Researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Science have developed metasurfaces capable of manipulating the polarization of light with an unprecedented degree of control.



Because the brain responses in children with different forms of autism overlapped, future therapies that are effective for Phelan-McDermid syndrome could potentially help other autistic children with similar neural patterns, Siper says.
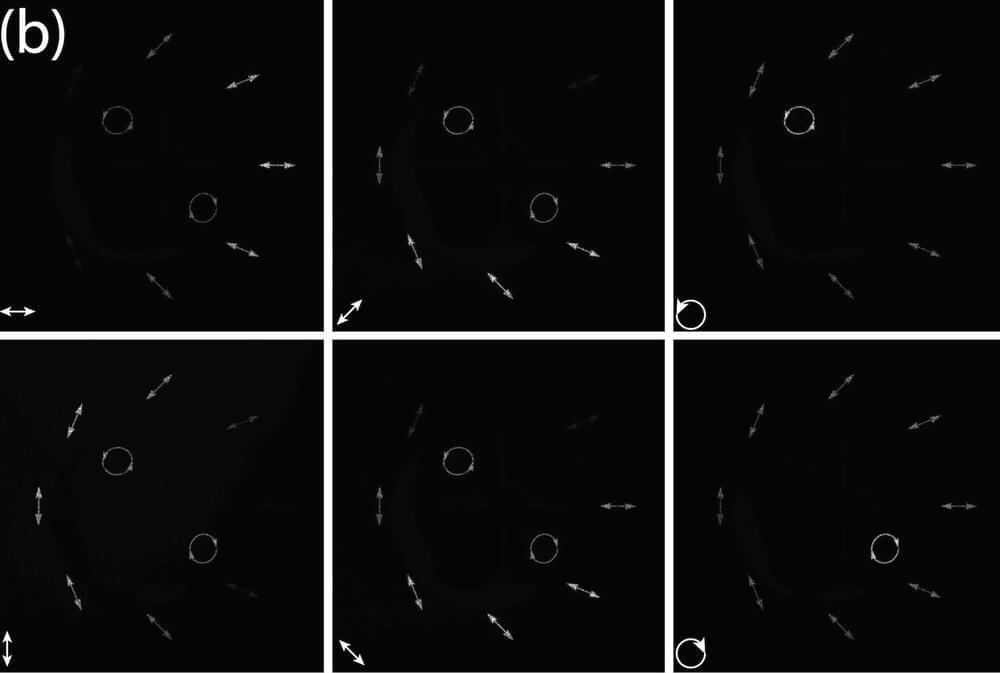
Brain responses to visual stimuli are smaller and weaker in children with Phelan-McDermid syndrome, an autism-linked genetic condition, than in non-autistic children, according to a new study. The difference in response is greater in children with larger genetic mutations.
Mutations or deletions in SHANK3, one of the genes most strongly linked to autism, cause Phelan-McDermid syndrome. More than 80 percent of people with the condition have autism; they also often have intellectual disability, developmental delays and other medical issues, though these traits and their severity can vary widely.
The new study is the first to use electroencephalography (EEG) to measure visual evoked potentials — brain responses that occur shortly after a person views a visual stimulus — in people with Phelan-McDermid syndrome. The team previously identified differences in these responses in people with ‘idiopathic’ autism, or autism with no known genetic cause. Other researchers have linked atypical visual evoked potentials to other single-gene causes of autism, such as Rett syndrome.

Hurray.
Tesla has started to hire roboticists to build its recently announced “Tesla Bot,” a humanoid robot to become a new vehicle for its AI technology.
When Elon Musk explained the rationale behind Tesla Bot, he argued that Tesla was already making most of the components needed to create a humanoid robot equipped with artificial intelligence.
The automaker’s computer vision system developed for self-driving cars could be leveraged for use in the robot, which could also use things like Tesla’s battery system and suite of sensors.
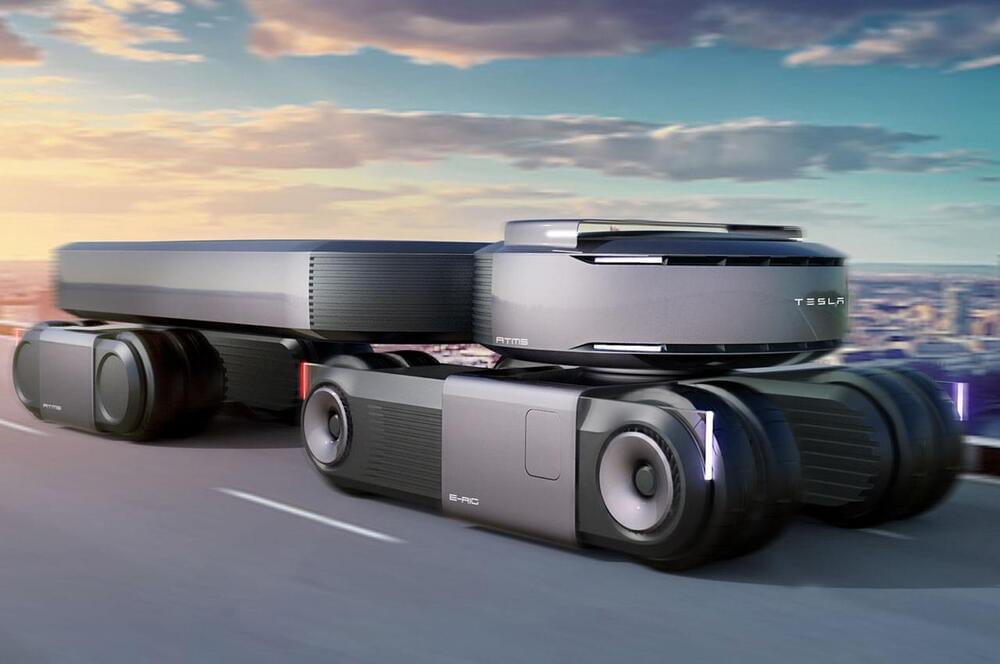

