Cornell astronomers plot how to take spectra from extrasolar earths trapped in orbits around dying white dwarfs.
I was confident enough to turn it in. However, I then was looking online and found out there’s a really easy way to find out if an essay was written by GPT-2. It’s to feed it to GPT-2 and if it’s able to predict the next words, then it was written by the AI. It’s easier to find out than normal plagiarism.
I knew that the business school had software that they were using to look out for plagiarism in all the essays that are turned in to their online platform, which is how I turned in my essays. So I was slightly worried that the company that sold them the anti-plagiarism software would have made an update.
I don’t think the professors even considered the possibility of GPT-2 writing the essays, but I was slightly worried that the company making the software added a module. But not that much.
Over at the always interesting Small Wars Journal, Tony Corn has a stimulating piece on the implications of the European crisis for world politics. He sees a clueless German policy establishment recklessly moving toward an unsustainable quest for power reminiscent in too many ways of problems Germany has had in its past.
Germany, warns Corn, is planning to use its financial domination of Europe to remake the EU into an extension of German power — more or less the way that Prussia used the Zollverein to bring northern Germany under its control and then dominated the Bismarckian Reich through a rigged constitutional system. Once that is in place, he writes, the Germans will continue their policy of deepening relations with Russia at the expense of NATO and transatlantic ties, and end Europe’s embargo on arms sales to China.
As an analyst, Corn sometimes goes to what we more placid types at VM consider overexcited conclusions about Eurasian power realignments. Safely ensconced among the storied oaks and elms, gazebos, pergolas, ha-has, follies and deer parks surrounding the stately Mead manor in glamorous Queens, we tend to take a wait-and-see attitude toward organizations like the Shanghai Cooperation Organization which Russia and China have sometimes posited as a kind of embryonic counter-NATO. Corn, in our perhaps excessively complacent view, can be too quick to take vague Eurasian fantasies and aspirations about diplomatic revolutions as accomplished facts; it is easier to dream about firm Russian and Chinese anti-US cooperation than for those two countries to make it work. But that said, there is no doubt that Corn’s industry, historical grounding and sensitive, even over-sensitive nerve endings give him the ability to produce original and striking ideas.
Bot Sentinel conducted an analysis and found bots and trolls are using hashtags like #ReopenAmericaNow and #StopTheMadness to spread disinformation.
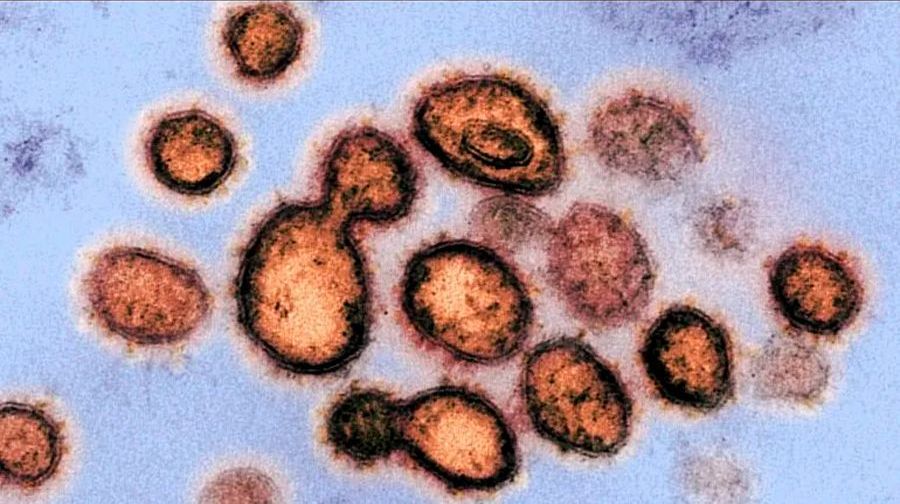
COVID-19 can remain in the air in closed spaces.
Tras la propagación del virus, científicos se han dedicado a comprobar si es posible el contagio por medio del aire
Investigadores del laboratorio Estatal de Virología de la Universidad de Wuhan indicaron que debido a la pandemia causada por el creciente número de contagios por coronavirus, distintos estudios se han dedicado a comprobar si es posible el contagio por medio del aire.
