To evaluate the performance of robotics algorithms and controllers, researchers typically use software simulations or real physical robots. While these may appear as two distinct evaluation strategies, there is a whole other range of possibilities that combine elements of both.
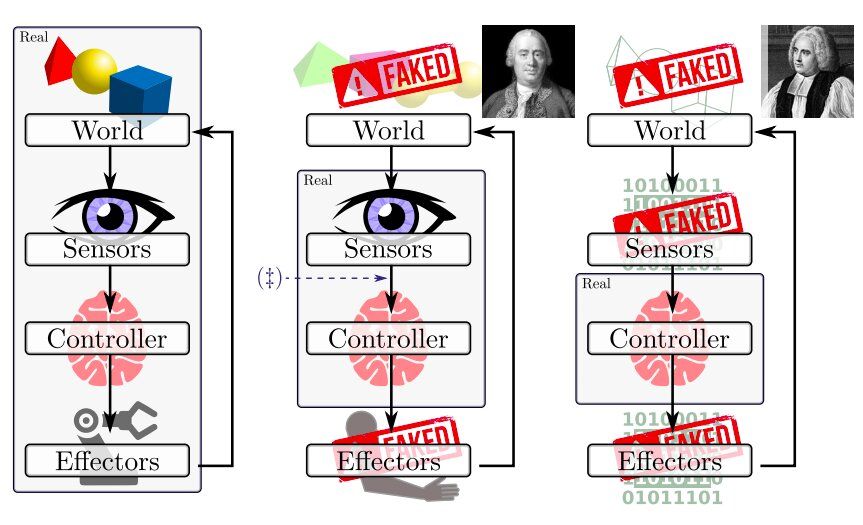
In a recent study, researchers at Texas A&M University and the University of South Carolina have set out to examine evaluation and execution scenarios that lie at an intersection between simulations and real implementations. Their investigation, outlined in a paper pre-published on arXiv, specifically focuses on instances in which real robots perceive the world via their sensors, where the environment they sense could be seen as a mere illusion.
“We consider problems in which robots conspire to present a view of the world that differs from reality,” Dylan Shell and Jason O’Kane, the researchers who carried out the study, wrote in their paper. “The inquiry is motivated by the problem of validating robot behavior physically despite there being a discrepancy between the robots we have at hand and those we wish to study, or the environment for testing that is available versus that which is desired, or other potential mismatches in this vein.”