Harvard University scientists have created an artificial leaf that’s even better than the real thing.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Faces of Technology — Women of NASA 2020
On this Women in Engineering Day, meet some of the NASA — National Aeronautics and Space Administration women who are making contributions to the technologies that make space exploration, including NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon, possible. WATCH https://go.nasa.gov/319sH4X #INWED20
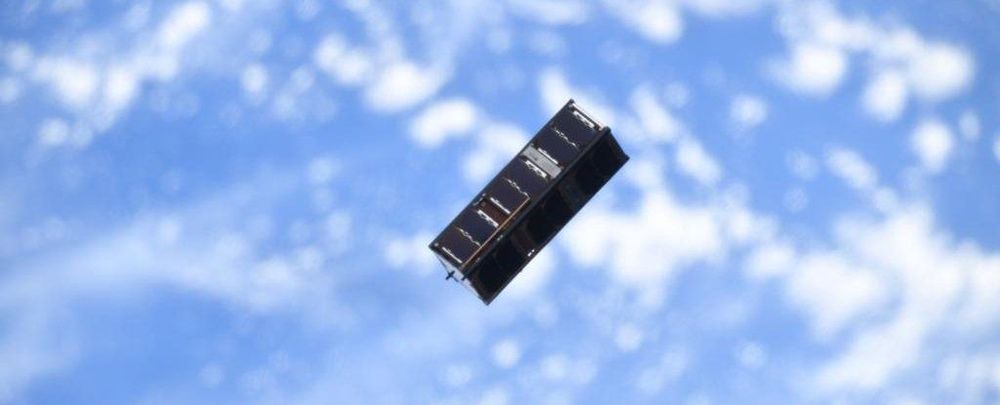


Scientists Have Demonstrated Quantum Entanglement on a Tiny Satellite Orbiting Earth
In the strange field of quantum physics, quantum entanglement – what Einstein called “spooky action at a distance” – stands out as one of the most intriguing phenomena. And now scientists just managed to successfully demonstrate it again, this time onboard a CubeSat satellite orbiting Earth.
Quantum entanglement is where two particles become inextricably linked across a distance, so that one serves as an indicator of the other in a certain aspect. That unbreakable link might one day form the basis of a super-fast, super-secure quantum internet.
While a quantum internet is still some way off, if we want to make it work, it’s going to require something other than optical fibres.
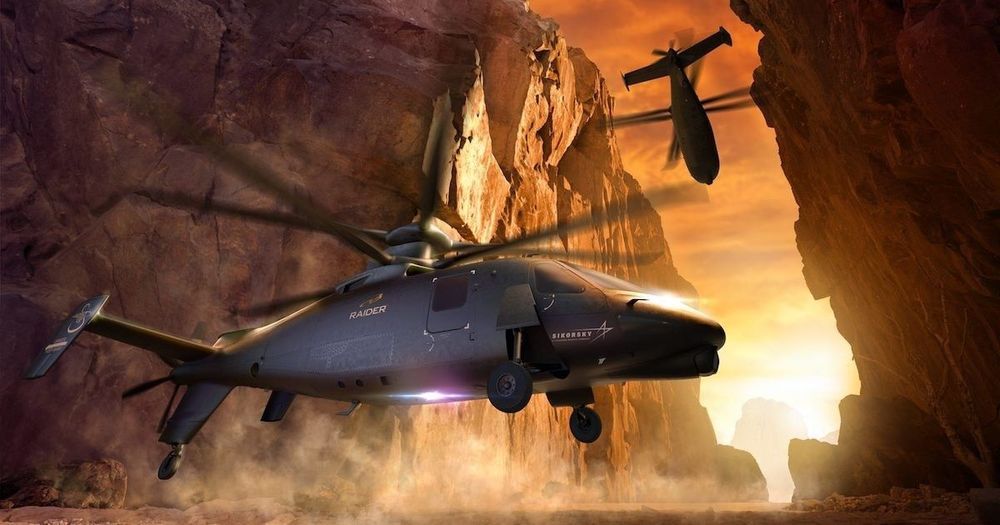

A new scout helicopter will replace half the Army’s Apache fleet
Undeterred by decades of failure, the U.S. Army is trying again to acquire a new scout helicopter. The new rotorcraft is supposed to restore the dedicated aerial scout mission the Army gave up when in 2017 it retired its roughly 300 Bell OH-58D Kiowa Warrior copters.
And here’s a surprise. The new Future Attack Reconnaissance Aircraft also will replace half of the ground-combat branch’s 700 Boeing AH-64 Apache attack helicopters.

