Nvidia’s sales are up more than sixfold since its business was transformed by the release of OpenAI’s ChatGPT in late 2022.
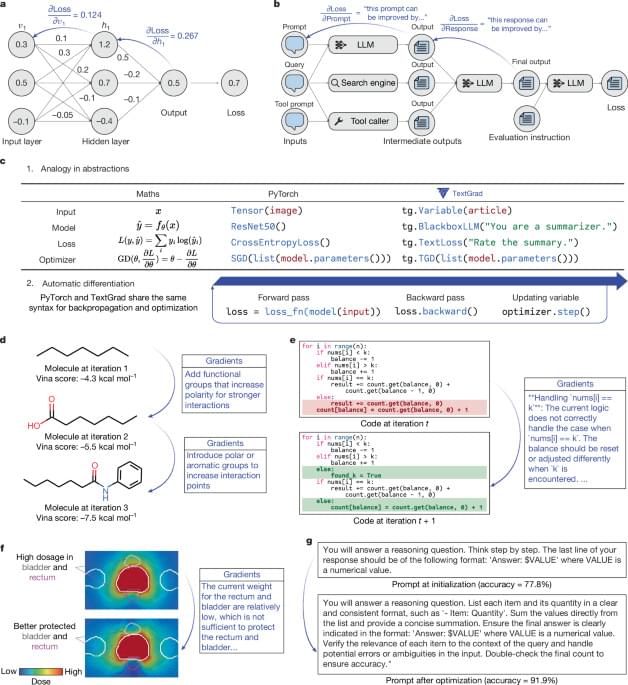
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) systems can be optimized using TextGrad, a framework that performs optimization by backpropagating large-language-model-generated feedback; TextGrad enables optimization across diverse tasks, including radiotherapy treatment plans and molecule generation.
A little over a year ago, Joseph Coates was told there was only one thing left to decide. Did he want to die at home, or in the hospital?
Coates, then 37 and living in Renton, Wash., was barely conscious. For months, he had been battling a rare blood disorder called POEMS syndrome, which had left him with numb hands and feet, an enlarged heart and failing kidneys. Every few days, doctors needed to drain liters of fluid from his abdomen. He became too sick to receive a stem cell transplant — one of the only treatments that could have put him into remission.
“I gave up,” he said. “I just thought the end was inevitable.”
But Coates’s girlfriend, Tara Theobald, wasn’t ready to quit. So she sent an email begging for help to a doctor in Philadelphia named David Fajgenbaum, whom the couple met a year earlier at a rare disease summit.
Scientists are using machine learning to find new treatments among thousands of old medicines.
This is the Fourier Transform. You can thank it for providing the music you stream every day, squeezing down the images you see on the Internet into tiny little JPG files, and even powering your noise-canceling headphones. Here’s how it works.
The equation owes its power to the way that it lets mathematicians quickly understand the frequency content of any kind of signal. It’s quite a feat. But don’t just take my word for it—in 1867, the physicist Lord Kelvin expressed his undying love for this fine piece of mathematics, too. He wrote, “Fourier’s theorem is not only one of the most beautiful results of modern analysis, but it may be said to furnish an indispensable instrument in the treatment of nearly every recondite question in modern physics.” And so it remains.
Math Will Tear Us Apart
In today’s column, I debunk the common myth that if we attain artificial general intelligence (AGI) the resultant AI will be a solo colossus or said-to-be “one big brain”
Let’s talk about it.
This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining various impactful AI complexities (see the link here).
In March 2025, The International Society on General Relativity and Gravitation announced its newest elected members, including CIERA Director Vicky Kalogera.
As the ISGRG Fellowship announcement explains, Prof. Kalogera was recognized “for playing a leading role in the astrophysical interpretation of gravitational wave events produced by the merger of black holes and neutron stars”
Established in 1971, the Society aims to promote the study of General Relativity and Gravitation and to exchange information in the interest of its members and the profession. Fellows are elected from among leading scientists in the society’s membership. The full list of past ISGRG fellows may be found here.
