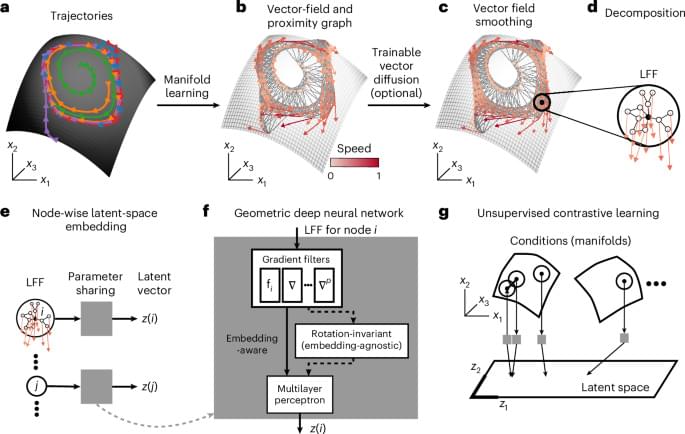
Summary: A new study reveals how AI-driven deep learning models can decode the genetic regulatory switches that define brain cell types across species. By analyzing human, mouse, and chicken brains, researchers found that some brain cell types remain highly conserved over 320 million years, while others have evolved uniquely.
This regulatory code not only sheds light on brain evolution but also provides new tools for studying gene regulation in health and disease. The findings highlight how AI can identify preserved and divergent genetic instructions controlling brain function across species.
The study also has implications for understanding neurological disorders by linking genetic variants to cognitive traits. Researchers are now expanding their models to study the brains of various animals and human disease states like Parkinson’s.