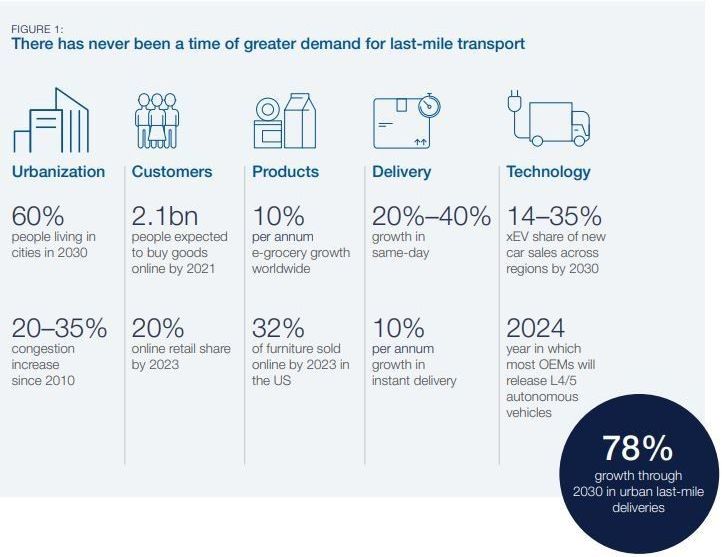
The COVID-19 pandemic has put an incredible strain on global supply chains, from medical supplies to household goods, as spikes in demand stress-test logistics infrastructures. There is an opportunity for unmanned delivery vehicles to assist in addressing this demand and help to reduce the risk of spreading infection.
Here’s a look at some of the challenges and opportunities for automated vehicles (AVs) in last-mile deliveries and local logistics.