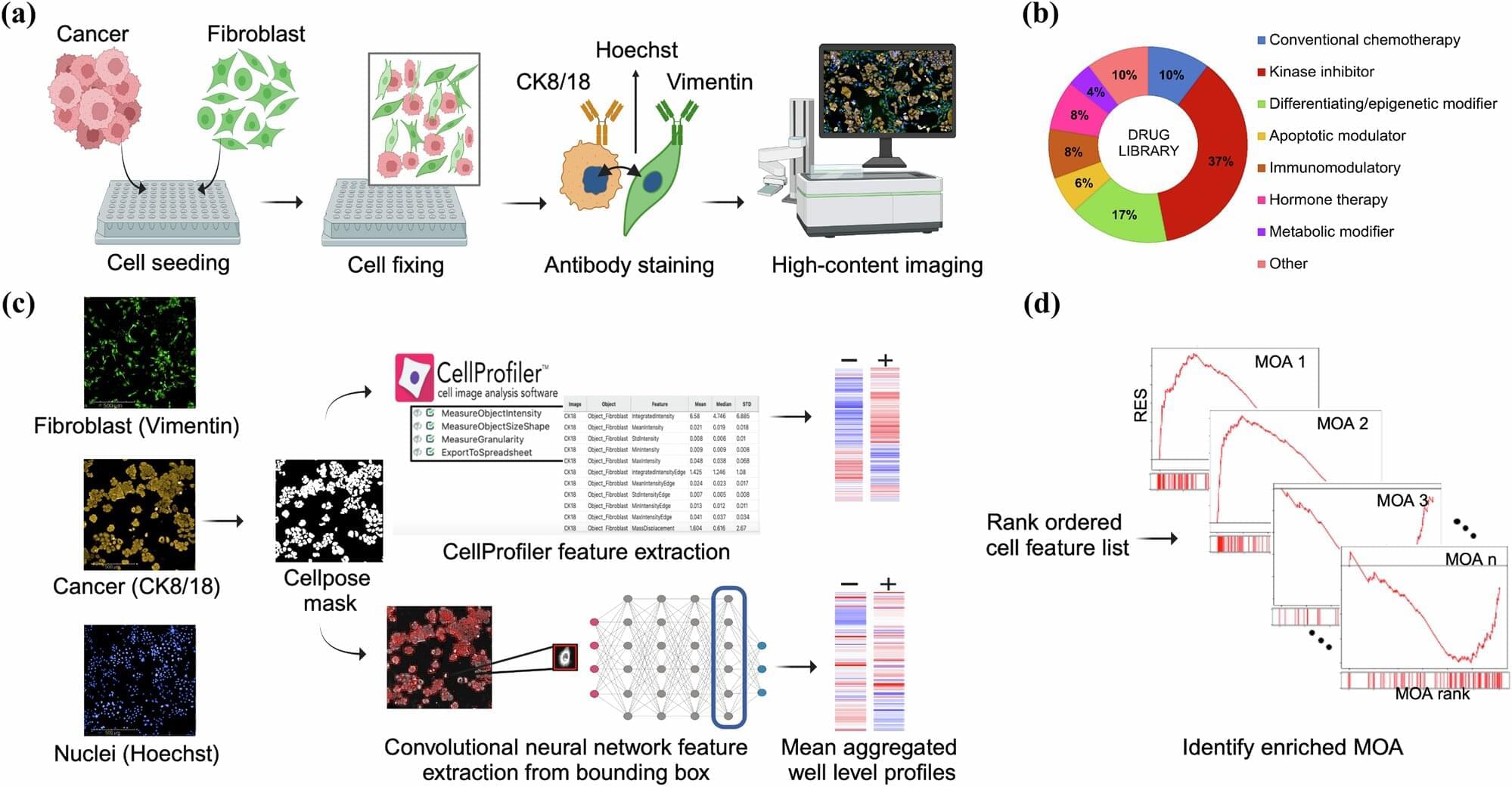
In a study on ovarian cancer cells, researchers from Karolinska Institutet demonstrate how the tumor environment influences how cancer cells respond to drugs by using AI. The study has been published in the journal Communications Biology.
