Electrical pulses boost copper’s efficiency in turning CO2 into ethylene, ethanol fuels.
Scientists found that applying pulsed electric potential treatments to copper single crystal surfaces boosts their ability to convert CO2 into fuels.


Alien eavesdropping: A new study shows how our signals might leak into space.
Imagine you’re an alien astronomer, pointing your telescope toward our solar system, listening for signs of intelligent life. Would you hear us? For decades, scientists have wondered the same thing.
A new study by researchers from Penn State University and NASA suggests we may finally have a clue. By carefully mapping the directions and timing of Earth’s strongest space communications, they’ve shown that our radio messages, meant for spacecraft like those near Mars, leak into the cosmos in predictable patterns.
Dark matter could turn exoplanets into tiny black holes, shocking study reveals.
A study suggests that exoplanets could be used to search for dark matter — the elusive substance that makes up 85% of the universe’s matter.
Dark matter’s gravitational pull proves it exists, but we’ve never been able to directly find it.
Now, the University of California, Riverside, study proposes that exoplanets, especially large, gaseous ones like Jupiter, could act as natural laboratories for dark matter search.
Could pig plasma fractions really rejuvenate aging rats? Join me as I interview Nicolás and Nina from the Rejuvenation Science Institute (Brazil), who are working to reproduce the headline-creating “pig plasma rejuvenation” results. We explore the origins, science, controversies, challenges, and hopes surrounding this research—plus their plans for the next breakthrough longevity experiment and open science collaboration.
https://www.rejuvenescimento.org/english.
https://www.rejuvenescimento.org/news… https://journals.tmkarpinski.com/inde… Timestamps 00:00 – Introduction: The Pig Plasma Rat Rejuvenation Debate 02:00 – Origins: Why try to reproduce these results? 08:30 – What is being injected? Fraction preparation explained 15:40 – Acute toxicity and safety results: did the rats survive? 26:00 – The next experiment: timelines, scale-up, and open science goals Find me on Twitter — / eleanorsheekey Support the channel through PayPal — https://paypal.me/sheekeyscience?coun… through Patreon —
/ thesheekeyscienceshow Please note that The Sheekey Science Show is distinct from Eleanor Sheekey’s teaching and research roles. The information provided in this show is not medical advice, nor should it be taken or applied as a replacement for medical advice. The Sheekey Science Show and guests assume no liability for the application of the information discussed. Icons in intro; “https://www.freepik.com/free-photos-v…Background“Background vector created by freepik — www.freepik.com.
https://journals.tmkarpinski.com/inde…
Timestamps.
00:00 – Introduction: The Pig Plasma Rat Rejuvenation Debate.
02:00 – Origins: Why try to reproduce these results?
08:30 – What is being injected? Fraction preparation explained.
15:40 – Acute toxicity and safety results: did the rats survive?
26:00 – The next experiment: timelines, scale-up, and open science goals.
Find me on Twitter — / eleanorsheekey.
Support the channel.
through PayPal — https://paypal.me/sheekeyscience?coun…
through Patreon — / thesheekeyscienceshow.
Please note that The Sheekey Science Show is distinct from Eleanor Sheekey’s teaching and research roles. The information provided in this show is not medical advice, nor should it be taken or applied as a replacement for medical advice. The Sheekey Science Show and guests assume no liability for the application of the information discussed.
Icons in intro; \.
