International AI symposium on Oct 27 at Seoul Dragon City. Join AI leaders.

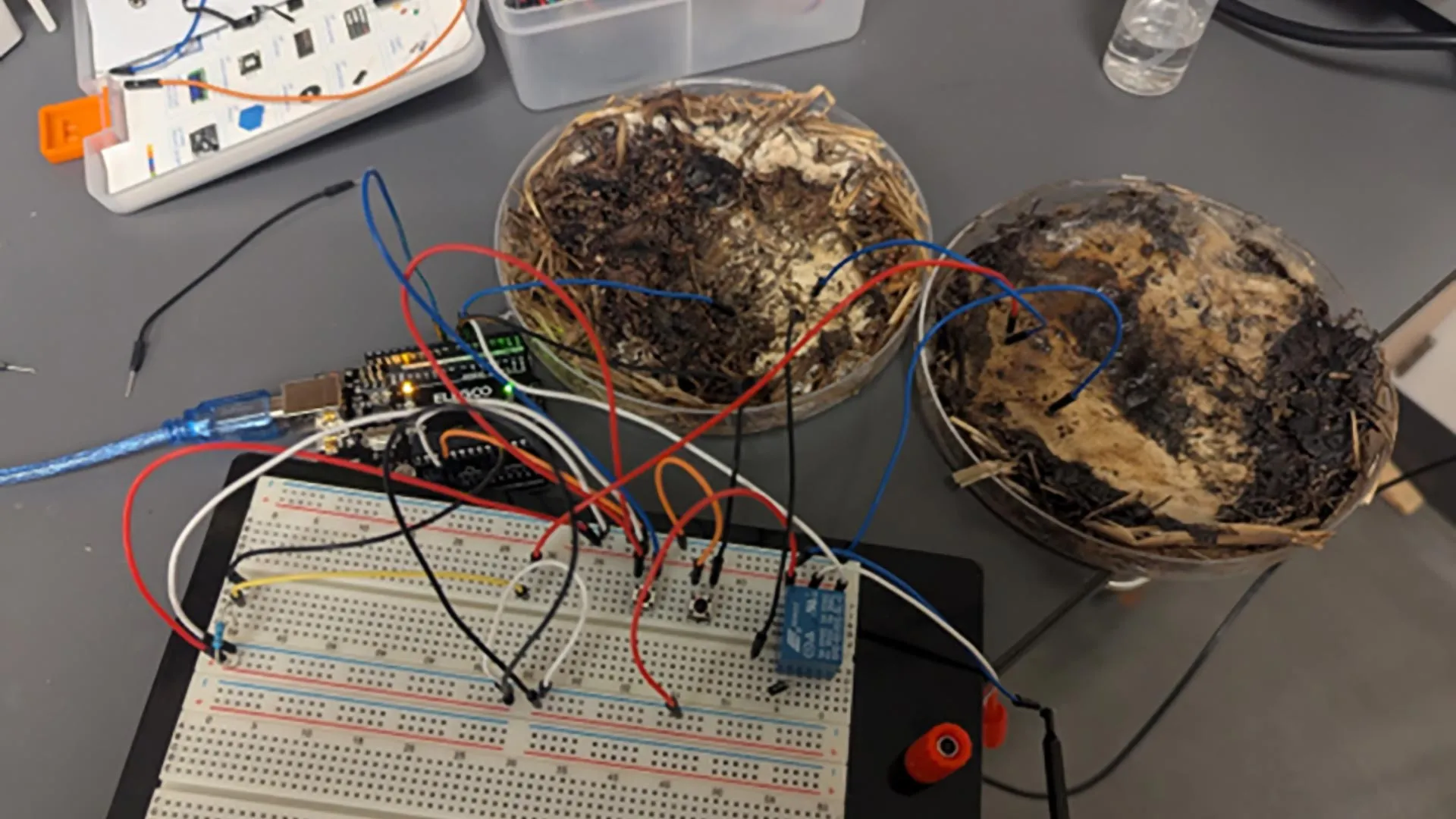
Mushrooms are known for their toughness and unusual biological properties, qualities that make them attractive for bioelectronics. This emerging field blends biology and technology to design innovative, sustainable materials for future computing systems.
