A large Mayo Clinic study finds that treating COVID-19 patients with two monoclonal antibodies — casirivimab and imdevimab — can help avoid hospitalization.
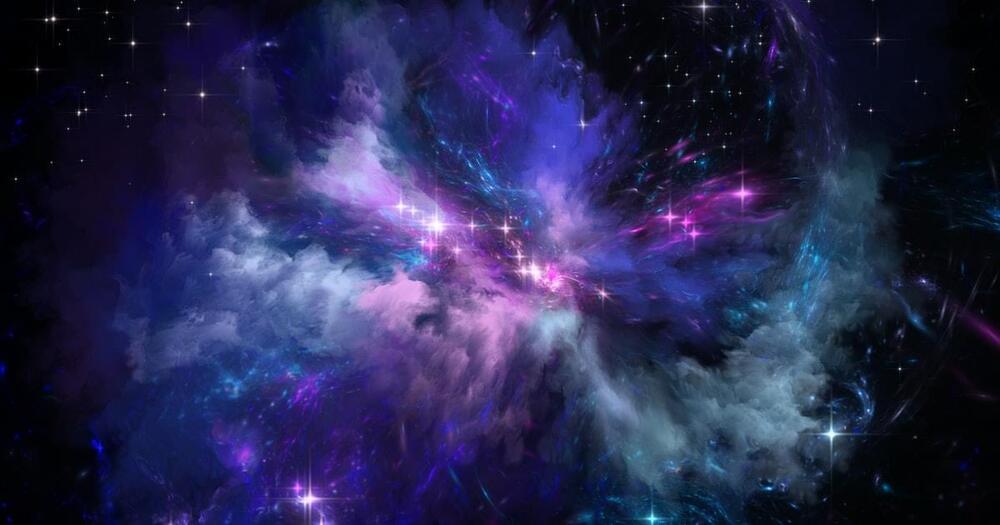



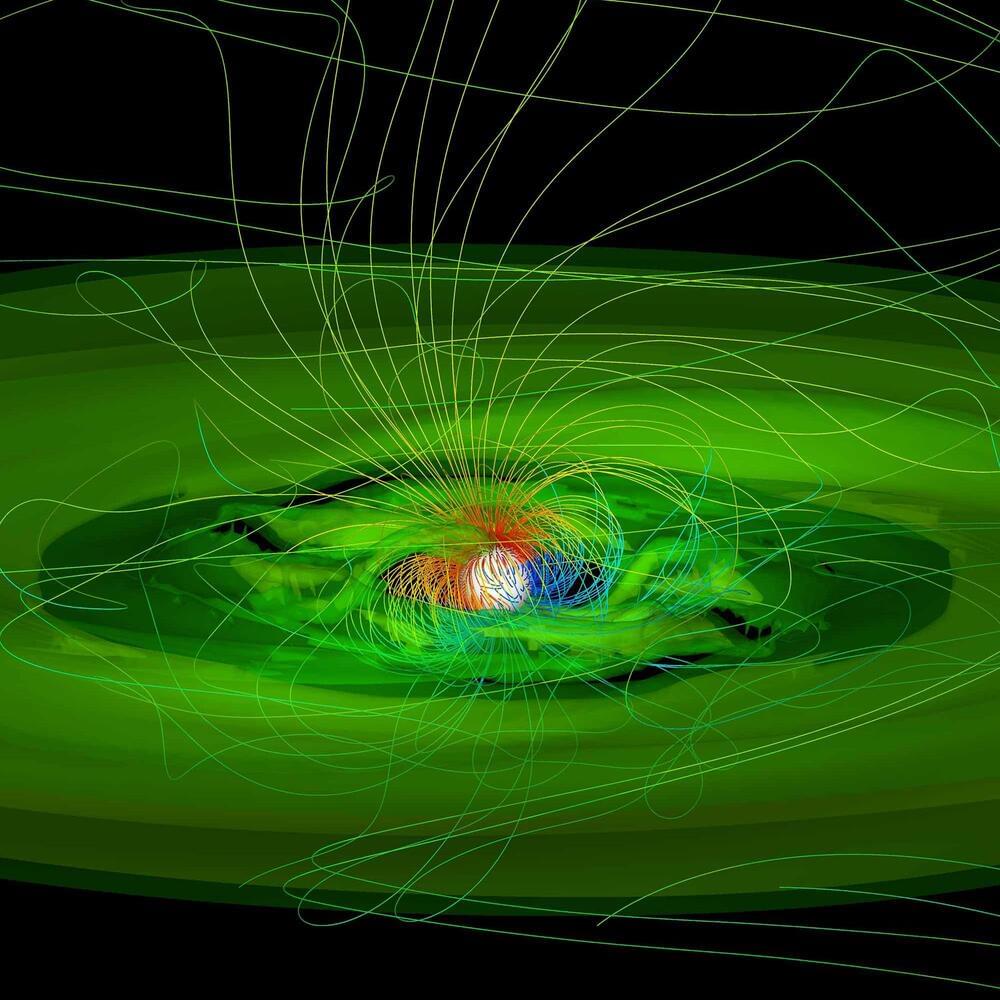
Astronomers have discovered a strangely shaped spot on the surface of a baby star 450 million light-years away, revealing new insights into how our solar system formed.
