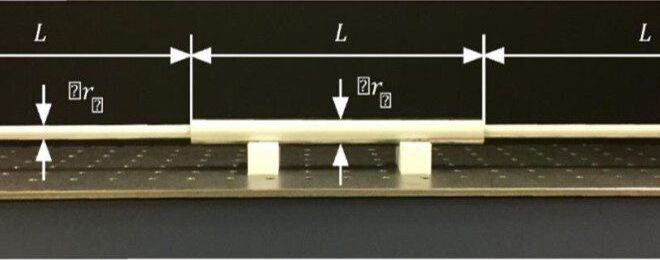
Light and sound waves are at the basis of energy and signal transport and fundamental to some of our most basic technologies—from cell phones to engines. Scientists, however, have yet to devise a method that allows them to store a wave intact for an indefinite period of time and then direct it toward a desired location on demand. Such a development would greatly facilitate the ability to manipulate waves for a variety of desired uses, including energy harvesting, quantum computing, structural-integrity monitoring, information storage, and more.
In a newly published paper in Science Advances, a group of researchers led by Andrea Alù, founding director of the Photonics Initiative at the Advanced Science Research Center (ASRC) at The Graduate Center, CUNY, and by Massimo Ruzzene, professor of Aeronautics Engineering at Georgia Tech, have experimentally shown that it is possible to efficiently capture and store a wave intact then guide it towards a specific location.
“Our experiment proves that unconventional forms of excitation open new opportunities to gain control over wave propagation and scattering,” said Alù. “By carefully tailoring the time dependence of the excitation, it is possible to trick the wave to be efficiently stored in a cavity, and then release it on demand towards the desired direction.”