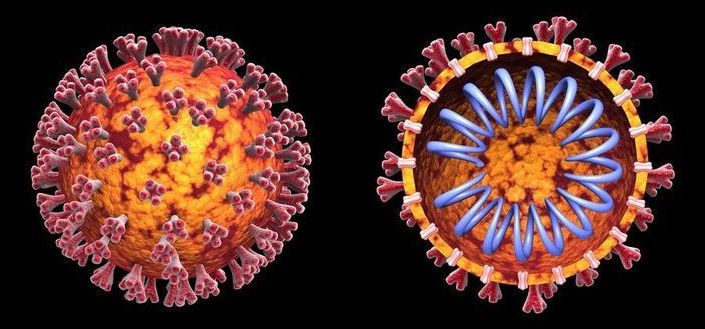
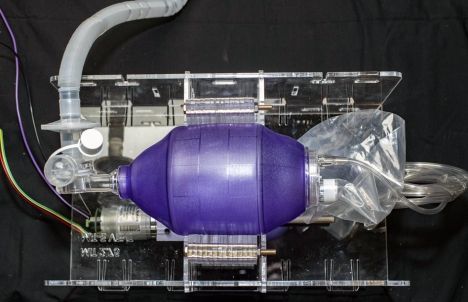
Artificial intelligence has already played a vital role in the outbreak since day 1—a reminder for the first time in a while that it can be a tool for good.
The Cuda is credited by some with being the first pony car. However, while the Mustang survives to this day, the Barracuda is dead… along with the whole Plymouth brand.
Samsung Galaxy S20 Ultra 5G
Posted in internet, mobile phones
Android smartphone. Announced Feb 2020. Features 6.9″ Dynamic AMOLED 2X display, Exynos 990 chipset, 5000 mAh battery, 512 GB storage, 16 GB RAM, Corning Gorilla Glass 6.
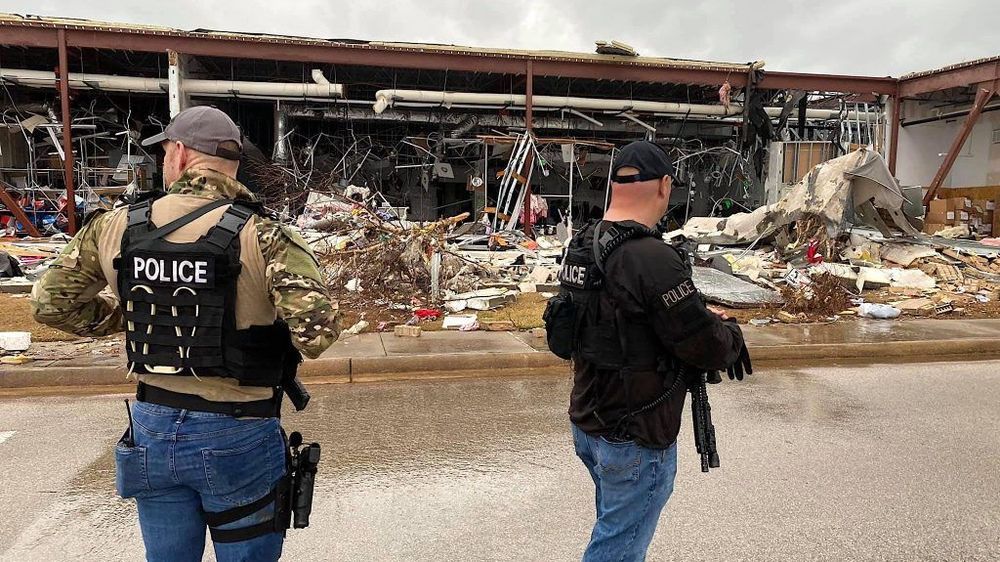
Search and rescue efforts continue as sunlight shows the extensive damage left after Jonesboro, Arkansas, took a direct hit from a tornado on Saturday, causing major damage.
Didymos, a 2,650-foot-wide asteroid, has an atypical cosmic companion— a 535 foot-wide satellite named Didymoon (10). These new two celestial bodies are not making a dangerous rendezvous with Earth, but they do provide an interesting opportunity for an apocalyptic dress rehearsal. NASA and ESA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) will head to Didymos, to knock Didymoon off course. Along with its six picture-snapping Italian Space Agency cubesats, the mission will also send a follow-up ESA spacecraft named Hera to definitively answer if we can manipulate the trajectory of Earth-bound asteroids.
We’re not going back to normal
Posted in futurism
Mar 17 2020
Social distancing is here to stay for much more than a few weeks. It will upend our way of life, in some ways forever.
Clinical and design considerations will be published online; goal is to support rapid scale-up of device production to alleviate hospital shortages.
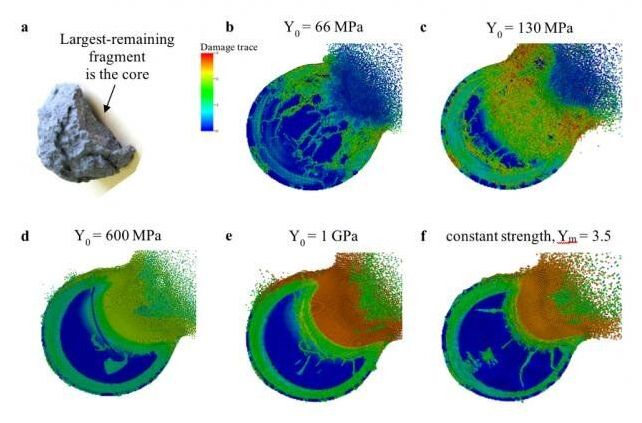
Planetary defense researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) continue to validate their ability to accurately simulate how they might deflect an Earth-bound asteroid in a study that will be published in the April issue of the American Geophysical Union journal Earth and Space Science.
The study, led by LLNL physicist Tané Remington, also identified sensitivities in the code parameters that can help researchers working to design a modeling plan for the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission in 2021, which will be the first-ever kinetic impact deflection demonstration on a near-Earth asteroid.
Asteroids have the potential to impact Earth and cause damage at the local to global scale. Humankind is capable of deflecting or disrupting a potentially hazardous object. However, due to the limited ability to perform experiments directly on asteroids, understanding how multiple variables might affect a kinetic deflection attempt relies upon large-scale hydrodynamic simulations thoroughly vetted against relevant laboratory‐scale experiments.
O,.,o.
Latest in flurry of launches draws particular criticism amid coronavirus pandemic.