Cambridge researchers discover that gut bacteria can flush PFAS from your body without drugs, neither bloodletting



Metr recently published a paper about the impact AI tools have on open-source developer productivity1. They show that when open source developers working in codebases that they are deeply familiar with use AI tools to complete a task, then they take longer to complete that task compared to other tasks where they are barred from using AI tools. Interestingly the developers predict that AI will make them faster, and continue to believe that it did make them faster, even after completing the task slower than they otherwise would!
Understanding of vitamin D physiology is important because about half of the population is being diagnosed with deficiency and treated with supplements. Clinical guidelines were developed based on observational studies showing an association between low serum levels and increased cardiovascular risk. However, new randomized controlled trials have failed to confirm any cardiovascular benefit from supplementation in the general population. A major concern is that excess vitamin D is known to cause calcific vasculopathy and valvulopathy in animal models. For decades, administration of vitamin D has been used in rodents as a reliable experimental model of vascular calcification. Technically, vitamin D is a misnomer. It is not a true vitamin because it can be synthesized endogenously through ultraviolet exposure of the skin. It is a steroid hormone that comes in 3 forms that are sequential metabolites produced by hydroxylases. As a fat-soluble hormone, the vitamin D-hormone metabolites must have special mechanisms for delivery in the aqueous bloodstream. Importantly, endogenously synthesized forms are carried by a binding protein, whereas dietary forms are carried within lipoprotein particles. This may result in distinct biodistributions for sunlight-derived versus supplement-derived vitamin D hormones. Because the cardiovascular effects of vitamin D hormones are not straightforward, both toxic and beneficial effects may result from current recommendations.
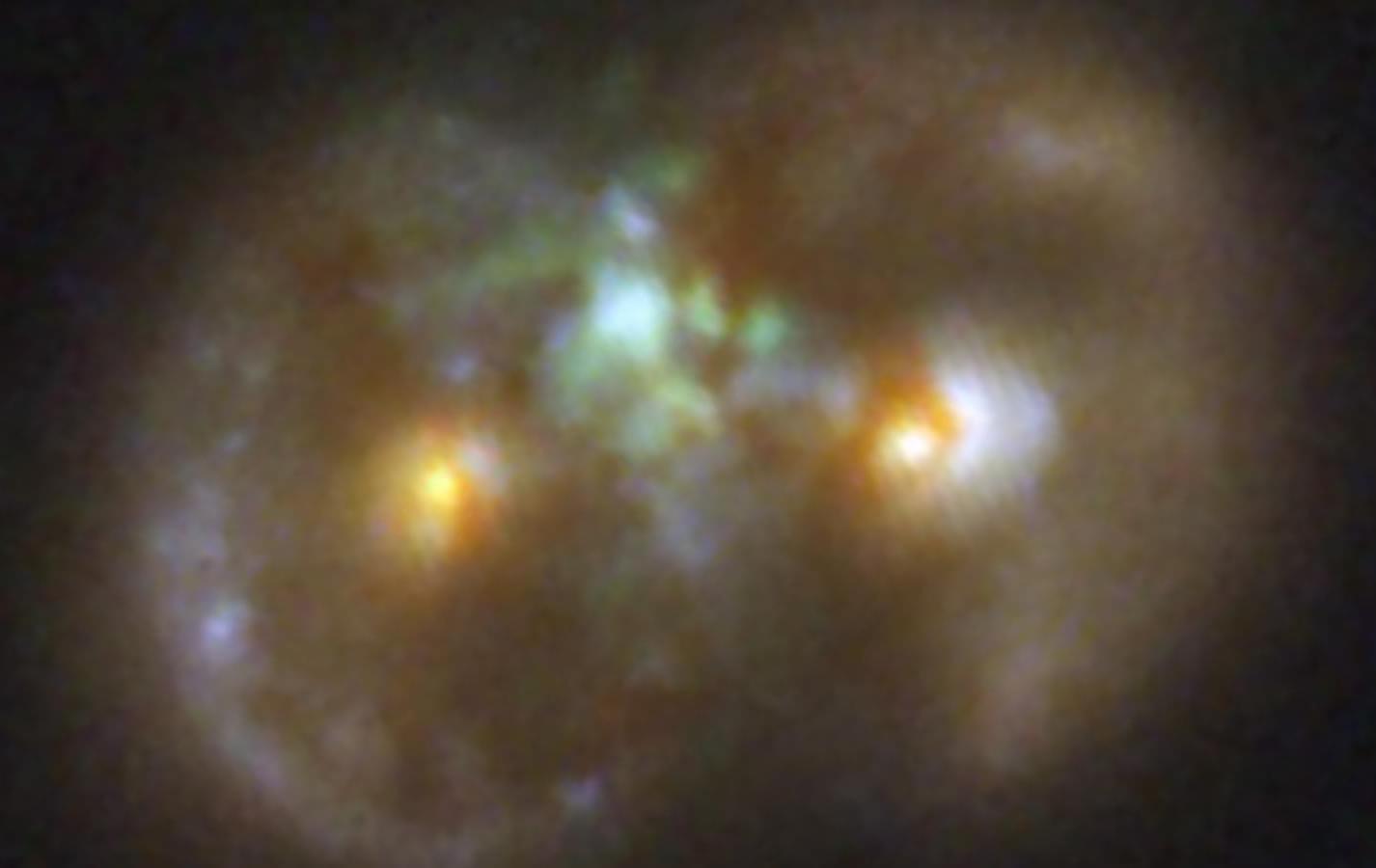

The researchers behind these findings uncovered the Infinity Galaxy while examining images from the JWST’s 255-hour treasury COSMOS-Web survey. In addition to the suspected direct collapse black hole that sits between the colliding galaxies, the team found that each nucleus of those galaxies also contains a supermassive black hole!
“Everything is unusual about this galaxy. Not only does it look very strange, but it also has this supermassive black hole that’s pulling a lot of material in,” team leader and Yale University researcher Pieter van Dokkum said in a statement. “The biggest surprise of all was that the black hole was not located inside either of the two nuclei but in the middle.
We asked ourselves: How can we make sense of this?

To analyze the genome of pancreatic cancer cells, NIST researchers used 13 distinct state-of-the-art whole genome measurement technologies, some of which were only recently developed.
Each method identifies the sequence of DNA nucleotides — adenine (A), cytosine ©, guanine (G) and thymine (T) — in an individual’s genome. However, the methods produce slightly varying results and have different strengths and weaknesses.
NIST’s dataset contains separate results for each of the 13 techniques used to sequence the cancer genome. Scientists performing their analysis can compare their data with NIST’s. If there are discrepancies, they can then determine whether their equipment is working properly and remedy the problem if not.