI specialists at MIT’s Media Lab has led a study looking into the brain impacts of large language model (LLM) use among people who engage with them for study or work. They report evidence that the use of LLMs may lead to an erosion of critical thinking skills. In their study, posted on the arXiv preprint server, the researchers asked groups of volunteers to write essays while connected to EEG monitors.
Over the past few years, the use of LLMs such as ChatGPT has become commonplace. Some use them for fun, while others use them to help with school or work responsibilities, and the team at MIT wondered what sort of impact LLM use might have on the brain.
To find out, they recruited 54 volunteers. The initial group was then split into three small groups, all of whom were asked to write a 20-minute essay on the topic of philanthropy—one group was asked to use ChatGPT for help, the second was asked to use Google Search, and the third “Brain-only” group was given no tools or resources at all. The participants remained in these same groups for three writing sessions.
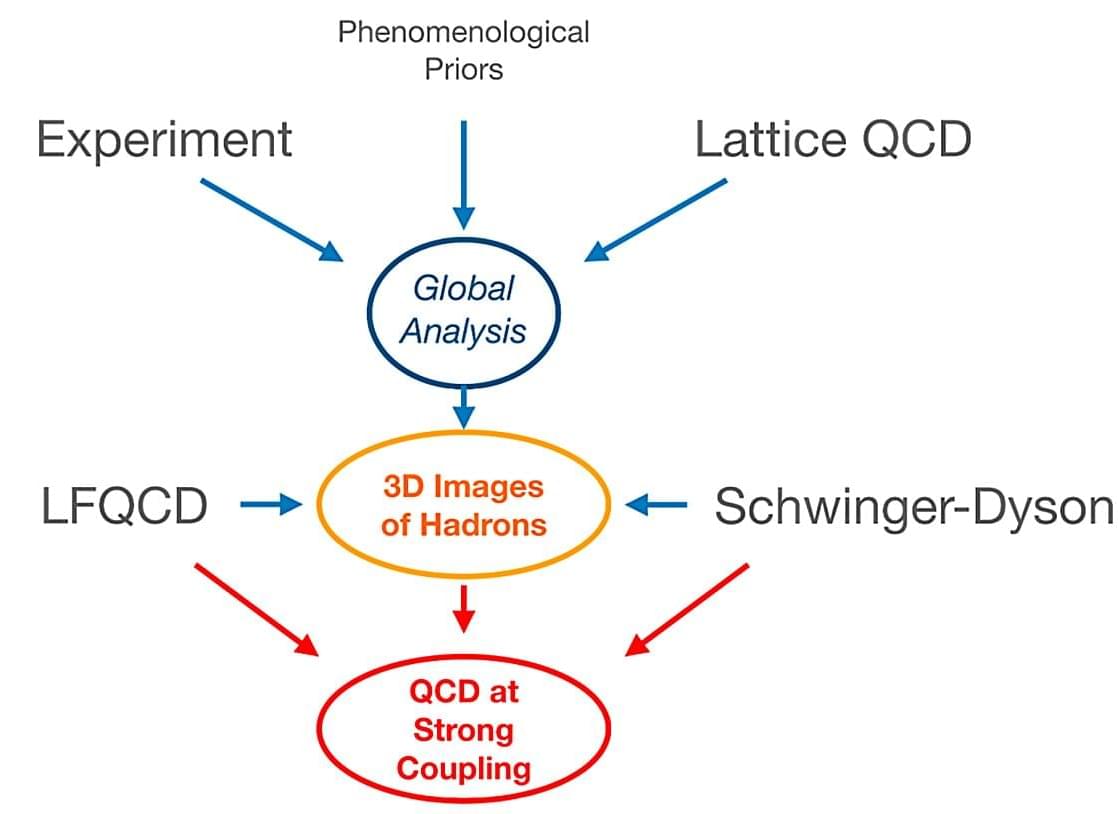
Researchers from the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), together with collaborators from the Instituto Tecnológico de Aeronáutica in Brazil and Iowa State University, have theoretically explored the influence mechanism of quark-gluon interactions on the parton distribution functions (PDFs) within hadrons, providing new insights into first-principles calculations of hadron structure.
Their findings are published as a letter in Physical Review D.
Hadrons are essential building blocks of the universe. These composite particles, which are composed of quarks and gluons, include protons, neutrons, pions, and others. Investigating the behavior of quarks and gluons within hadrons is crucial for unraveling the mysteries of the microscopic structure of matter.
