Like all metals, silver, copper, and gold are conductors. Electrons flow across them, carrying heat and electricity. While gold is a good conductor under any conditions, some materials have the property of behaving like metal conductors only if temperatures are high enough; at low temperatures, they act like insulators and do not do a good job of carrying electricity. In other words, these unusual materials go from acting like a chunk of gold to acting like a piece of wood as temperatures are lowered. Physicists have developed theories to explain this so-called metal-insulator transition, but the mechanisms behind the transitions are not always clear.
“In some cases, it is not easy to predict whether a material is a metal or an insulator,” explains Caltech visiting associate Yejun Feng of the Okinawa Institute for Science and Technology Graduate University. “Metals are always good conductors no matter what, but some other so-called apparent metals are insulators for reasons that are not well understood.” Feng has puzzled over this question for at least five years; others on his team, such as collaborator David Mandrus at the University of Tennessee, have thought about the problem for more than two decades.
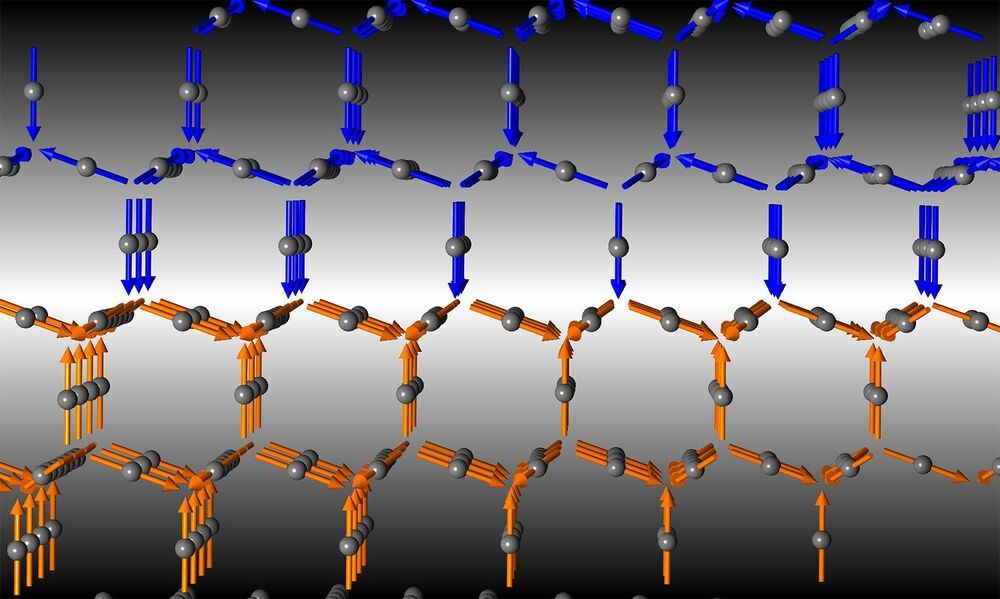
Now, a new study from Feng and colleagues, published in Nature Communications, offers the cleanest experimental proof yet of a metal-insulator transition theory proposed 70 years ago by physicist John Slater. According to that theory, magnetism, which results when the so-called “spins” of electrons in a material are organized in an orderly fashion, can solely drive the metal-insulator transition; in other previous experiments, changes in the lattice structure of a material or electron interactions based on their charges have been deemed responsible.