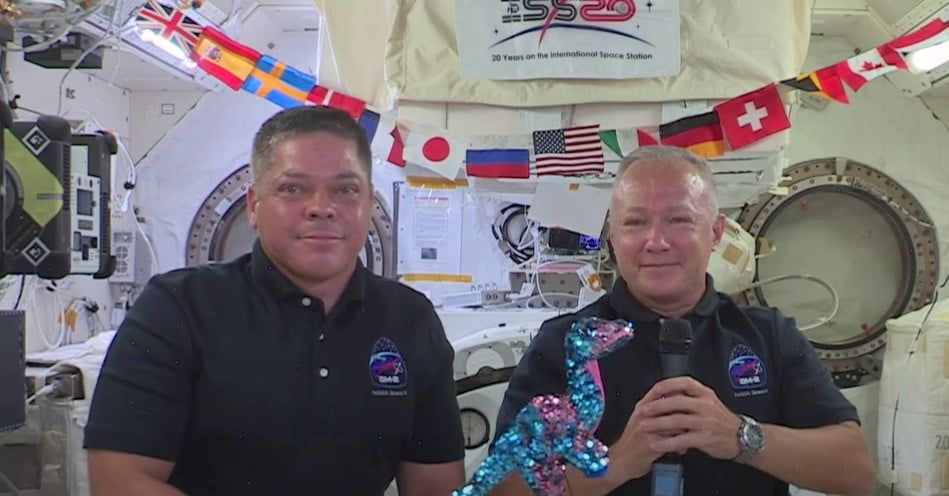
A week after their arrival, SpaceX Crew Dragon astronauts Doug Hurley and Bob Behnken have given their first interview from the International Space Station.
The Cambrian period was a time when every imaginable type of life-form evolved. Every imaginable life-form includes parasites. When exactly parasitism spawned is still a mystery, but it makes sense that parasites would have crawled out with all the other creatures that appeared during the burst of l…
SpaceX’s Starlink satellite constellation is still deep into testing mode, but it’s already generating 5 trillion bytes of data on a daily basis and getting software updates on a weekly basis.
Those are a couple of the nuggets coming from a weekend Reddit “Ask Me Anything” session featuring SpaceX’s software team.
The main focus of the online chat was SpaceX’s successful mission sending NASA astronauts Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley to the International Space Station in a Crew Dragon capsule — but one of the team members, Matt Monson, has moved on from Dragon to take charge of Starlink software development.
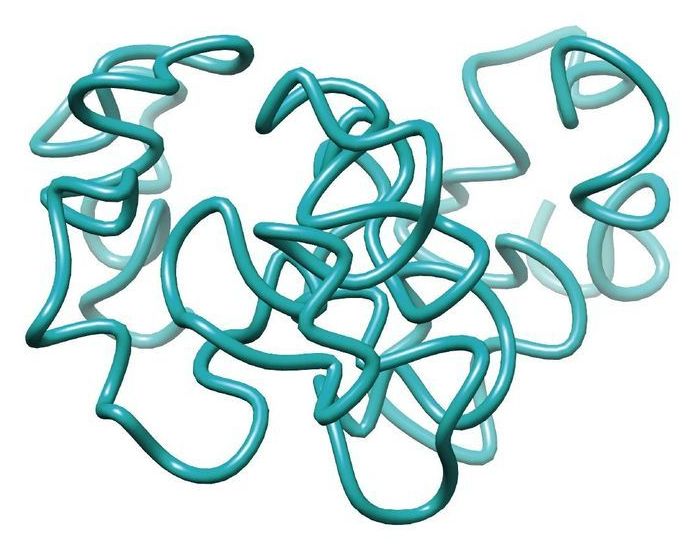
The three-dimensional structure of the human genome is essential for providing a rapid and robust inflammatory response but is surprisingly not vital for reprogramming one cell type into another, according to research published today in Nature Genetics. The findings shed new light on the fundamental relationship between how a genome folds and the function of a cell.
Billionaire investor Ron Baron believes there’s still plenty of room for growth for Elon Musk’s Tesla and SpaceX companies.
Baron said Tuesday morning on “Squawk Box” that he believes “there’s 10 times more to go” with Tesla. He also said SpaceX, a privately held company, will grow by a multiple of 20 in the next 10 years. He previously predicted similar growth for Tesla.
3. Evolution shifts to off-world human colonies.
4. Transhumanism will drive evolution.
Is natural selection still a major force in human evolution? As far back as high school biology, we’ve been taught to think the answer must be yes. But is it really true?
Charles Darwin published his groundbreaking On the Origin of Species back in 1859, around the same time that Charles Dickens was making a name for himself writing about social conditions in England. Dickens’ stories emerge from a period in which only 50 percent of British children survived to adulthood — a number not so different from animals in the jungle. In that vein, Darwin was right when he said natural selection was operating on humans full force.
Yet the forces that came into play in the 1850s are far different from those we experience today, prompting some high profile biologists to suggest that our advanced medical capabilities have, in effect, blunted natural selection. In a 2013 Radio Times interview, science communicator David Attenborough described it this way:
Is it possible to rapidly increase (or decrease) the amount of information the brain can store?
A new international study led by the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre (RI-MUHC) suggests it may be. Their research has identified a molecule that improves brain function and memory recall is improved. Published in the latest issue of Cell Reports, the study has implications for neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative diseases, such as autism spectrum disorders and Alzheimer’s disease.