Turning Mushrooms Into Living Memory Devices
Researchers at The Ohio State University recently discovered that edible fungi, such as shiitake mushrooms, can be cultivated and guided to function as organic memristors. These components act like memory cells that retain information about previous electrical states.
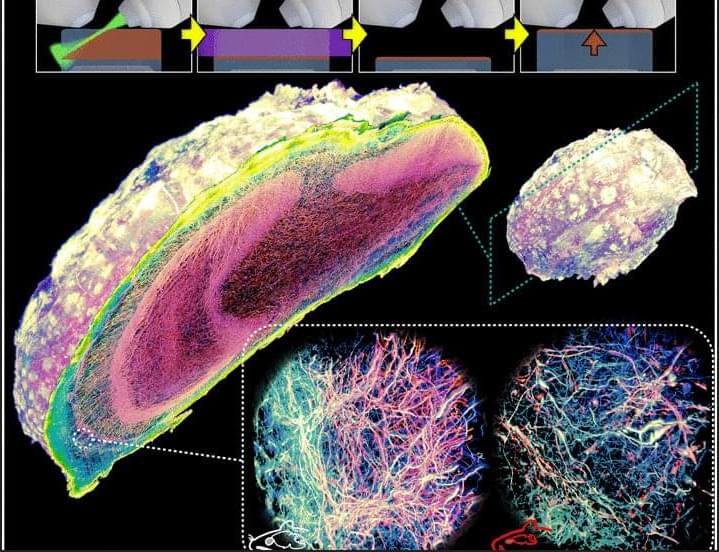
I first explored this amazing work back when it was a preprint! Wang et al. herein developed VIPS (volumetric imaging via photochemical sectioning), a way of using UV light to remove layers of expanded tissue-hydrogel, allowing combination of high-resolution lattice-light sheet microscopy with expansion microscopy. Link: [ https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adr9109]
In my opinion, this technology has enormous future promise for high-throughput connectomics! They will need to improve their labeling density so that higher expansion factors can be used, but this problem is well-studied and I think the issue will likely be solvable with additional resources/effort.
Optical nanoscopy of intact biological specimens has been transformed by recent advancements in hydrogel-based tissue clearing and expansion, enabling the imaging of cellular and subcellular structures with molecular contrast. However, existing high-resolution fluorescence microscopes are physically limited by objective-to-specimen distance, which prevents the study of whole-mount specimens without physical sectioning. To address this challenge, we developed a photochemical strategy for spatially precise sectioning of specimens. By combining serial photochemical sectioning with lattice light-sheet imaging and petabyte-scale computation, we imaged and reconstructed axons and myelin sheaths across entire mouse olfactory bulbs at nanoscale resolution.
Not many people realise how much posture impacts the body and mind. The way you hold yourself for 90–99% of the day has a powerful effect on your hormones and mood. Hunching over can lower testosterone and raise cortisol, while standing tall with your spine straight and shoulders back helps increase testosterone and reduce cortisol. You’ll also notice that when you’re upright, your breathing becomes deeper and easier, supporting relaxation and reducing stress. Slouching restricts breathing, leading to shallow breaths, lower oxygen levels, and negative effects on both energy and mood.
Slouching lowers testosterone:
Adjusting posture has the opposite effect: https://somaticmovementcenter.com/10-shocking-ways-posture-a…%20muscles, I%20gotten%20your%20attention%20yet?
Nervous about an upcoming presentation or job interview? Holding one’s body in “high-power” poses for short time periods can summon an extra surge of power and sense of well-being when it’s needed, according to Harvard Business School professor Amy J.C. Cuddy.

The effects of physical activity don’t stop when the movement does. In a new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Virginia Tech researchers, in collaboration with researchers at the University of Aberdeen and Shenzhen University, have found that being active adds to the total energy you use every day without causing the body to conserve energy in other ways.