The familiar star at the center of our solar system has had billions of years to mature and ultimately provide life-giving energy to us here on Earth. But a very long time ago, our sun was just a growing baby star. What did the sun look like when it was so young? That’s long been a mystery that, if solved, could teach us about the formation of our solar system—so-named because sol is the Latin word for sun—and other stellar systems made up of planets and cosmic objects orbiting stars.
“We’ve detected thousands of planets in other stellar systems in our galaxy, but where did all of these planets come from? Where did Earth come from? That’s what really drives me,” says Catherine Espaillat, lead author on the paper and a Boston University College of Arts & Sciences associate professor of astronomy.
Silvia Musolino defended her Ph.D. on new theoretical insights in quantum physics by studying gases at the lowest temperatures consisting of many atoms.
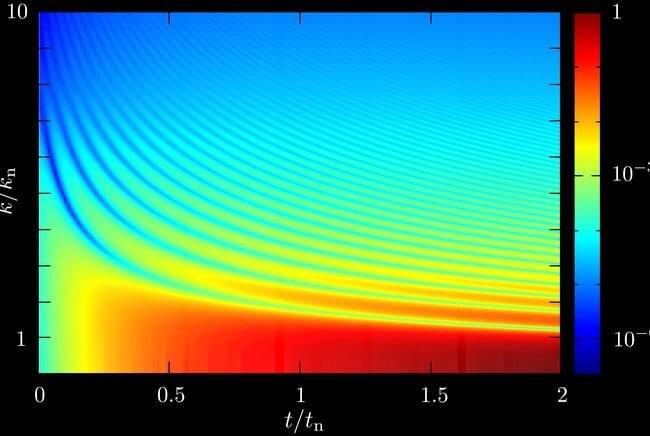
A practical way to study quantum mechanics is provided by gases that have extremely low density and consist of many atoms, often more than one hundred thousand, cooled down to temperatures close to the absolute zero. Silvia Musolino studied different types of interactions between these atoms, providing new pathways for future research on new technologies such as quantum computers.
Quantum mechanical laws govern the physics at the atomic scale and is distinguished by classical mechanics, which deals mainly with natural phenomena we can see, hear, or touch. However, even quantum mechanics influences our daily life. Transistors, which are crucial components of electronic devices, are based on quantum mechanical effects. Moreover, quantum mechanics paves the way for new technologies that may strongly impact our lives, such as quantum computers.

Astronomers may have captured the best view yet of matter colliding with the surface of a young star, findings that may shed light on what the sun looked like in its youth.
Newborn stars are surrounded by a disk of gas and dust from which planets, asteroids, comets and moons are born. The star’s magnetic field connects the star with this protoplanetary disk, “funneling material from the disk onto the star,” study lead author Catherine Espaillat, an astrophysicist at Boston University, told Space.com.

Innovative coronavirus disease2019(COVID-19) vaccines, with elevated global manufacturing capacity, enhanced safety and efficacy, simplified dosing regimens, and distribution that is less cold chain-dependent, are still global imperatives for tackling the ongoing pandemic. A previous phase I trial indicated that the recombinant COVID-19 vaccine (V-01), which contains a fusion protein (IFN-PADRE-RBD-Fc dimer) as its antigen, is safe and well tolerated, capable of inducing rapid and robust immune responses, and warranted further testing in additional clinical trials. Herein, we aimed to assess the immunogenicity and safety of V-01, providing rationales of appropriate dose regimen for further efficacy study.
