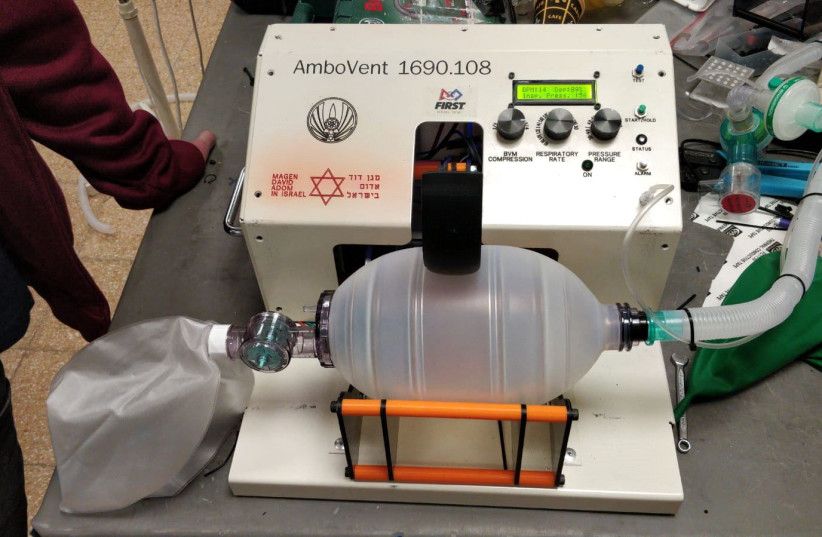
Is a low-cost Israeli #ventilator the key to saving #coronavirus patients in #Iran, Africa and more?
“We are not talking about a website for the general public, we are talking about engineers and other experts, and we know the groups who are working on it because they are in touch with us via WhatsApp and emails, to ask questions and understand how to proceed,” he said.
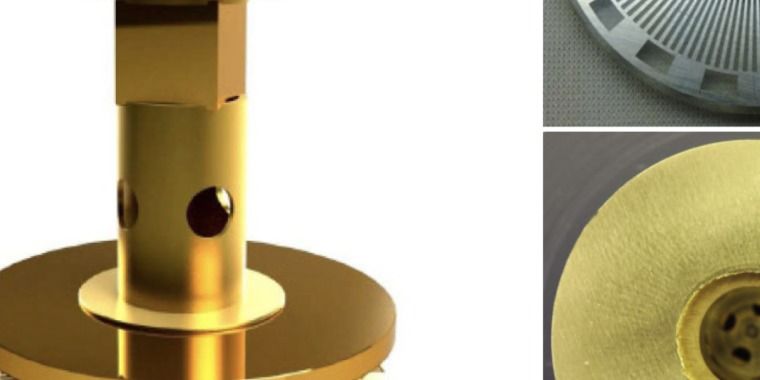
“AmboVent” is a device inspired by the bag-valve mask ventilators that paramedics use when they’re manually ventilating patients in an ambulance, which also offers controls for respiration rate, volume, and maximum peak pressure. Organizations involved in its development include the Magen David Adom, Israeli Air Force 108 Electronics Depot; physicians from Hadassah and Tel Aviv Sourasky medical centers; Microsoft; Rafael, an Israeli defense contractor; Israeli Aerospace Industries; and mentors and students from FIRST Israel, a student robotics organization.
A key feature of the project is that not only the technology is opensource, but its components can be easily built with limited tools and parts, for example 3D printers and car pieces, making the production much more accessible even in less developed country.
“We kept the design and every aspect of it very simple so it would be as easy as possible to be replicated from everywhere,” he said.