‘Organoid intelligence’ is still in its early stages, but it’s already raising tough questions.
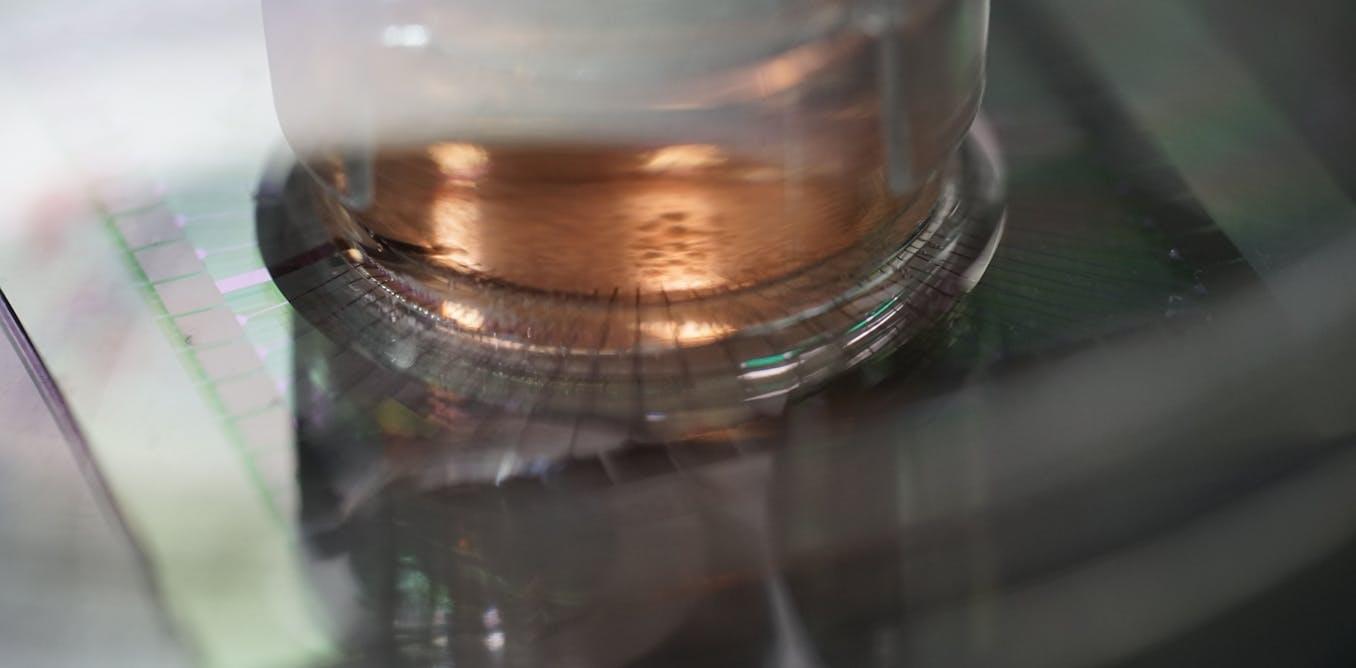


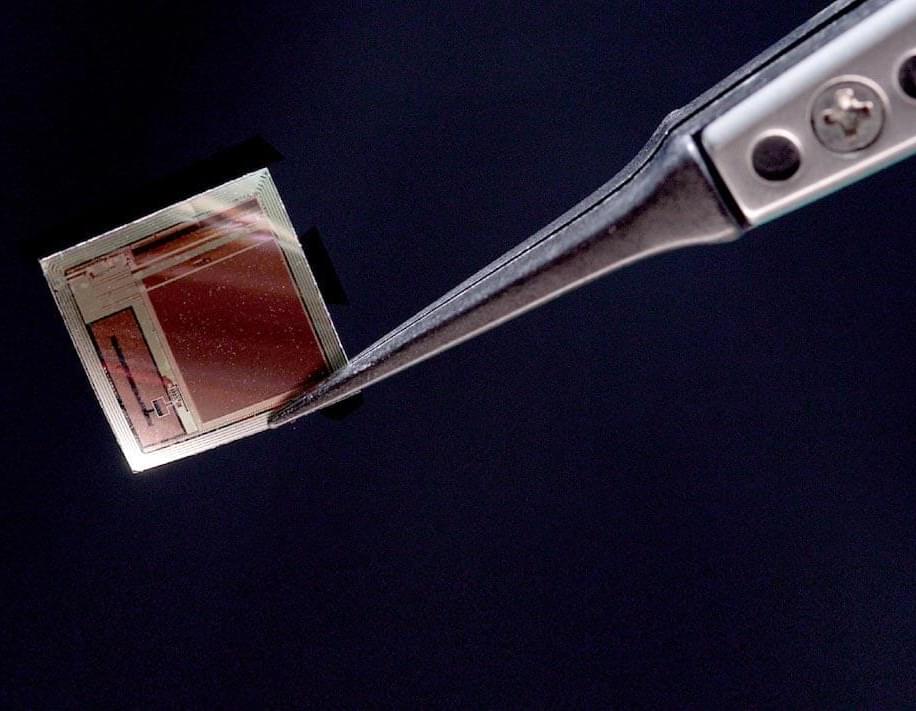
A radically miniaturized brain implant called BISC is redefining what’s possible in human–computer interaction, offering a paper-thin, wireless, high-bandwidth link directly to the brain.
With over 65,000 electrodes and unprecedented data throughput, it enables advanced AI decoding of thoughts, intentions, and sensory experiences while remaining minimally invasive.