Methods:
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II clinical trial was initiated at the Gaozhou Municipal Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (Guangdong, China) in March 2021. Both younger (n = 440; 18–59 years of age) and older (n = 440; ≥60 years of age) adult participants in this trial were sequentially recruited into two distinct groups: two-dose regimen group in which participants were randomized either to follow a 10 or 25 μg of V-01 or placebo given intramuscularly 21 days apart (allocation ratio, 3:3:1, n = 120 120, 40 for each regimen, respectively), or one-dose regimen groups in which participants were randomized either to receive a single injection of 50 μg of V-01 or placebo (allocation ratio, 3:1, n = 120 40, respectively). The primary immunogenicity endpoints were the geometric mean titers of neutralizing antibodies against live severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and specific binding antibodies to the receptor binding domain (RBD).
Scientists recently broke their own laser-fusion record! But they must replicate their success soon to preserve research in thermonuclear weapons.
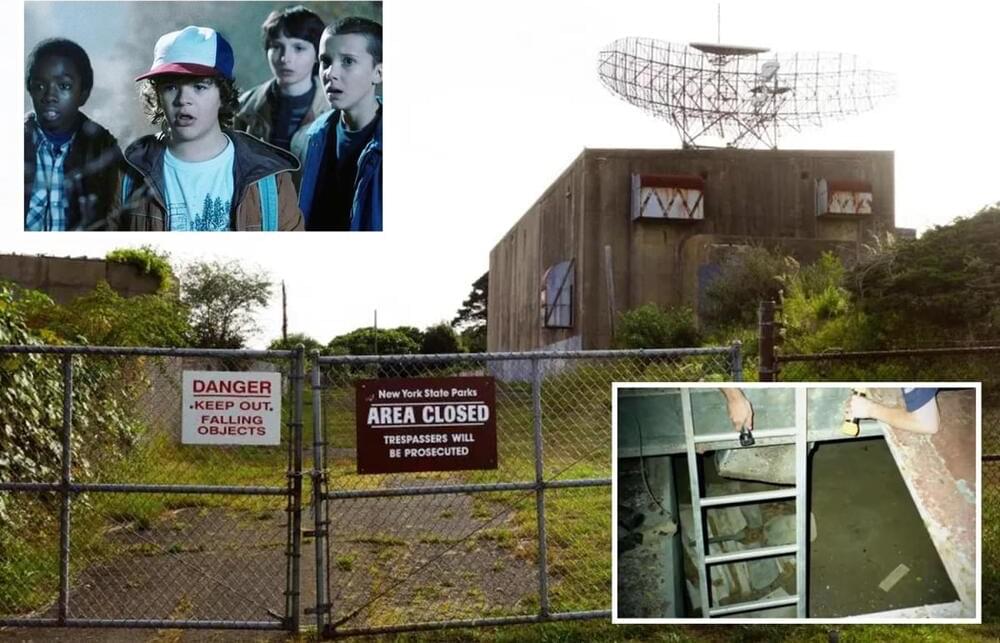

Circa 2019
STRANGER Things has attracted a global audience of over 20million viewers who love the show for its eerie plot lines involving secret government experiments and monsters from other dimensions.
But the alleged real-life stories that inspired the Netflix show — which was confirmed for a forth series on Monday - are more terrifying than anything in the fictional town of Hawkins, where the series is set.
Stranger Things stars Millie Bobby Brown and Winona Ryder and follows a group of children in the 1980s who uncover supernatural phenomena connected to a secret government laboratory in their town.
The Prime Minister, Boris Johnson, has reiterated that the Taliban must meet certain terms if they want frozen funds to be released to them.
Addressing several pots of money that have been frozen, the Prime Minister once again insisted that the Taliban must meet the West’s demands in order to access the funds.
Mr Johnson has recently said: “If the new regime in Kabul wants diplomatic recognition, or to unlock the billions that are currently frozen, they will have to ensure safe passage for those who wish to leave the country, to respect the rights of women and girls, to prevent Afghanistan from, again, becoming an incubator for global terror, because that would be disastrous for Afghanistan.”
Get the latest headlines: https://www.telegraph.co.uk/
Telegraph.co.uk and YouTube.com/TelegraphTV are websites of The Telegraph, the UK’s best-selling quality daily newspaper providing news and analysis on UK and world events, business, sport, lifestyle and culture.