😃
Approach could speed up search and rescue missions and forest surveys.
😃
Approach could speed up search and rescue missions and forest surveys.

O,.o.
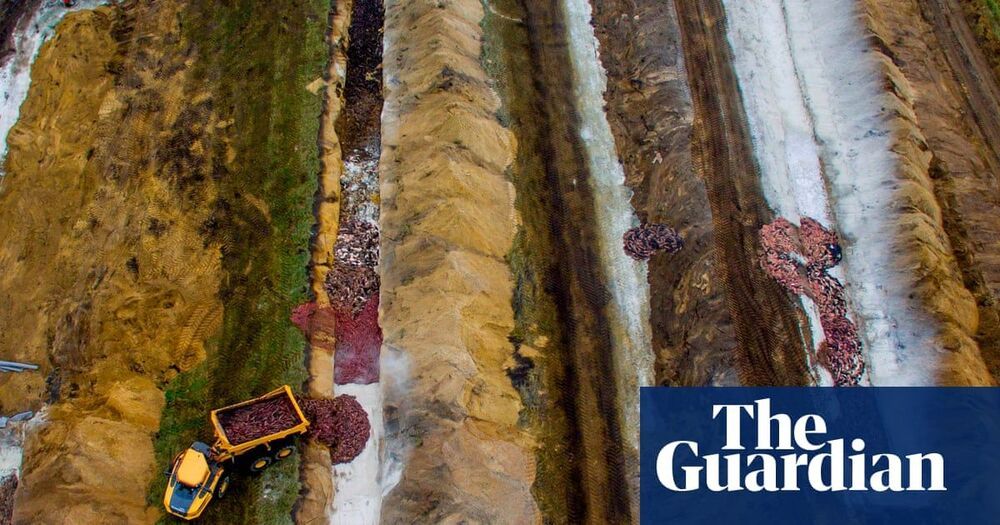
Google will use large batteries to replace the diesel generators at one of its data centers in Belgium, describing the project as a first step towards using cleaner technologies to provide backup power for its millions of servers around the world.
“Our project in Belgium is a first step that we hope will lay the groundwork for a big vision: a world in which backup systems at data centers go from climate change problems to critical components in carbon-free energy systems,” said Joe Kava, Vice President for Data Centers at Google. “We’re aiming to demonstrate that a better, cleaner solution has advanced far enough to keep the internet up and running.”
Google becomes the second major hyperscale cloud operator to pursue a strategy to move beyond diesel generators. In July, Microsoft said it will eliminate its reliance on diesel fuel by the year 2030 and has begun testing hydrogen fuel cells as an alternative. These announcements have implications beyond company-built facilities, as Google and Microsoft are major tenants in third-party data centers, most of which use diesel generators for backup power.

Pancreatic cancer is one of the most dangerous forms of tumors due to its aggressive growth, early metastases, and poor response to any known therapeutic treatments. Being a fourth major cause of cancer death nowadays and with foresight to become a second cause of cancer death after lung cancer by 2030, there is an urgent need in new therapeutic strategies that might improve the disease outcome.1 Recently, a growing interest in the anticancer activity of cannabinoids has led to numerous studies that cover more and more types of cancer.2, 3 Natural and synthetic cannabinoids have shown the capability to influence proliferation, migration, and apoptosis of cancer cells by both direct and indirect activation of cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2. In pancreatic cancer, the amount of CB1 and CB2 receptors expression in tumor cells was shown to be significantly higher than that in normal cells, opening a path for utilizing cannabinoids’ anticancer capabilities to kill cancer cells without affecting normal pancreatic tissue.
Journal dedicated to the clinical, translational and basic science of malignancies of the pancreas and peripancreatic region.

Tests showed that the material was able to store energy for more than four months.
“Free” Energy
“The material functions a bit like phase change materials, which are used to supply heat in hand warmers,” Lancaster University senior lecturer John Griffin, co-author of a paper about the research published in the journal Chemistry of Materials, said in a statement.

