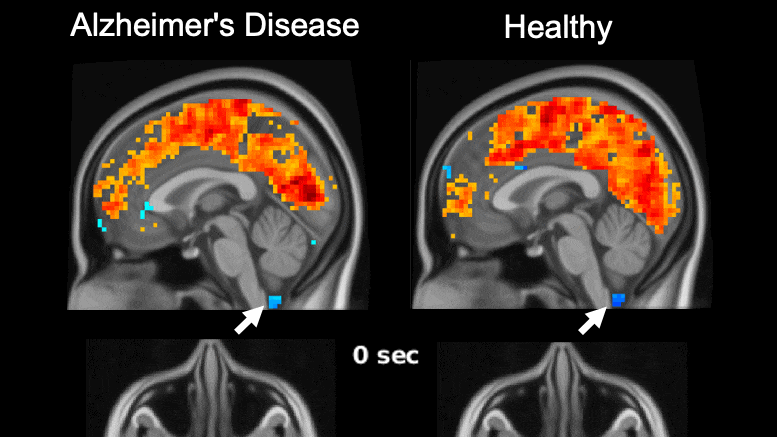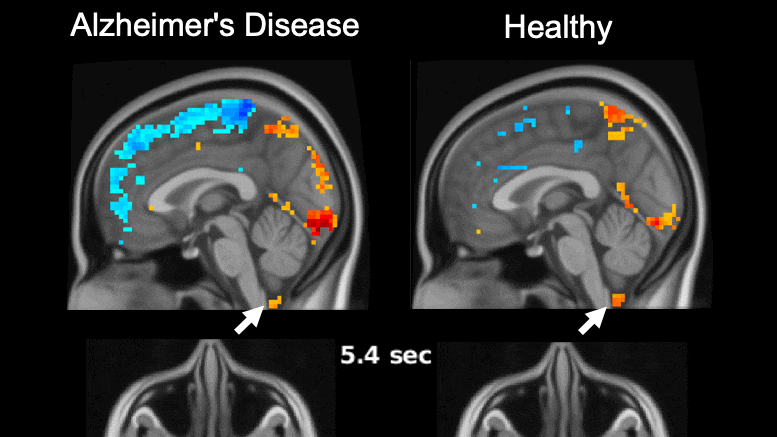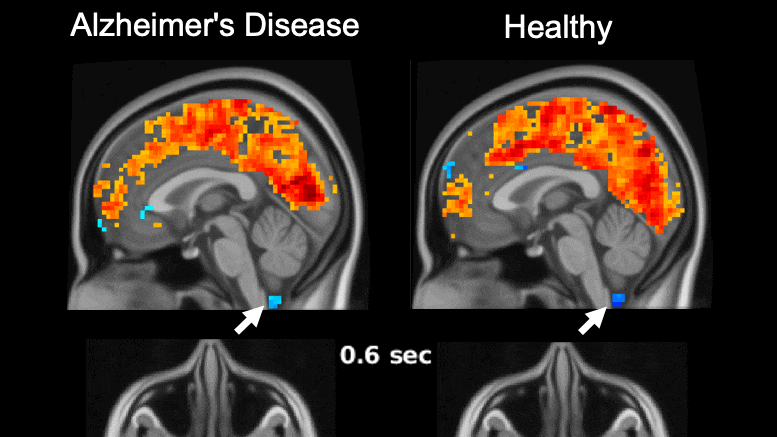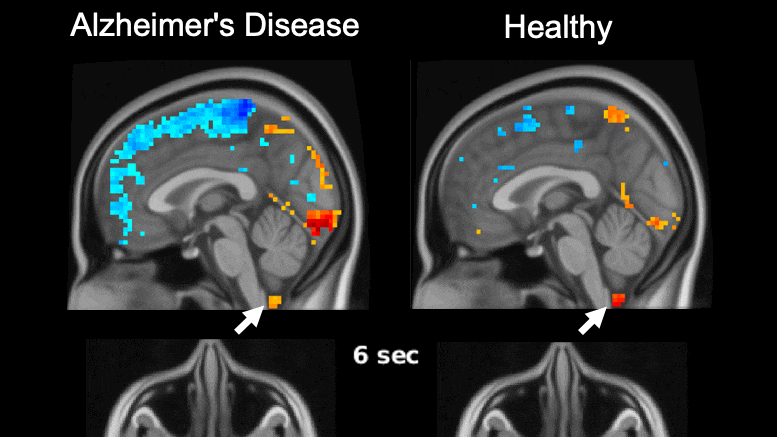
For reference, we can go back to the HRNet paper. The researchers used a dedicated Nvidia V100, a massive and extremely expensive GPU specially designed for deep learning inference. With no memory limitation and no hindrance by other in-game computations, the inference time for the V100 was 150 milliseconds per input, which is ~7 fps, not nearly enough to play a smooth game.
Development and training neural networks
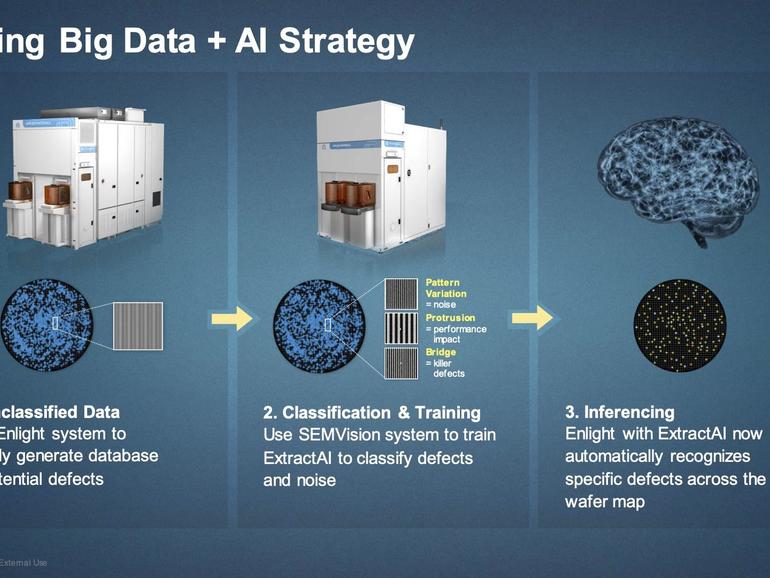
Another vexing problem is the development and training costs of the image-enhancing neural network. Any company that would want to replicate Intel’s deep learning models will need three things: data, computing resources, and machine learning talent.