STARLINK.


Lean, mean bricklaying machine.
Construction is difficult to automate because of the complex, individualized and customized work it requires.
But a company called Construction Robotics has developed a one-of-a-kind robot that can lay bricks six times faster than a human.

LONDON — Artificial intelligence researchers don’t like it when you ask them to name the top AI labs in the world, possibly because it’s so hard to answer.
There are some obvious contenders when it comes to commercial AI labs. U.S. Big Tech — Google, Facebook, Amazon, Apple and Microsoft — have all set up dedicated AI labs over the last decade. There’s also DeepMind, which is owned by Google parent company Alphabet, and OpenAI, which counts Elon Musk as a founding investor.
DeepMind, OpenAI, and Facebook AI Research are fighting it out to be the top AI research lab in the world.
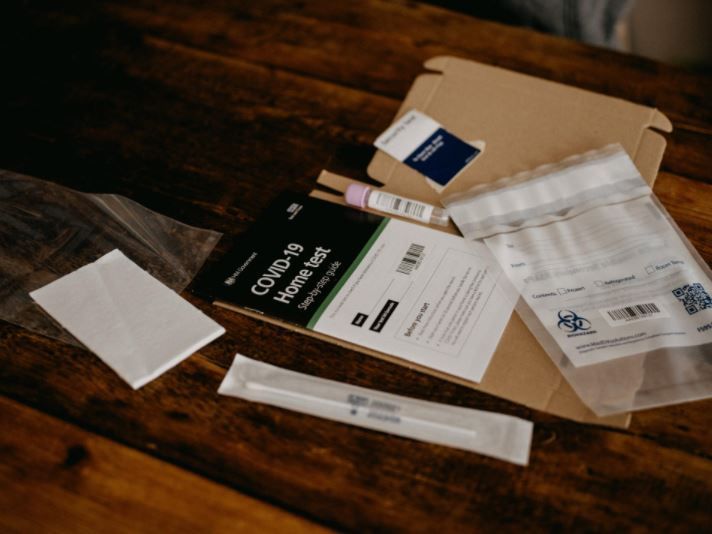
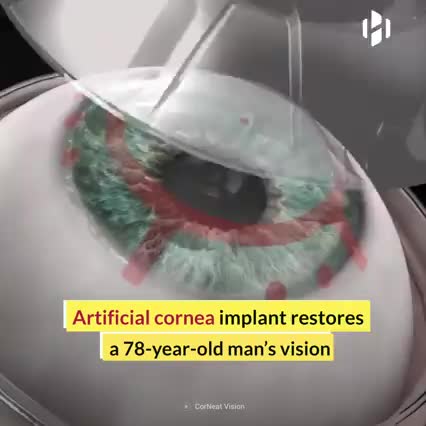

The race is on. Tech startups across the globe are competing to deliver to the rest of us what Google employees already enjoy : regular at-home COVID tests.
At-home medical testing was gaining steam pre-pandemic and is now a red-hot market with more than two dozen companies developing at-home COVID tests.

The ultimate goal of the Old World alchemist was to turn inexpensive metals into gold. Modern-day physicists at the University of Rochester’s Institute of Optics (Rochester, NY), have turned aluminum and other metals goldin color if not chemistry. A femtosecond laser processing technique created by professor Chunlei Guo and his assistant Anatoliy Vorobeyv alters the surface properties of aluminum, platinum, titanium, tungsten, silver, and gold to create tints of gold, blue, gray, black, and even multicolored irridescence.