I remember questioning this data, as it was not even research on animals, it was observation of people’s medical files.
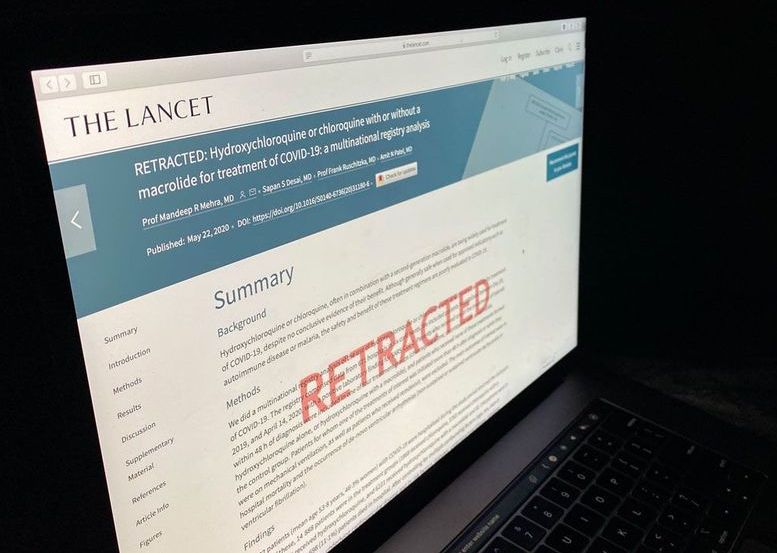
Three unlikely collaborators are at the heart of the fast-moving COVID-19 research scandal, which led to retractions last week by The Lancet and The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM), and the withdrawal of an online preprint, after the trove of patient data they all relied on was challenged. The three physician-scientists never were at the same institution nor had they ever before written together, but they are the only authors in common on the disputed papers, and the other co-authors all have ties to at least one of them. Their partnership, which seized a high-impact role during a global public health crisis, has now ended disastrously.
The first author for both retracted papers was cardiac surgeon Mandeep Mehra, an eminent Harvard University professor who works at Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH) and is known internationally for cardiovascular medicine and heart transplants. He provided the kind of gravitas that can fast-track papers to leading journals. In a statement provided by BWH, Mehra said he had met another of the trio, cardiac surgeon Amit Patel, in “academic and medical circles,” and that Patel had introduced him to Sapan Desai, a vascular surgeon and founder of Surgisphere, the tiny company that supplied the data. Journal disclosures, however, also indicate Mehra received compensation from Triple-Gene, a gene therapy company Patel co-founded to develop cardiovascular treatments.
Author partnership on coronavirus papers is “completely bizarre” and should have been a red flag, former journal editor says.
Another link on diet/healthspan.
Studies by Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute (BDI), have provided a new understanding into the roles two essential amino acids play in metabolic health, which may help scientists in the fight against obesity.
Led by Dr. Adam Rose, the recent finding, published in Nature Communications, shows that by reducing the amount of two amino acids —threonine and tryptophan—in young healthy mice, they were able to burn more calories than they consumed, without calorie reduction, keeping them lean and healthy and without the side-effect of lower muscle mass. A low-threonine diet even protected mice that were morbidly obese and prone to developing type 2 diabetes.
While a moderate reduction in dietary protein and therefore essential amino acids can enhance vitality, diets devoid of this component can make people sick very quickly and are not recommended. However, this study has shown that a reconsideration of the functions of these two amino acids in nutrition warrants further exploration.
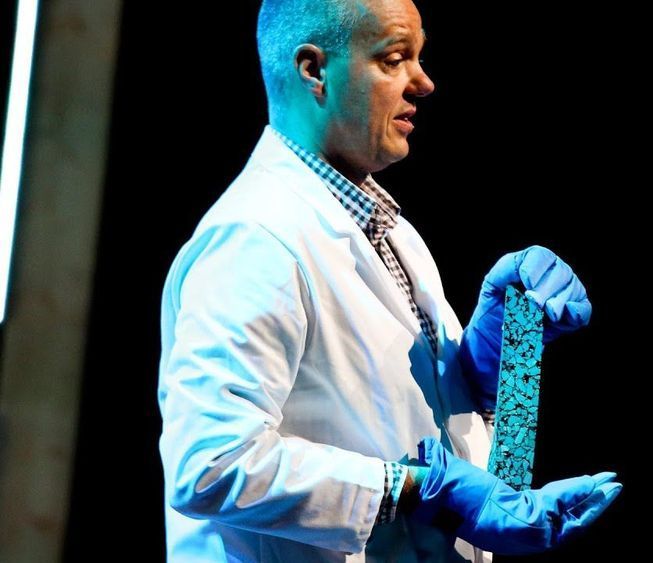
Paved roads are nice to look at, but they’re easily damaged and costly to repair. Erik Schlangen demos a new type of porous, asphalt made of simple materials with an astonishing feature: When cracked, it can be “healed” by induction heating. (Filmed at TEDxDelft.)
TEDTalks is a daily video podcast of the best talks and performances from the TED Conference, where the world’s leading thinkers and doers give the talk of their lives in 18 minutes (or less). Look for talks on Technology, Entertainment and Design — plus science, business, global issues, the arts and much more.
Find closed captions and translated subtitles in many languages at http://www.ted.com/translate
Follow TED news on Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/tednews
Like TED on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/TED