The cancer cells were cultured together with fibroblasts, a type of support cell, and treated with different drugs. Advanced computer programs were used to analyze images of the cancer cells to see how they changed. Fibroblasts play an important role in the tumor microenvironment. They can promote tumor growth, spread, and drug resistance, as well as affect the immune system.
“Our study shows that ovarian cancer cells cultured together with fibroblasts change their appearance when treated with drugs. This demonstrates how the tumor environment influences how cancer cells respond to drugs,” says Osheen Sharma, Ph.D. student at the Department of Oncology-Pathology, Karolinska Institutet, and the study’s first author.
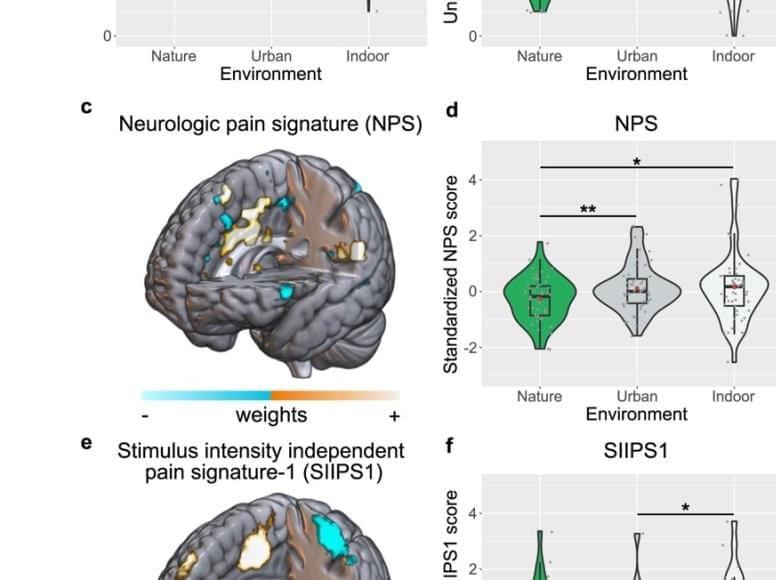
A new neuroimaging study has revealed that viewing nature can help ease how people experience pain, by reducing the brain activity linked to pain perception.
Published in the journal Nature Communications, the research offers a promising foundation for new types of non-pharmacological pain treatments.
Using an fMRI scanner, researchers monitored the brain activity of 49 participants in Austria, as they received pain delivered through a series of small electric shocks. When they were watching videos of a natural scene compared to a city or an indoor office, participants not only reported feeling less pain, but scans showed the specific brain responses associated with processing pain changed too.
The study used advanced machine-learning to analyse the brain networks related to pain processing. The team discovered that the raw sensory signals the brain receives when something hurts were reduced when watching a carefully designed, high quality, virtual nature scene. The study confirmed previous findings that suggest nature can reduce subjective reports of pain, and also marks the first clear demonstration of how natural environments influence the brain, helping to buffer against unpleasant experiences.
A recent study challenges the effectiveness of microdosing LSD for treating ADHD. Despite self-reported improvements, the clinical trial found no significant difference between low-dose LSD and placebo in reducing ADHD symptoms.
Normal glucose regulation (NGR) for prediabetes remission.
Prediabetes remission to normal glucose regulation (NGR), in addition to standard weight loss, lowers type 2 diabetes (T2D) risk more than standard weight loss alone.
Remission of prediabetes to NGR should be considered in guidelines and recommendations for the delay and prevention of T2D.
Future studies will provide evidence whether or not prediabetes remission can protect against incident T2Drelated comorbidities such as cardiovascular and/or chronic kidney disease (CKD). https://sciencemission.com/Prediabetes-remission
Prediabetes is a highly prevalent and increasingly common condition affecting a significant proportion of the global population. The heterogeneous nature of prediabetes presents a challenge in identifying individuals who particularly benefit from lifestyle or other therapeutic interventions aiming at preventing type 2 diabetes (T2D) and associated comorbidities. The phenotypic characteristics of individuals at risk for diabetes are associated with both specific risk profiles for progression and a differential potential to facilitate prediabetes remission and reduce the risk of future T2D. This review examines the current definition and global prevalence of prediabetes and evaluates the potential of prediabetes remission to reduce the alarming increase in the global burden of T2D.