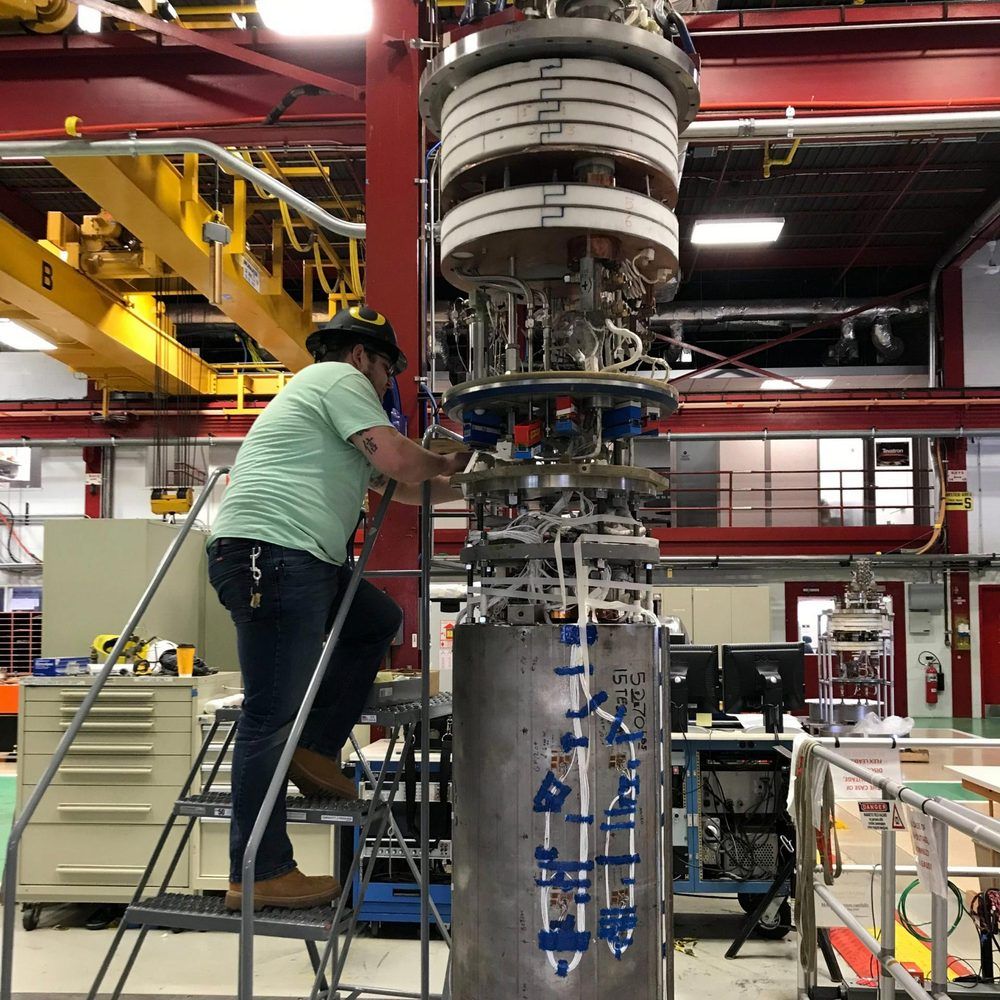
The Fermilab magnet team has done it again. After setting a world record for an accelerator magnet in 2019, they have broken it a year later.
In a June 2020 test, a demonstrator magnet designed and built by the magnet team at the Department of Energy’s Fermilab achieved a 14.5-tesla field strength for an accelerator steering dipole magnet, surpassing their previous record of 14.1 T.
This test is an important step toward addressing the demanding magnet requirements of a future hadron collider under discussion in the particle physics community. If built, such a collider would be four times larger and almost eight times more powerful than the 17-mile-circumference Large Hadron Collider at the European laboratory CERN, which operates at a steering field of 7.8 T. Current future-collider designs estimate the field strength for a steering magnet — the magnet responsible for bending particle beams around a curve — to be up to 16 T.