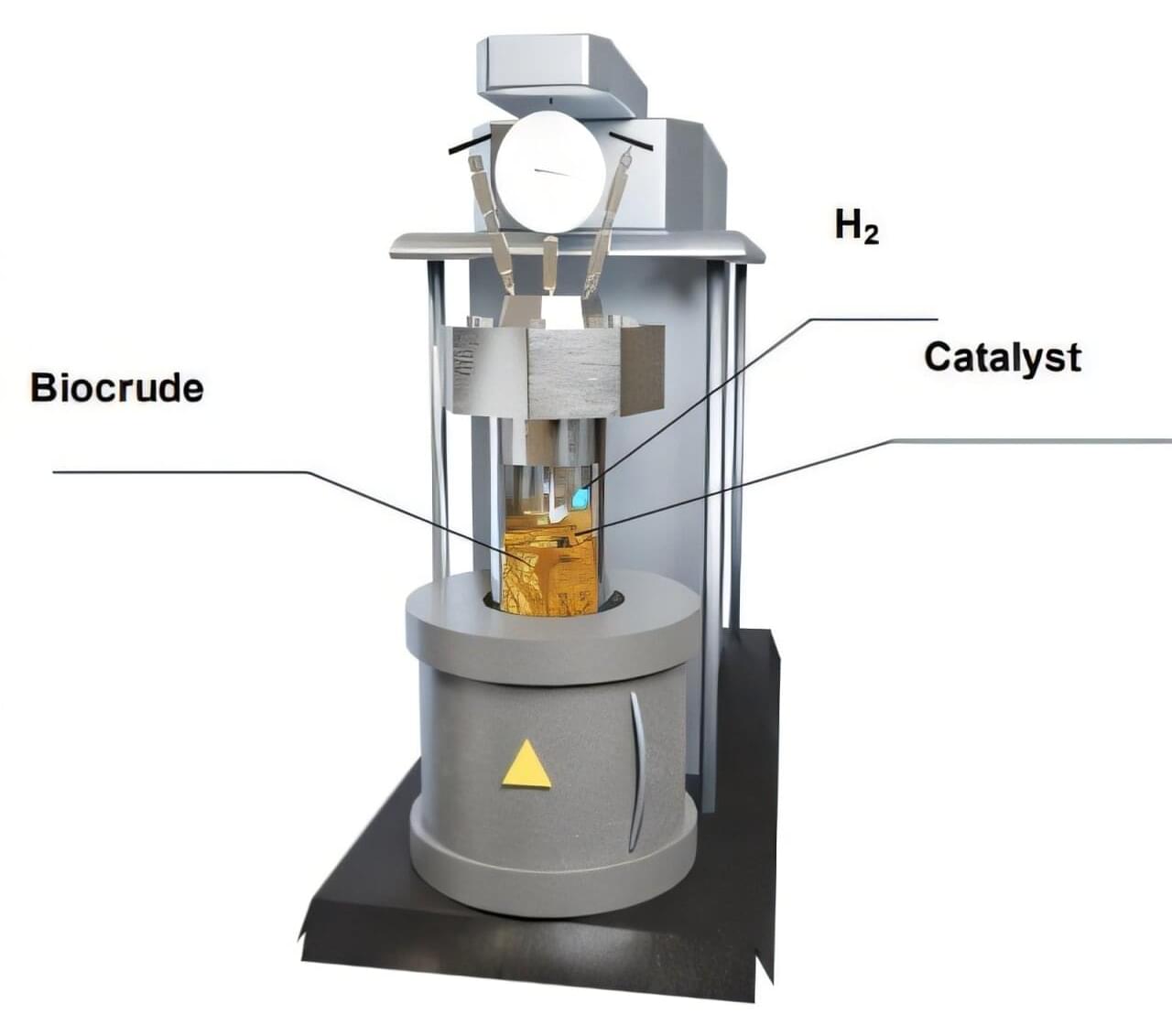
For researchers from The Grainger College of Engineering at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, a new avenue for reducing carbon emissions can be found on the side. A side of salad dressing, that is.
In 2020, the United States federal government committed to achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. An important step toward carbon neutrality is embracing sustainable aviation fuel (SAF), an alternative to conventional jet fuel that is made from renewable feedstocks. As part of this initiative, Grainger engineers have been hard at work creating the critical nanocatalysts for converting biocrude oil from food waste such as salad dressing into sustainable aviation fuel.
Hong Yang, a professor of chemical & biomolecular engineering, and Yuanhui Zhang, a professor of agricultural & biological engineering, joined forces to tackle this problem.


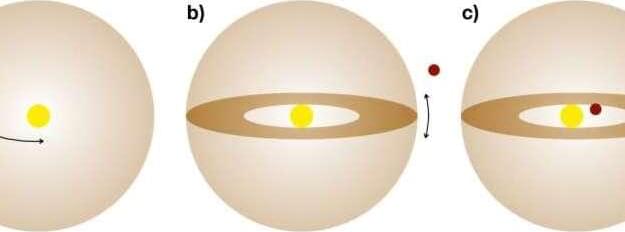
Stars die and vanish from sight all the time, but astronomers were puzzled when one that had been stable for more than a decade almost disappeared for eight months.
Between late 2024 and early 2025, one star in our galaxy, dubbed ASASSN-24fw, dimmed in brightness by about 97%, before brightening again. Since then, scientists have been swapping theories about what was behind this rare, exciting event.
Now, an international team led by scientists at The Ohio State University may have come up with an answer to the mystery. In a new study recently published in The Open Journal of Astrophysics, astronomers suggest that because the color of the star’s light remained unchanged during its dimming, the event wasn’t caused by the star evolving in some way, but by a large cloud of dust and gas around the star that occluded Earth’s view of it.
