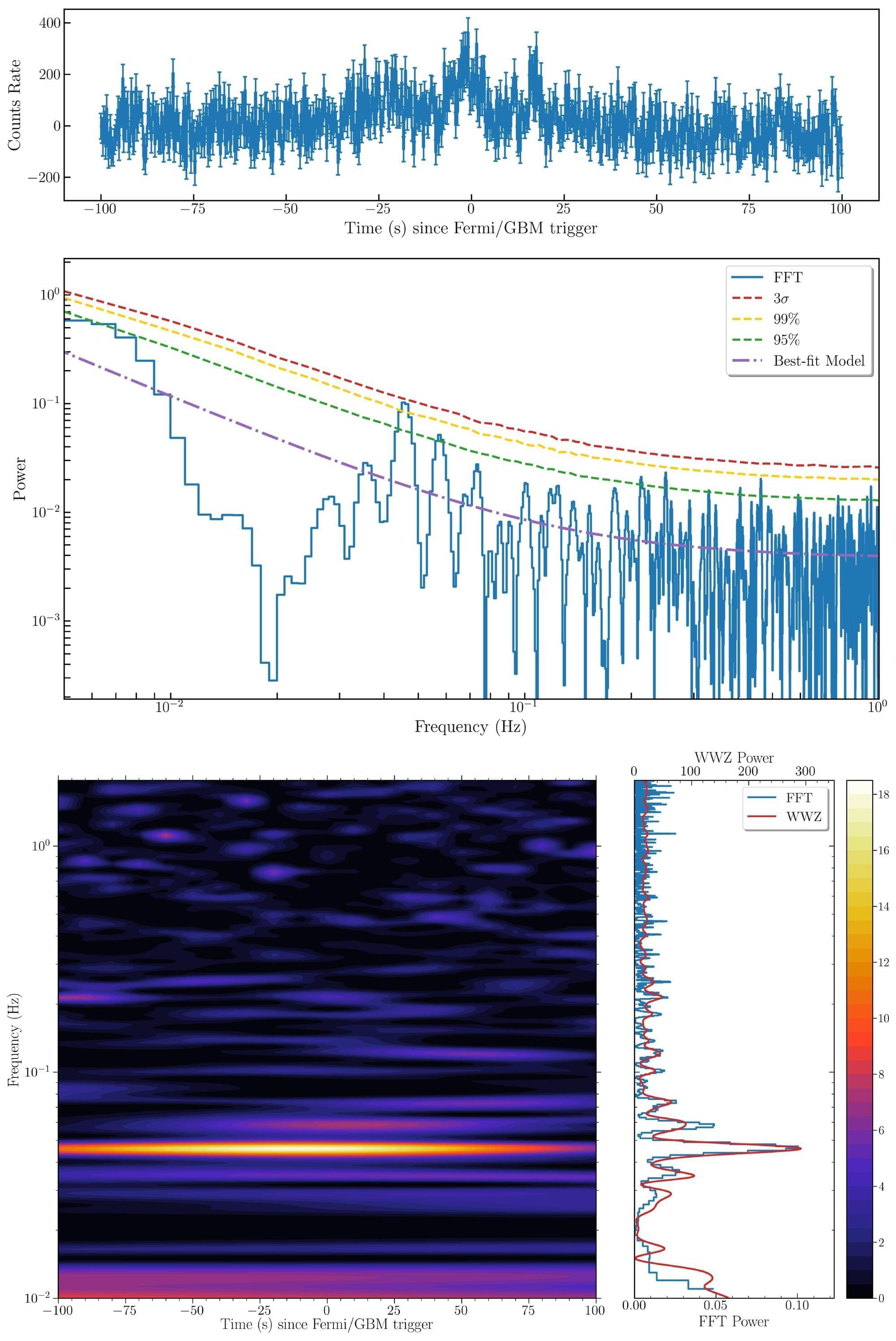
A new study led by the Yunnan Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has detected quasi-periodic oscillation (QPO) signals in an unusual gamma-ray burst (GRB) event. The findings are published in The Astrophysical Journal.
GRBs are short-timescale, highly energetic explosive phenomena typically associated with the collapse of massive stars or the mergers of compact objects. On July 2, 2025, the Gamma-ray Burst Monitor (GBM) aboard NASA’s Fermi satellite detected an unusual high-energy burst—designated GRB 250702DBE—that triggered the Fermi/GBM system three times.
Despite being named in accordance with standard GRB conventions, the event exhibited striking anomalies: its duration spanned several hours, far exceeding that of typical GRBs. The same source, also detected in the X-ray band by the Einstein Probe (EP) as EP250702a, has drawn scientific interest due to its long duration and unclear physical origin and radiation mechanisms.