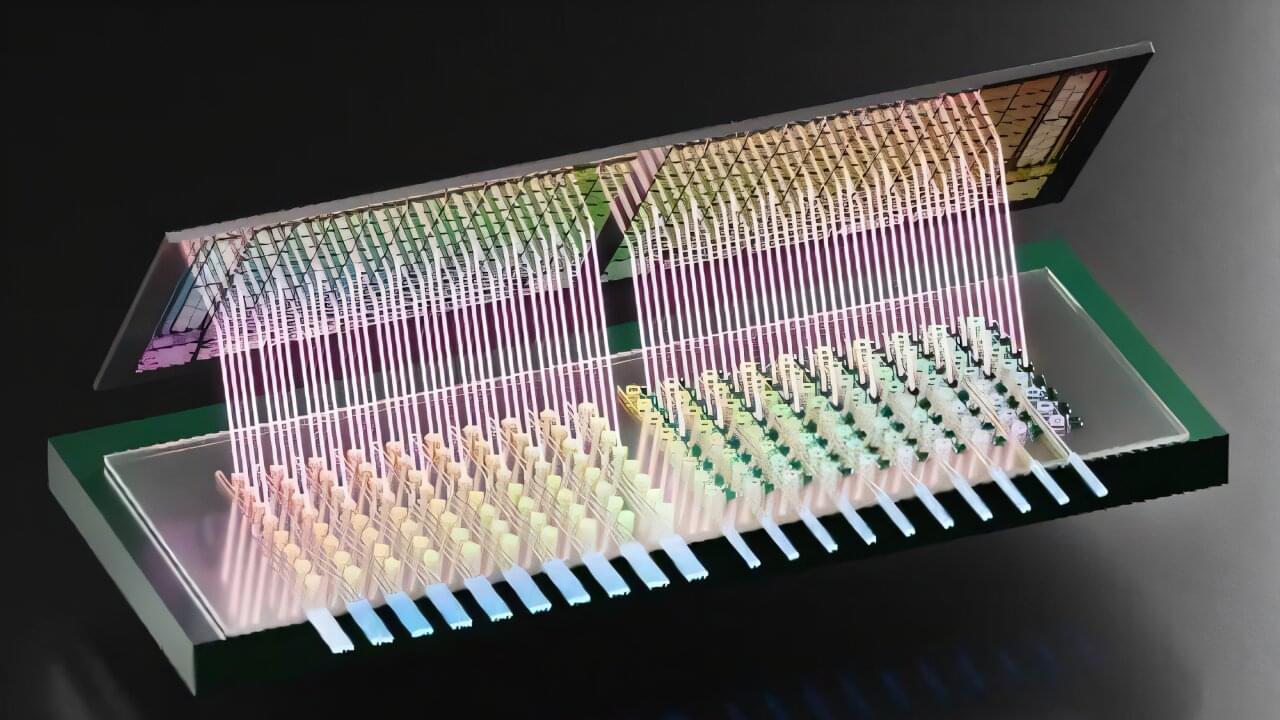
Artificial intelligence (AI) systems promise transformative advancements, yet their growth has been limited by energy inefficiencies and bottlenecks in data transfer. Researchers at Columbia Engineering have unveiled a groundbreaking solution: a 3D photonic-electronic platform that achieves unprecedented energy efficiency and bandwidth density, paving the way for next-generation AI hardware.
The study, “3D Photonics for Ultra-Low Energy, High Bandwidth-Density Chip Data Links,” led by Keren Bergman, Charles Batchelor Professor of Electrical Engineering, is published in Nature Photonics.
The research details a pioneering method that integrates photonics with advanced complementary-metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) electronics to redefine energy-efficient, high-bandwidth data communication. This innovation addresses critical challenges in data movement, a persistent obstacle to realizing faster and more efficient AI technologies.