An international collaboration led by Cornell researchers used a combination of psilocybin and the rabies virus to map how – and where – the psychedelic compound rewires the connections in the brain.
Specifically, they showed psilocybin weakens the cortico-cortical feedback loops that can lock people into negative thinking. Psilocybin also strengthens pathways to subcortical regions that turn sensory perceptions into action, essentially enhancing sensory-motor responses.
The findings published Dec. 5 in Cell. The lead author is postdoctoral researcher Quan Jiang.

A joint effort between two of the world’s largest neutrino experiments has brought scientists closer to understanding how the universe survived its violent beginnings.
The findings could reveal why matter exists at all — and why everything didn’t vanish long ago.
Scientists unite to explore why the universe exists.
High-resolution imaging has revealed the internal layout of chromatin condensates, showing how DNA fibers fold and interact within these droplet-like structures. The findings connect molecular architecture to the broader behaviors of these droplets in cells.

Viazovska was born in Kyiv, the oldest of three sisters. Her father was a chemist who worked at the Antonov aircraft factory and her mother was an engineer. [ 6 ] She attended a specialized secondary school for high-achieving students in science and technology, Kyiv Natural Science Lyceum No. 145. An influential teacher there, Andrii Knyazyuk, had previously worked as a professional research mathematician before becoming a secondary school teacher. [ 7 ] Viazovska competed in domestic mathematics Olympiads when she was at high school, placing 13th in a national competition where 12 students were selected to a training camp before a six-member team for the International Mathematical Olympiad was chosen. [ 6 ] As a student at Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv, she competed at the International Mathematics Competition for University Students in 2002, 2003, 2004, and 2005, and was one of the first-place winners in 2002 and 2005. [ 8 ] She co-authored her first research paper in 2005. [ 6 ]
Viazovska earned a master’s from the University of Kaiserslautern in 2007, PhD from the Institute of Mathematics of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine in 2010, [ 2 ] and a doctorate (Dr. rer. nat.) from the University of Bonn in 2013. Her doctoral dissertation, Modular Functions and Special Cycles, concerns analytic number theory and was supervised by Don Zagier and Werner Müller. [ 9 ]
She was a postdoctoral researcher at the Berlin Mathematical School and the Humboldt University of Berlin [ 10 ] and a Minerva Distinguished Visitor [ 11 ] at Princeton University. Since January 2018 she has held the Chair of Number Theory as a full professor at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) in Switzerland after a short stint as tenure-track assistant professor. [ 4 ] .
An international research team has uncovered a surprising ally in the fight against insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: a microbial metabolite called trimethylamine (TMA). Published in Nature Metabolism, the study reveals that TMA, produced by gut bacteria from dietary choline, can block a key immune pathway and improve blood sugar control.
The study was led by Professor Marc-Emmanuel Dumas at Imperial College London & CNRS together with Prof. Patrice Cani (Imperial & University of Louvain, UCLouvain), Dr. Dominique Gauguier (Imperial & INSERM, Paris) and Prof. Peter Liu (University of Ottawa Heart Institute).

According to a new study, lower doses of approved immunotherapy for malignant melanoma can give better results against tumors, while reducing side effects. This is reported by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
“The results are highly interesting in oncology, as we show that a lower dose of an immunotherapy drug, in addition to causing significantly fewer side effects, actually gives better results against tumors and longer survival,” says last author Hildur Helgadottir, a researcher at the Department of Oncology–Pathology at Karolinska Institutet, who led the study.
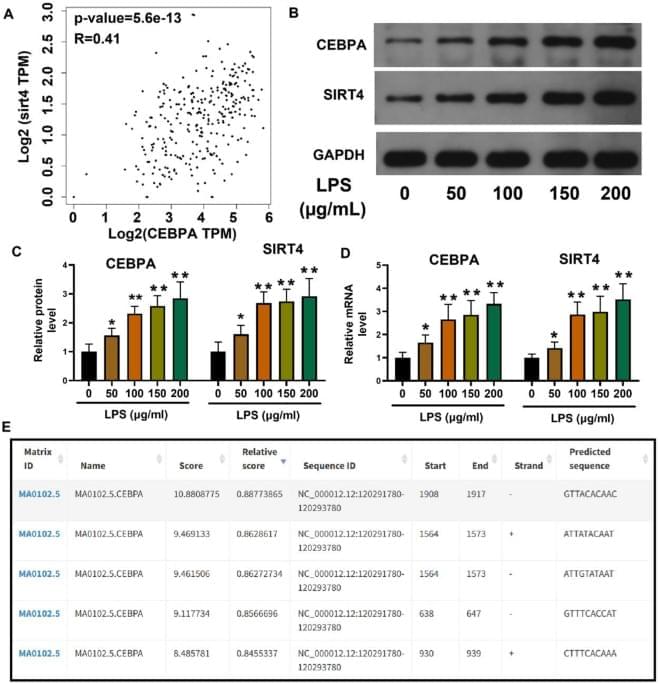
Wu, Z., Gou, K., Wang, Y. et al. Transcription factor CEBPA suppresses sepsis induced lung injury by activating SIRT4 transcription. Sci Rep 15, 42,128 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-25975-5