Oct 9, 2019
Tau-mediated RNA splicing errors linked to Alzheimer’s disease
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: biotech/medical, genetics, neuroscience
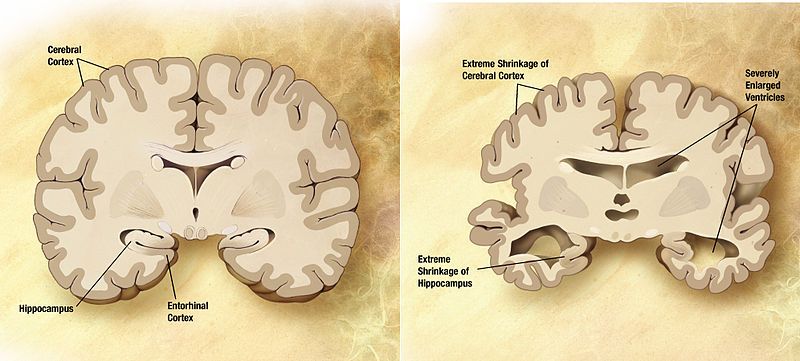
A collaborative study published today in the journal Cell Reports provides evidence for a new molecular cause for neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. The study, led by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute at Texas Children’s Hospital, integrates data from human brain autopsy samples and fruit flies to reveal a novel mechanistic link between alterations in RNA splicing and tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease.
“Cells carry out their functions by producing specific proteins encoded in their genes. To produce proteins, genes encoded in the DNA are first transcribed into RNA molecules, which subsequently are translated into proteins,” said corresponding author Dr. Joshua Shulman, associate professor of neurology, neuroscience and molecular and human genetics at Baylor and investigator at the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute.
In this study, Shulman and his colleagues investigated a molecular mechanism called RNA splicing that is involved in the production of mature RNA molecules necessary to produce working proteins. They looked into the possibility that aggregates of tau protein within neurons, a key marker of Alzheimer’s disease, interfered with RNA splicing.