Intelligent machine vision could get a boost from unconventional hardware design.


A collaborative effort between Meta, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and Los Alamos National Laboratory leverages Los Alamos’ expertise in building tools for molecular screening capabilities. The release of “Open Molecules 2025”, an unprecedented dataset of molecular simulations, can accelerate opportunities for machine learning to transform research in fields such as biology, materials science and energy technologies.
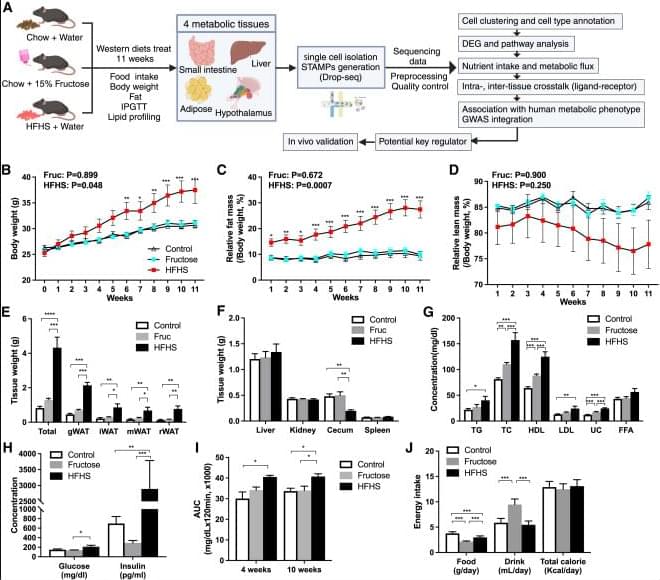
Chen et al. compared scRNA-seq profiles of four tissues in metabolic syndrome (MetS) models induced by fructose or high-fat high-sucrose diets, revealing differential tissue, cellular, and molecular vulnerability between diets. Regulatory genes and pathways were identified, and networks were rewired in MetS. mt-Rnr2 was validated as a key regulator.
There are new hints that the fabric of space-time may be made of “memory cells” that record the whole history of the universe. If true, it could explain the nature of dark matter and much more



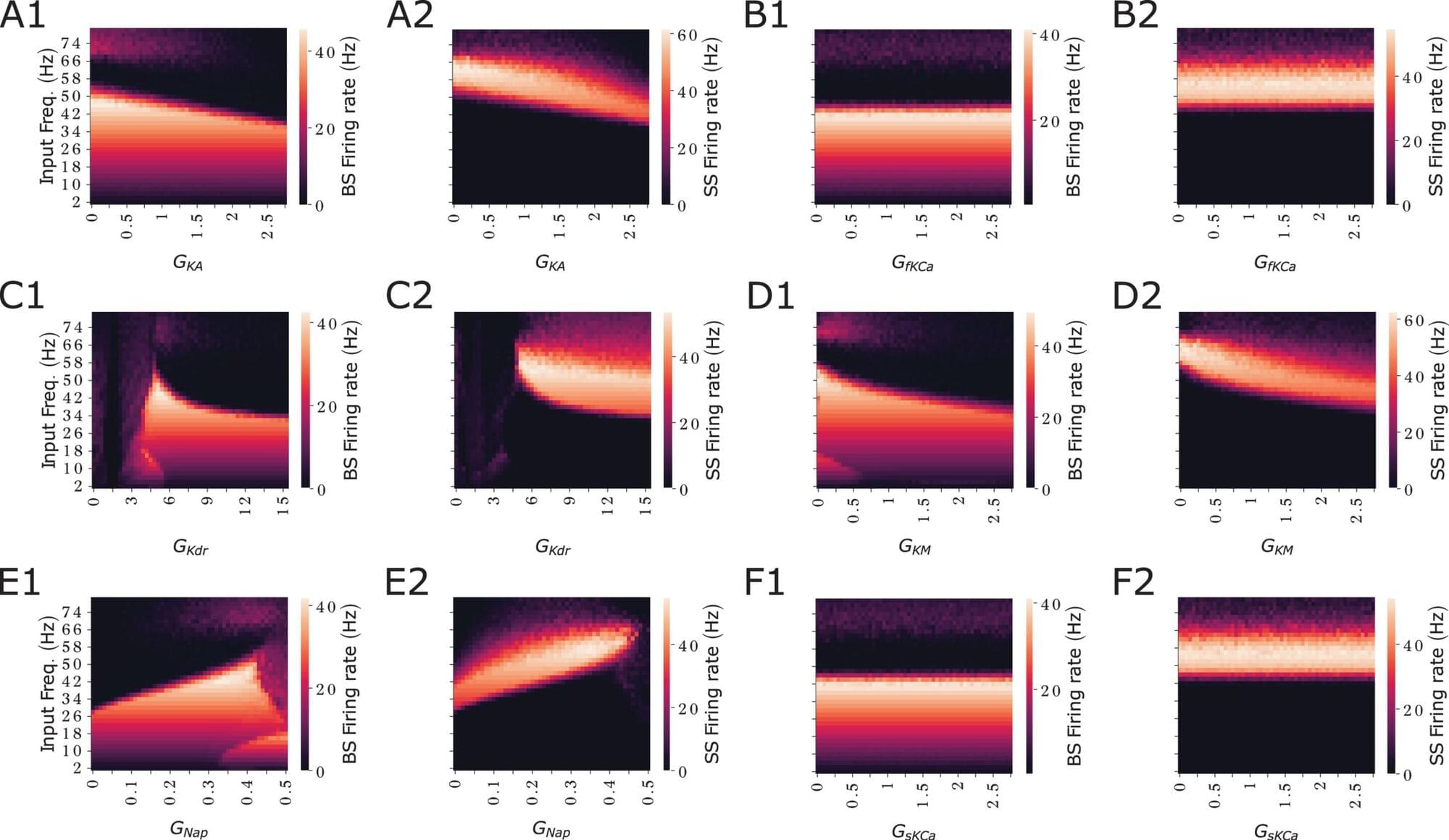
The brain is constantly mapping the external world like a GPS, even when we don’t know about it. This activity comes in the form of tiny electrical signals sent between neurons—specialized cells that communicate with one another to help us think, move, remember and feel. These signals often follow rhythmic patterns known as brain waves, such as slower theta waves and faster gamma waves, which help organize how the brain processes information.
Understanding how individual neurons respond to these rhythms is key to unlocking how the brain functions related to navigation in real time—and how it may be affected in disease.
A new study by Florida Atlantic University and collaborators from Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, Netherlands, and the University of Amsterdam, Netherlands, has uncovered a surprising ability of brain cells in the hippocampus to process and encode and respond to information from multiple brain rhythms at once.