De acuerdo con el estudio publicado en la revista Nature, el coronavirus puede permanecer en el aire de los espacios que carecen de ventilación, es importante mencionar que el mayor factor de riesgo es el contacto con las gotículas de una persona infectada.
This robot is a drone and a generator that can go on surveillance missions. Is there anything it can’t do?
#OopsMyBad #Busted 🤔
Yes you read this right. The WHO criticized a drug and used a reference that was neither peer reviewed or published 🙄…Then they removed it as if no one would notice.
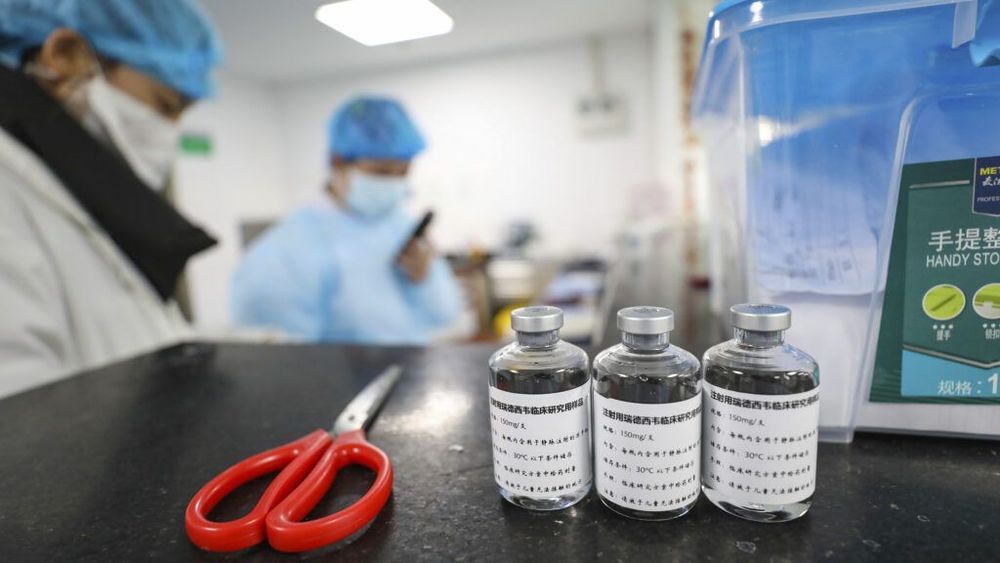
The antiviral medicine remdesivir from Gilead Sciences failed to speed the improvement of patients with Covid-19 or prevent them from dying, according to results from a long-awaited clinical trial conducted in China. Gilead, however, said the data suggest a “potential benefit.”
A summary of the study results was inadvertently posted to the website of the World Health Organization and seen by STAT on Thursday, but then removed.
“A draft manuscript was provided by the authors to WHO and inadvertently posted on the website and taken down as soon as the mistake was noticed. The manuscript is now undergoing peer review and we are waiting for a final version before WHO comments on it,” said WHO spokesperson Daniela Bagozzi.
Eric klein.
If you followed the world of pop-culture or tech for some time now, then you know that advances in artificial intelligence are heating up. In reality, AI has been the talk of mainstream pop-culture and sci-fi since the first Terminator movie came out in 1984. These movies present an example of something called “Artificial General Intelligence.” So how close are we to that?
No, not how close are we to when the terminators take over, but how close are we to having an AI capable of navigating nearly any problem it’s presented with.