This is important because the health benefits of increasing physical activity are already well-documented, but there is less research about how exercise impacts a person’s “energy budget,” or the allocation of energy to different bodily functions.
It has been thought that a person’s energy budget functions in one of two ways: like a fixed salary where energy is redistributed from other functions to cover the cost of movement, or like a flexible, commission-based system that is additive and allows for increased energy expenditure. The team wanted to determine which model better explains how the energy budget actually changes across different levels of physical activity.
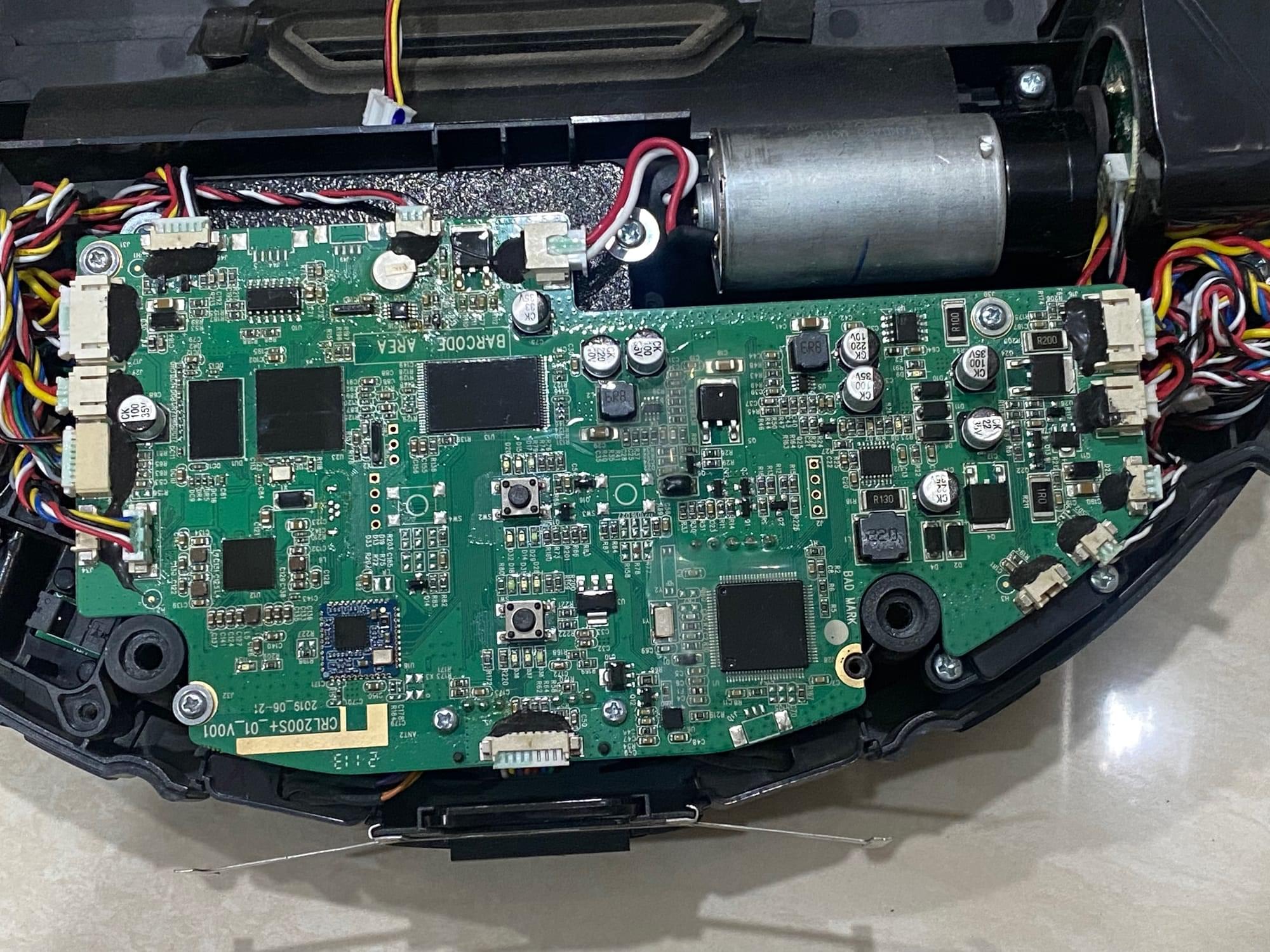
Would you allow a stranger to drive a camera-equipped computer around your living room? You might have already done so without even realizing it.