The Washington Post linked the hack, which occurred over the weekend, to a group working for the Russian foreign intelligence service.
The FBI is currently investigating the group, known among private-sector cybersecurity firms as APT29 or Cozy Bear. The hackers are also believed to have breached the State Department, Joint Chiefs of Staff and the White House networks during the Obama administration.
The latest revelation comes less than a month after President Donald Trump fired Christopher Krebs, the nation’s top cybersecurity official.

However, a breakthrough by researchers at UVA’s College and Graduate School of Arts & Sciences, the California Institute of Technology and the U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and Brookhaven National Laboratory could eliminate a critical obstacle from the process, a discovery that represents a giant stride toward a clean-energy future.
One way to harness solar energy is by using solar electricity to split water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen. The hydrogen produced by the process is stored as fuel, in a form that can be transferred from one place to another and used to generate power upon demand. To split water molecules into their component parts, a catalyst is necessary, but the catalytic materials currently used in the process, also known as the oxygen evolution reaction, are not efficient enough to make the process practical.
We all know you thought about it and we’ve though about it. Now we are going to do it. RC vs Supercars is a new segment we started and hopefully takes off depending on the success of this video.
What’s more exciting than racing? We pitted the Lp550-2 against our Badass Mad Drift and let them loose on a 300+ feet runway.
Want to see more? Like and share this video to help support more videos.
Check out the Mad Drift here: http://bit.ly/SyUaA1
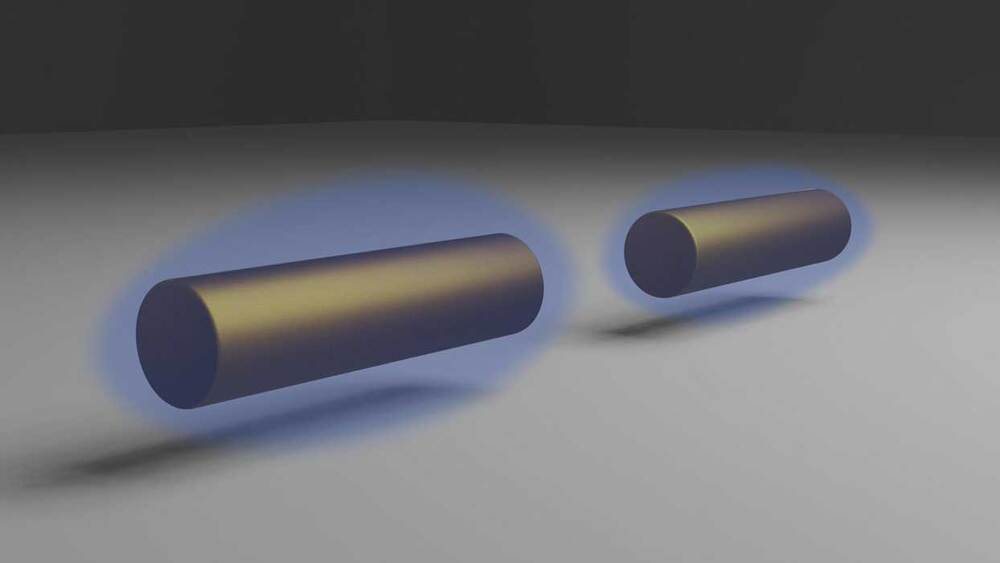
How electrons move together as a group inside cylindrical nanoparticles?
Scientists from the University of Exeter seems to find out the answer to this question. They even have made a breakthrough in the field of electromagnetism, with perspectives for metamaterials research.
In collaboration with the University of Strasbourg, scientists hypothesized how electrons move collectively in tiny metal nanoparticles shaped like cylinders.

THE FINANCE industry has had a long and profitable relationship with computing. It was an early adopter of everything from mainframe computers to artificial intelligence (see timeline). For most of the past decade more trades have been done at high frequency by complex algorithms than by humans. Now big banks have their eyes on quantum computing, another cutting-edge technology.
A fundamentally new kind of computing will shake up finance—the question is when.
