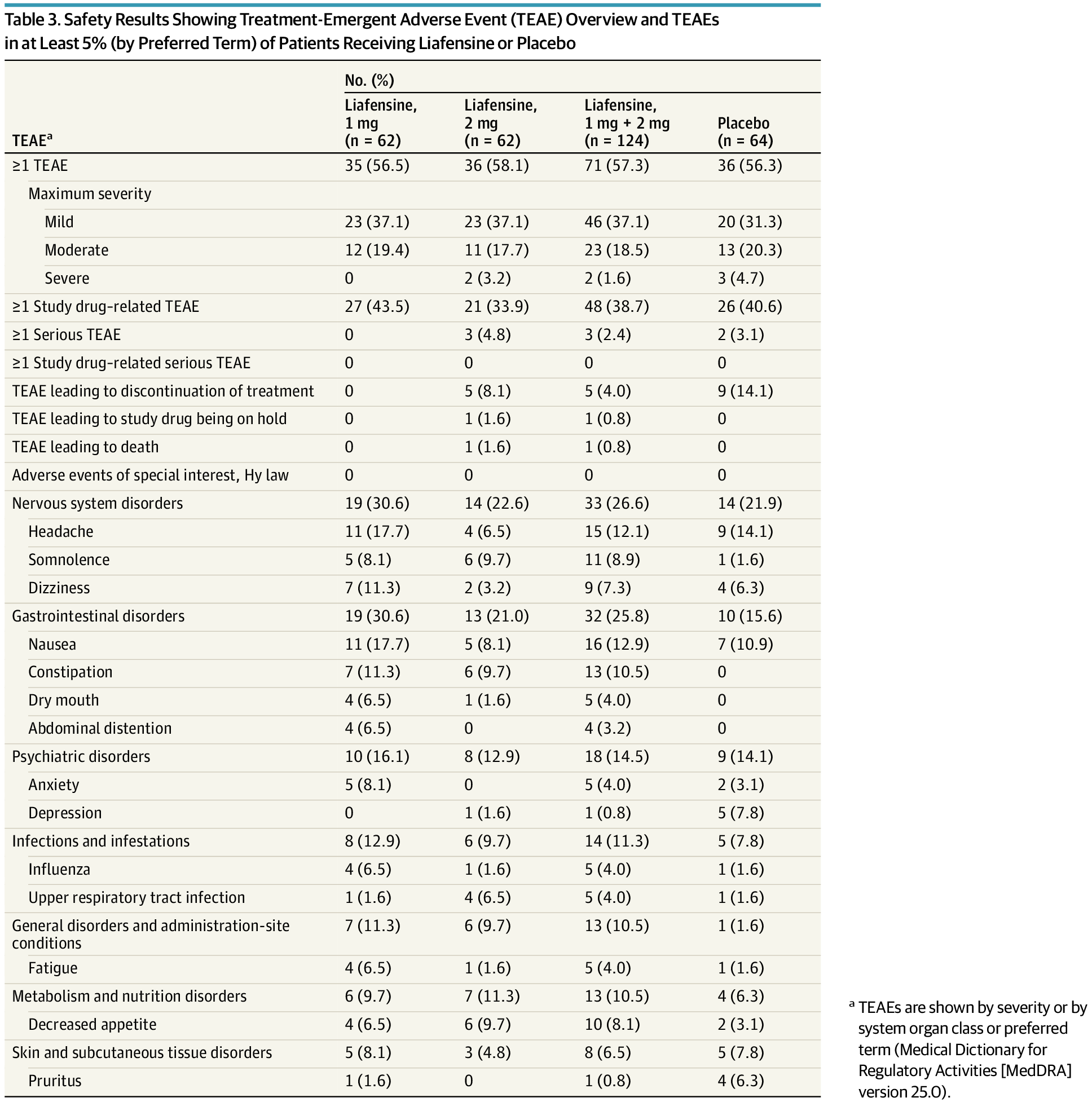
Liafensine was efficacious and well tolerated in ANK3-positive patients with treatment-resistant depression, with clinically meaningful and statistically significant improvements over placebo, highlighting ANK3 as a predictive genetic biomarker for liafensine.
Question Does the newly discovered ANK3 pharmacogenomic biomarker predict the response of patients with treatment-resistant depression (TRD) to liafensine, a triple reuptake inhibitor, despite failure in a non–biomarker-selected TRD patient population in prior phase 2b trials?
Findings In this randomized clinical trial including 189 ANK3-positive patients with TRD, liafensine demonstrated a 4.4-point Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale improvement over placebo, a clinically meaningful and statistically significant difference.
Meaning This represents a first successful genetic biomarker-guided clinical trial in psychiatry, advancing a new treatment for TRD and providing a new path for developing precision medicines in the field.