It all started innocently enough. I had recently bought an iLife A11 smart vacuum—a sleek, affordable, and technologically advanced robot promising effortless cleaning and intelligent navigation. As a curious engineer, I was fascinated by its workings. After leaving it to operate for the entire year, my curiosity got the better of me.
I’m a bit paranoid—the good kind of paranoid. So, I decided to monitor its network traffic, as I would with any so-called smart device.
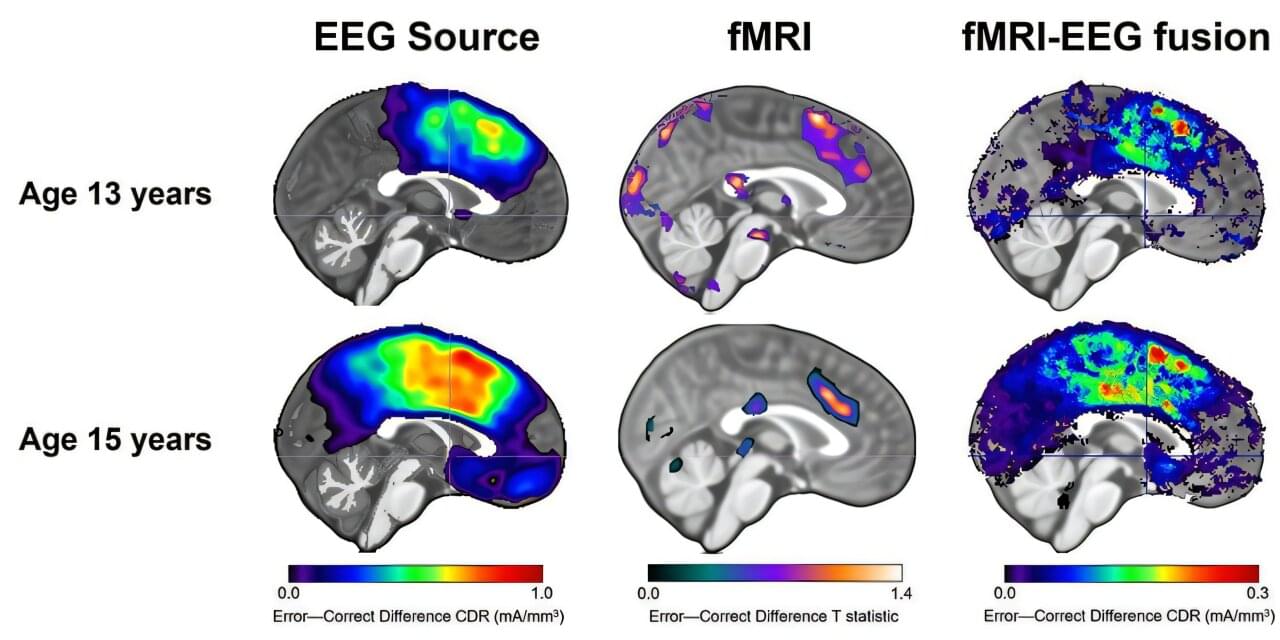
When you’re a teenager, it’s easy to feel like the world is watching your every mistake. For some kids, that sense of self‐consciousness fades as they grow up. For others, it deepens into full‐blown anxiety.
A new study led by researchers at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences may help explain why—and could eventually make it easier to spot teens most at risk before anxiety takes hold.
The research, published in JAMA Network Open, found that combining two kinds of brain scans can better predict which teens are likely to experience greater anxiety as they get older. The work sheds new light on how the adolescent brain responds to mistakes and why those responses vary from person to person.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhDDiscount Links/Affiliates: Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.u…