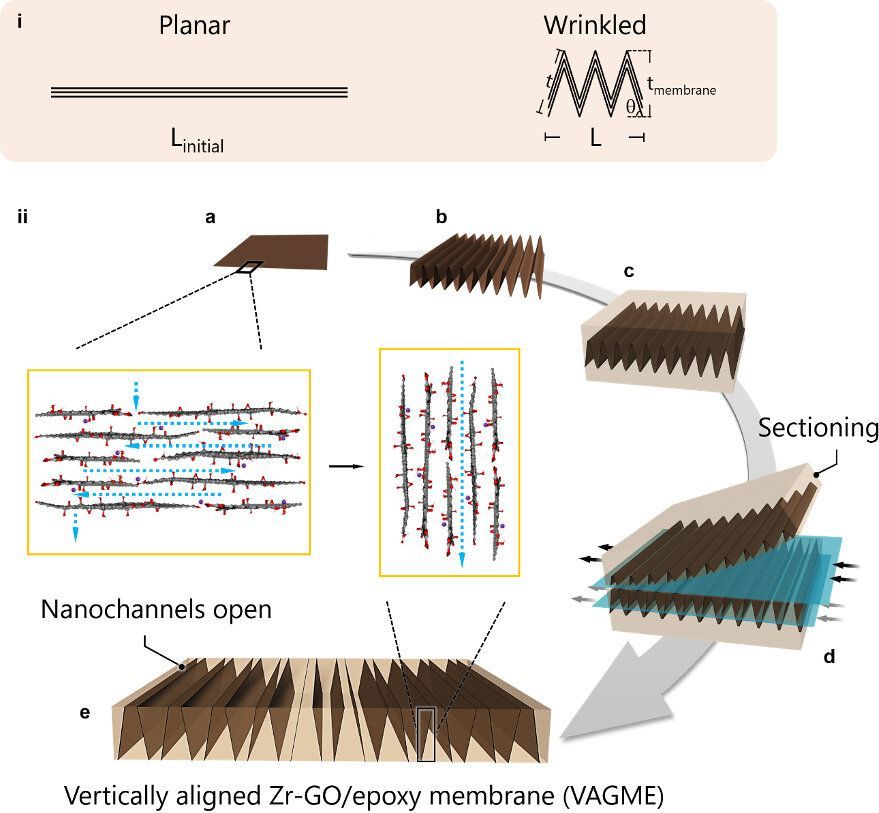
When sheets of two-dimensional nanomaterials like graphene are stacked on top of each other, tiny gaps form between the sheets that have a wide variety of potential uses. In research published in the journal Nature Communications, a team of Brown University researchers has found a way to orient those gaps, called nanochannels, in a way that makes them more useful for filtering water and other liquids of nanoscale contaminants.
“In the last decade, a whole field has sprung up to study these spaces that form between 2-D nanomaterials,” said Robert Hurt, a professor in Brown’s School of Engineering and coauthor of the research. “You can grow things in there, you can store things in there, and there’s this emerging field of nanofluidics where you’re using those channels to filter out some molecules while letting others go through.”
There’s a problem, however, with using these nanochannels for filtration, and it has to do with the way those channels are oriented. Like a notebook made from stacked sheets of paper, graphene stacks are thin in the vertical direction compared to their horizontal length and width. That means that the channels between the sheets are likewise oriented horizontally. That’s not ideal for filtration, because liquid has to travel a relatively long way to get from one end of a channel to the other. It would be better if the channels were perpendicular to the orientation of the sheets. In that case, liquid would only need to traverse the relatively thin vertical height of the stack rather than the much longer length and width.
A new algorithm capable of inferring goals and plans could help machines better adapt to the imperfect nature of human planning.
In a classic experiment on human social intelligence by psychologists Felix Warneken and Michael Tomasello (see video below), an 18-month old toddler watches a man carry a stack of books towards an unopened cabinet. When the man reaches the cabinet, he clumsily bangs the books against the door of the cabinet several times, then makes a puzzled noise.

Circa 2011 o.o
A green sea slug appears to be part animal, part plant. It’s the first critter discovered to produce the plant pigment chlorophyll.
The sneaky slugs seem to have stolen the genes that enable this skill from algae that they’ve eaten. With their contraband genes, the slugs can carry out photosynthesis — the process plants use to convert sunlight into energy.