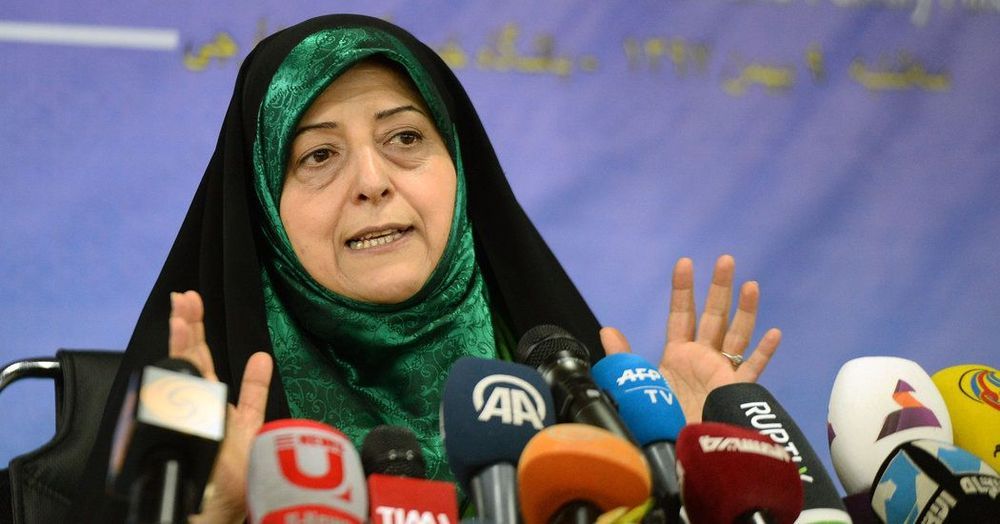
Artist’s concept of the AREE Venus rover. The rover would be wind-powered and able to last on Venus’ hellish surface much longer than previous landers. Image via NASA/ JPL-Caltech.
There’ve been missions to Venus over the past decades, but Venus is a tough place to visit, with temperatures on its surface hot enough to melt lead. The last probe that landed on Venus’ hellish surface was part of the Vega 2 mission in 1985; it transmitted data from Venus’ surface for 57 minutes. Now NASA wants to visit Venus’ surface again, not with just another lander … but with a rover.
On February 21, 2020, NASA announced a public challenge to help design a future Venus rover called Automaton Rover for Extreme Environments (AREE). The challenge – Exploring Hell: Avoiding Obstacles on a Clockwork Rover – is specifically to develop an obstacle-avoidance sensor for the rover. The concept is being funded by a grant from the NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts program.