Lockheed Martin’s New F-21 Fighter on offer to India has F-22 and F-35 ‘DNA’
New Delhi could select its new fighter in 2019. If it picks the F-21 and opts to keep Lockheed’s designation for the type, it rightfully could claim to be the first operator of a brand-new fighter.
Lockheed Martin in mid-February 2019 offered to sell India a new fighter the company calls the “F-21.”
Only it doesn’t look like a new fighter at all. The F-21 looks like an F-16.
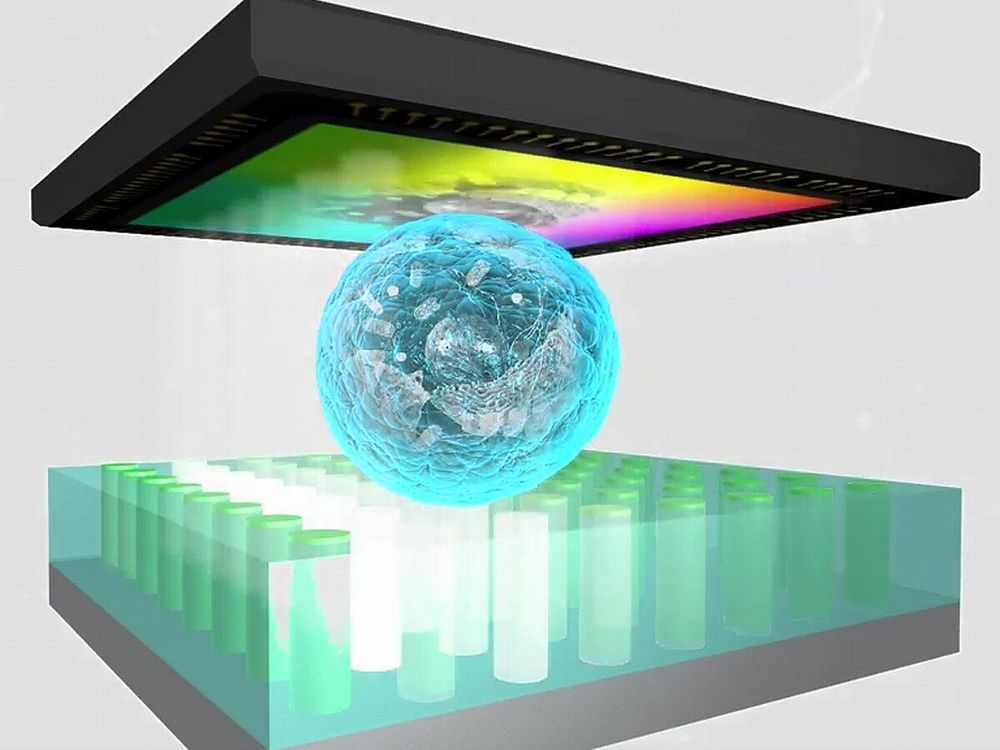
ChipScope – a new approach to optical microscopy
For half a millennium, people have tried to enhance human vision by technical means. While the human eye is capable of recognizing features over a wide range of size, it reaches its limits when peering at objects over giant distances or in the micro- and nanoworld. Researchers of the EU funded project ChipScope are now developing a completely new strategy towards optical microscopy.
The conventional light microscope, still standard equipment in laboratories, underlies the fundamental laws of optics. Thus, resolution is limited by diffraction to the so called Abbe limit’ – structural features smaller than a minimum of 200 nm cannot be resolved by this kind of microscope.
So far, all technologies for going beyond the Abbe limit rely on complex setups, with bulky components and advanced laboratory infrastructure. Even a conventional light microscope, in most configurations, is not suitable as a mobile gadget to do research out in the field or in remote areas. In the ChipScope project funded by the EU, a completely new strategy towards optical microscopy is explored. In classical optical microscopy the analyzed sample area is illuminated simultaneously, collecting the light which is scattered from each point with an area-selective detector, e.g. the human eye or the sensor of a camera.
Chris Webby — Our Planet (feat. Bria Lee) [Official Video]
This is a really cool message. Please spread it around.
Welcome to #WebbyWednesday!
Music video by Chris Webby performing Our Planet (feat. Bria Lee). Footage edited by Emery Kash & Mike Squires. Produced by JP On Da Track & Nox Beatz. © 2019 EightyHD
Available now: https://foundation-media.ffm.to/ourplanet
Donate to The Rainforest Trust: https://www.rainforesttrust.org/savetherainforest/

SpaceX Starship — Anywhere on Earth in under an hour(60 minutes)
Click on photo to start video.
#MustWatch
#SpaceX
#SpaceExploration
Yes…you heard it right!! & to most of the places people would be able to reach within 30 minutes.
Also, a live video test of Grasshopper(by SpaceX) is attached in this video(watch that too)

Could Doomsday Bunkers Become the New Normal?
He stresses that these are not “luxury bunkers” for the top 1 percent, and only a small part of the calls are coming from Doomsday preppers or Cold War-era holdovers. Rather, about two-thirds of his business comes from consumers who pay approximately $25,000 for an underground livable dwelling. Since the outbreak of the coronavirus pandemic, Mr. Woodworth said he has been unable to keep up with the demand.
When we were told to stay inside our homes, a portion of the population quietly went below ground.