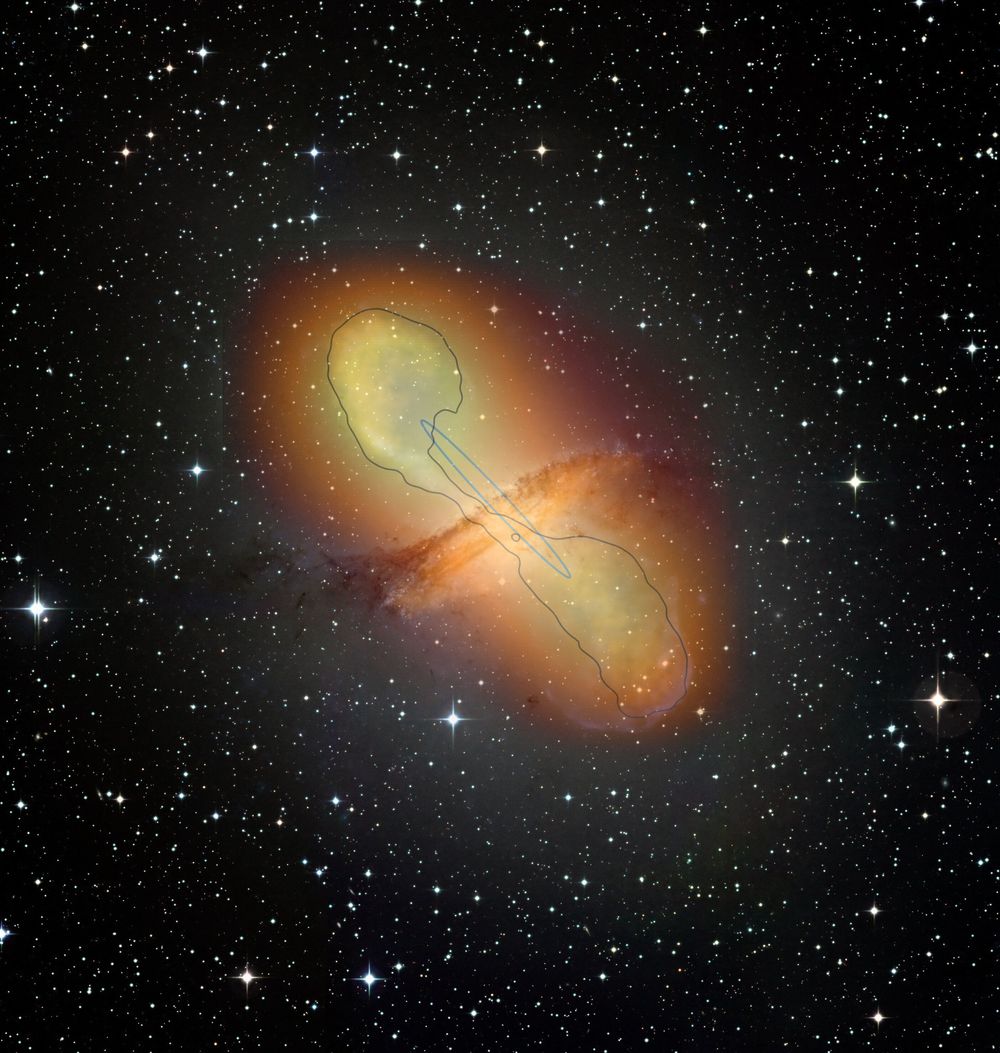
An international collaboration bringing together over 200 scientists from 13 countries has shown that the very high-energy gamma-ray emissions from quasars, galaxies with a highly energetic nucleus, are not concentrated in the region close to their central black hole, but in fact, extend over several thousand light-years along jets of plasma. This discovery shakes up current scenarios for the behavior of such plasma jets. The work, published in the journal Nature on June 18, 2020, was carried out as part of the H.E.S.S collaboration, involving in particular the CNRS and CEA in France, and the Max Planck society and a group of research institutions and universities in Germany.
Over the past few years, scientists have observed the universe using gamma rays, which are very high-energy photons. Gamma rays, among the cosmic rays that constantly bombard the Earth, originate from regions of the universe where particles are accelerated to huge energies unattainable in human-built accelerators. Gamma rays are emitted by a wide range of cosmic objects such as quasars, which are active galaxies with a highly energetic nucleus.
The intensity of the radiation emitted from these systems can vary over very short timescales of up to one minute. Scientists therefore believed that the source of this radiation was very small and located in the vicinity of a supermassive black hole, which can have a mass several billion times that of the sun’s. The black hole is thought to gobble up the matter spiraling down into it and eject a small part of it in the form of large jets of plasma at relativistic speeds, close to the speed of light, thus contributing to the redistribution of matter throughout the universe.