A Tesla semi-truck with a very Tesla-worthy aesthetics highlighted by the contoured yet sharp design language that in a way reminds me of the iPhone 12!
Tesla’s visionary Semi all-electric truck powered by four independent motors on the rear is scheduled for production in 2022. The semi is touted to be the safest, most comfortable truck with an acceleration of 0–60 mph in just 20 seconds and a range of 300–500 miles. While the prototype version looks absolutely badass, how the final version will look is anybody’s guess.

Proteins are essential to life, and understanding their 3D structure is key to unpicking their function. To date, only 17% of the human proteome is covered by an experimentally determined structure. Two papers in this week’s issue dramatically expand our structural understanding of proteins. Researchers at DeepMind, Google’s London-based sister company, present the latest version of their AlphaFold neural network. Using an entirely new architecture informed by intuitions about protein physics and geometry, it makes highly accurate structure predictions, and was recognized at the 14th Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction last December as a solution to the long-standing problem of protein-structure prediction. The team applied AlphaFold to 20,296 proteins, representing 98.5% of the human proteome.

The business of private survival shelters has grown during the pandemic. They’re not just for survivalists and doomsday preppers anymore. Bunkers buried in backyards or remote landscapes are capable of withstanding nuclear fallout and hurricanes, as well as violent conflict.
WATCH MORE SO EXPENSIVE NEWS VIDEOS:
How The Tokyo Olympics Became The Most Expensive Summer Games Ever | So Expensive.
Why The Texas Polar Vortex Is So Expensive | So Expensive.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=689nDiplmIk.
Why Is Housing In Hong Kong So Expensive? | So Expensive.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cs5L3c40cvk.
#SurvivalBunkers #StormShelter #BusinessInsider.
Business Insider tells you all you need to know about business, finance, tech, retail, and more.
Visit us at: https://www.businessinsider.com.
Subscribe: https://www.youtube.com/user/businessinsider.
BI on Facebook: https://read.bi/2xOcEcj.
BI on Instagram: https://read.bi/2Q2D29T
BI on Twitter: https://read.bi/2xCnzGF
BI on Amazon Prime: http://read.bi/PrimeVideo.
Why survival bunkers are so expensive | so expensive.
What is your mind? It’s a strange question, perhaps, but if pressed, you might describe it as the part of yourself that makes you who you are—your consciousness, dreams, emotions, and memories. Scientists believed for a long time that such aspects of the mind had specific brain locations, like a circuit for fear, a region for memory, and so on.
But in recent years we’ve learned that the human brain is actually a master of deception, and your experiences and actions do not reveal its inner workings. Your mind is in fact an ongoing construction of your brain, your body, and the surrounding world.

The human body can be genetically inclined to attack its own cells, destroying the beta cells in the pancreas that make insulin, which helps convert sugar into energy. Called Type 1 diabetes, this disorder can occur at any age and can be fatal if not carefully managed with insulin shots or an insulin pump to balance the body’s sugar levels.
But there may be another, personalized option on the horizon, according to Xiaojun “Lance” Lian, associate professor of biomedical engineering and biology at Penn State. For the first time, Lian and his team converted human embryonic stem cells into beta cells capable of producing insulin using only small molecules in the laboratory, making the process more efficient and cost-effective.
Stem cells can become other cell types through signals in their environment, and some mature cells can revert to stem cells—induced pluripotency. The researchers found that their approach worked for human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells, both derived from federally approved stem cell lines. According to Lian, the effectiveness of their approach could reduce or eliminate the need for human embryonic stem cells in future work. They published their results today (Aug. 26) in Stem Cell Reports.