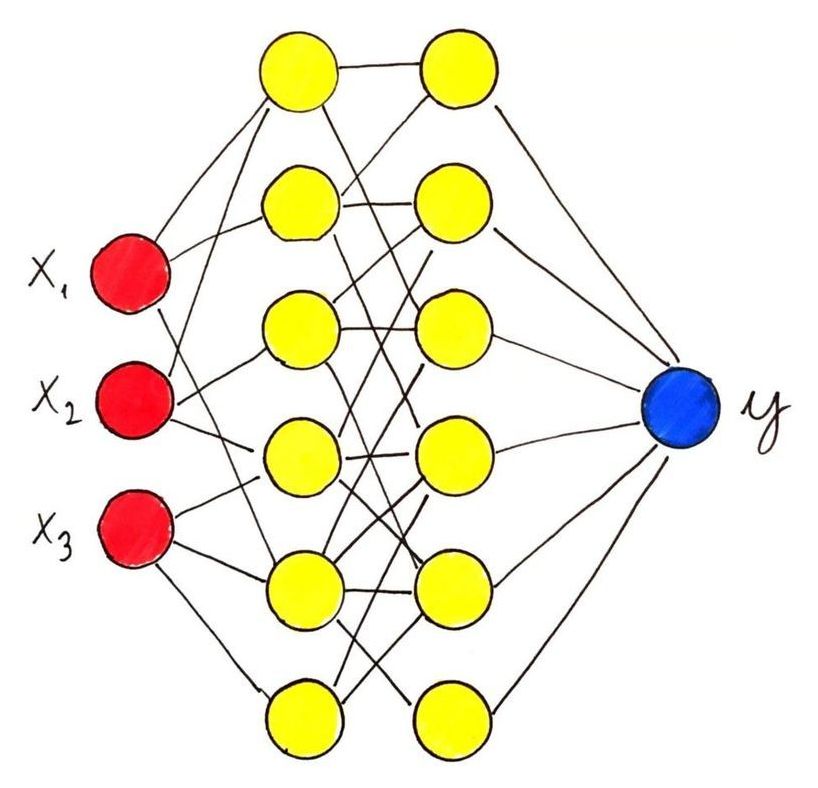
Some immune responses may be enough to make a person impervious to reinfection, but scientists don’t yet know how the human body reacts to this new virus.
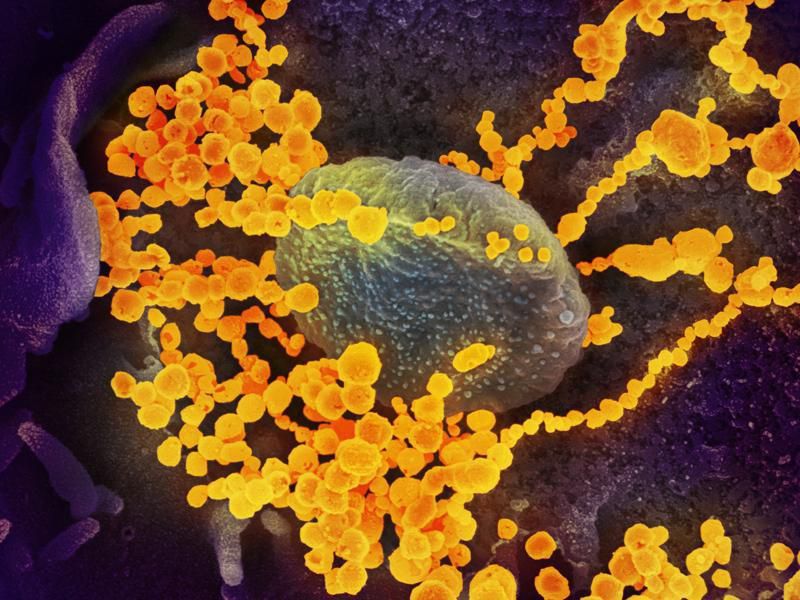


CRISPR gene-editing trials have taken off—and may hold the key to medical breakthroughs.
[Illustration: Jamie Cullen]

Vox interviewed Bill Gates in 2015 about his fears of a global pandemic. Now that we’re living in that reality, what does he think comes next?
Watch our 2015 interview with Bill Gates here: https://youtu.be/9AEMKudv5p0
This interview was conducted on April 25, 2020. You can listen to the rest of the interview on the Ezra Klein Show, available wherever you listen to podcasts, or read it here: https://bit.ly/2TCZx9O
For more information on The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation’s efforts to fight coronavirus: https://bit.ly/3elJyog
For more of our sources:
The latest data on the pandemic around the world: https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus
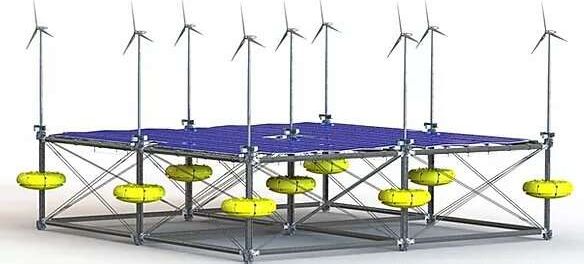
A German power firm will launch demonstrations of a one-of-a-kind, triple-threat power generating platform off Iraklio, Greece, later this year.
SINN Power has been testing wave energy converter modules for five years. Buoys attached to steel frame components generate energy as waves push them up and down. The modular nature of the platform is unique in the industry.
“The modular design has been a key element since we started developing maritime technologies that allow flexibility and a wide variety of applications,” according to SINN Power CEO Philipp Sinn. “The floating platform can supply renewable energy to islands across the world … and contribute to the worldwide implementation of offshore wind farms.”

A group of scientists from NUST MISIS developed a ceramic material with the highest melting point among currently known compounds. Due to the unique combination of physical, mechanical and thermal properties, the material is promising for use in the most heat-loaded components of aircraft, such as nose fairings, jet engines and sharp front edges of wings operating at temperatures above 2000 degrees C. The results are published in Ceramics International.

EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: The US Department of Defense has been working with American companies for the past year on a project to develop a prototype for a portable nuclear microreactor, a device intended for use by the US military in security scenarios around the world. The US Department of Energy is also involved in the project, with the aim of providing electricity to remote sites that are difficult to link to the grid. The project thus represents a symbiosis between military and civilian technological development.
A symbiotic relationship between military and civilian aspects of technological development gained momentum in the US after the end of WWII. This was particularly visible among applications in the communication, computing, and aerospace fields, but was also present in the field of nuclear technology. Some technology projects were presented as dual-use in order to justify the cost of their development.
One example of nuclear energy symbiosis was the development of nuclear power-generating reactors. By 1956, more than a decade after the destruction of the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki by nuclear bombs, only the UK’s Calder Hall nuclear power plant, which had four reactors each producing 60 MW electricity (MWe), was in operation. However, as of December 2019, 443 nuclear power generators were operating worldwide, with a total output of 395 gigawatts electric (GWe)—an average output of nearly 900 MWe per reactor.