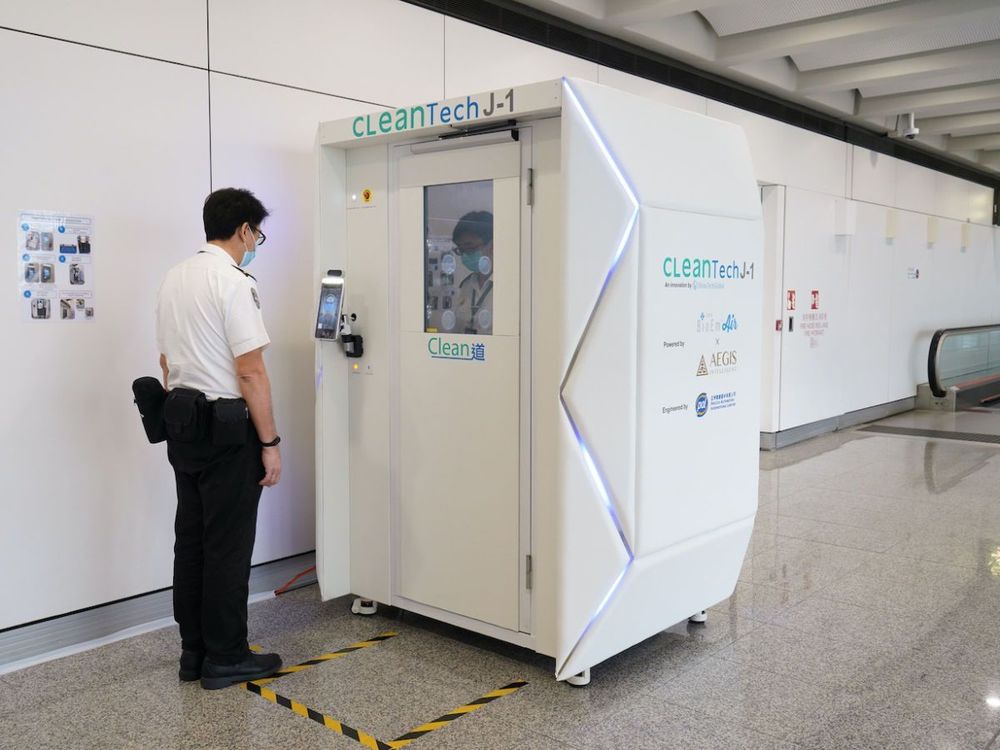
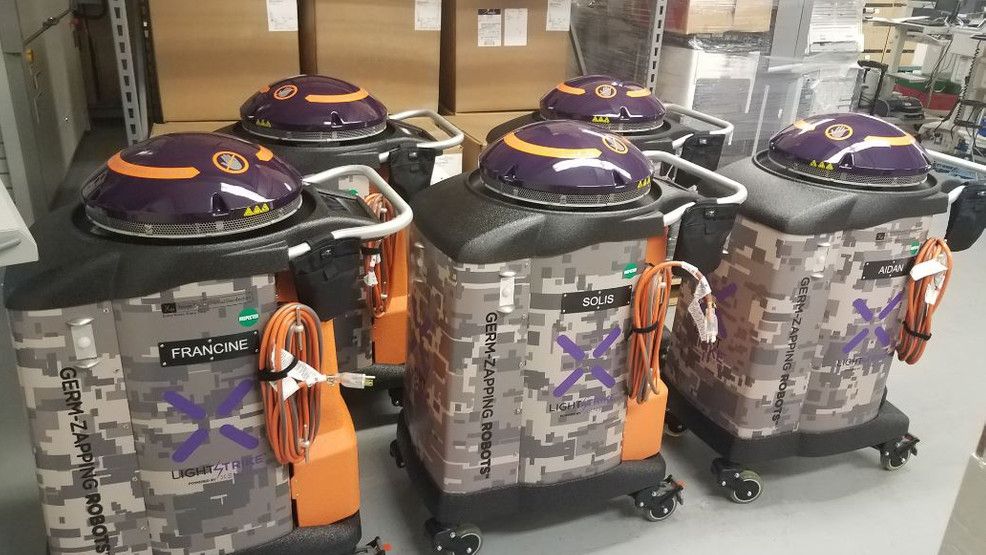
Xenex Disinfection Services found out today its ultraviolet light technology is 99.9 percent effective in eradicating the virus, according to the Texas Biomedical Research Center.
“This is what the world has been looking for„” says Xenex CEO Morris Miller, “to make sure there’s a device that can actually kill the real virus.”
Xenex robots cost $125,000 and are now being ordered by hospitals, hotels, airlines and even the Governor of Texas.
SAN ANTONIO — A local company has learned its robot completely removes COVID-19 from rooms and masks. Xenex Disinfection Services found out today its ultraviolet light technology is 99. 9 percent effective in eradicating the virus, according to the Texas Biomedical Research Center. “This is what the world has been looking for„” says Xenex CEO Morris Miller, “to make sure there’s a device that can actually kill the real virus. ”.