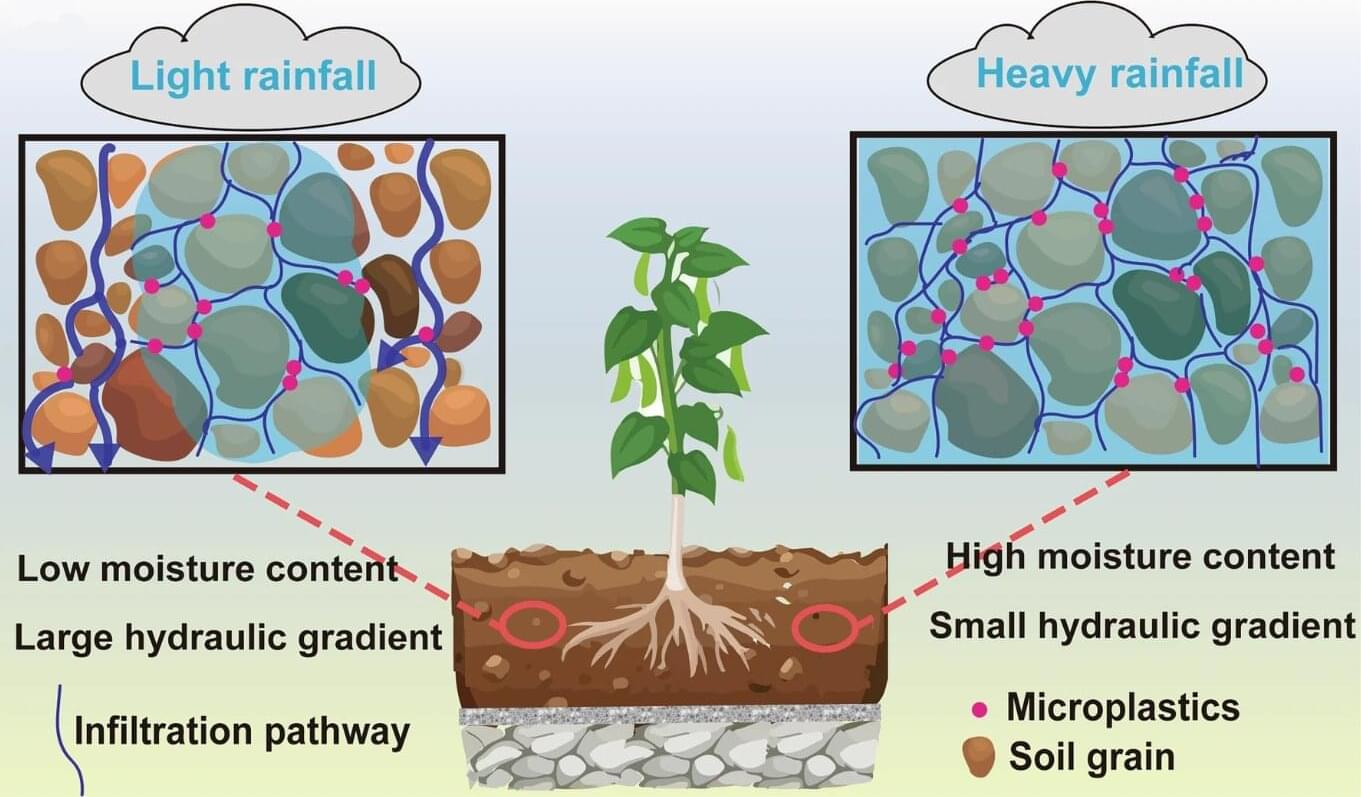
A small team of researchers at Tongji University, working with a colleague from the Shanghai Academy of Landscape Architecture Science and Planning, both in China, has found that growing plants on roofs can serve as an effective way to remove microplastics from the air. In their study, published in the journal Communications Earth & Environment, the group measured the amounts of microplastics found on plants and the soil in which they grow.
Prior research has shown that growing plants on roofs can reduce heating and cooling bills and also clear pollution from the surrounding air. The research team wondered if that also included microplastics.
To find out, they built a simulated roof environment in their lab, where, in a thin layer of fresh soil, they planted two kinds of plants commonly used on rooftops in the city of Shanghai. They also introduced microplastic particles into the air above the plants at levels common to Shanghai. They then conducted simulated rains, measuring microplastic levels on the plants and in the soil.