Like.
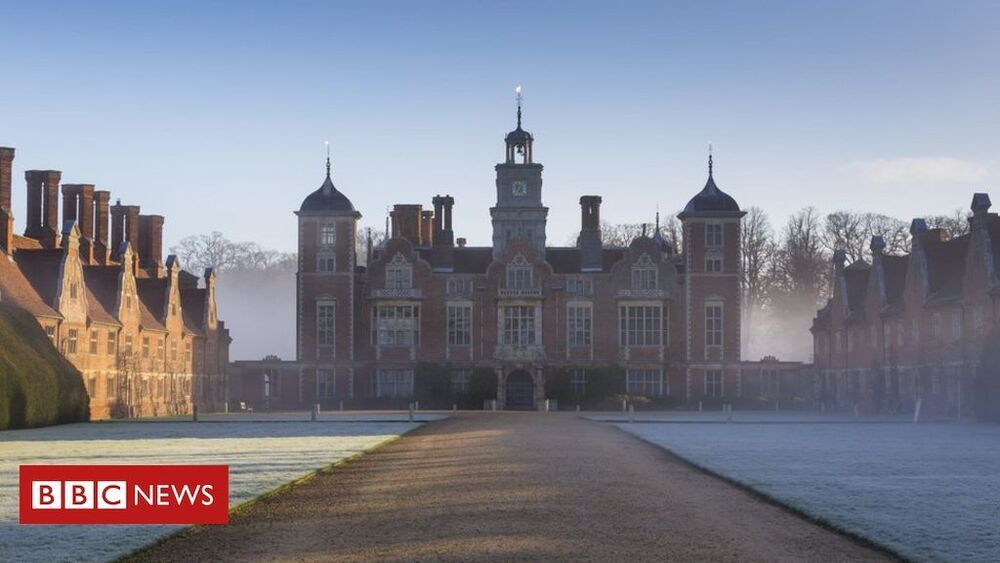
Pests and moulds are thriving at historic properties in lockdown, the National Trust says.

A baby has been born following a uterus transplant for the first time ever in France, the hospital treating mother and infant said Wednesday. Such births are extremely rare but not unprecedented, and come after a cutting-edge procedure to transplant a healthy uterus into a woman whose own is damaged or missing. The baby, a girl weighing 1.845 kilogrammes (4.059 pounds), was born on Friday, according to the team at the Foch hospital outside Paris.
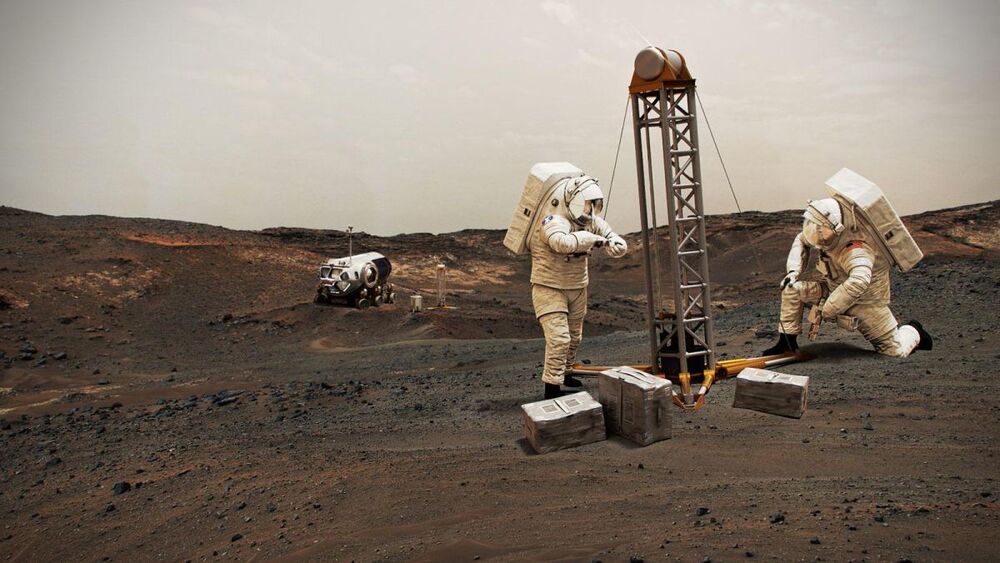

The booster appeared to miss the landing pad of the company’s droneship in the Atlantic Monday night.



Imperial College expert warns new coronavirus wave could kill tens of thousands of Britons by late summer if lockdown is completely lifted too early.
Professor Azra Ghani revealed how a new model made at Imperial College London forecasts a wave of deaths by summer 2021 if restrictions are eased in July — even despite a successful vaccine rollout.

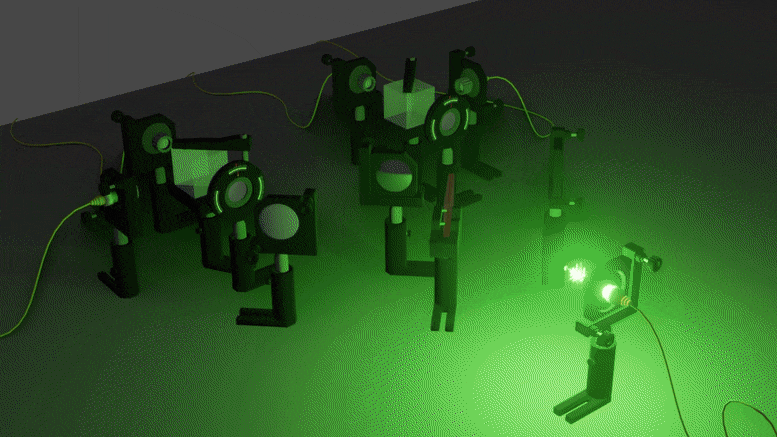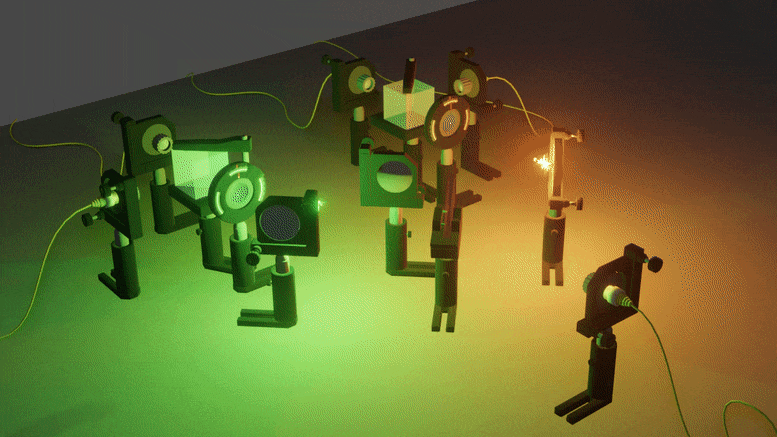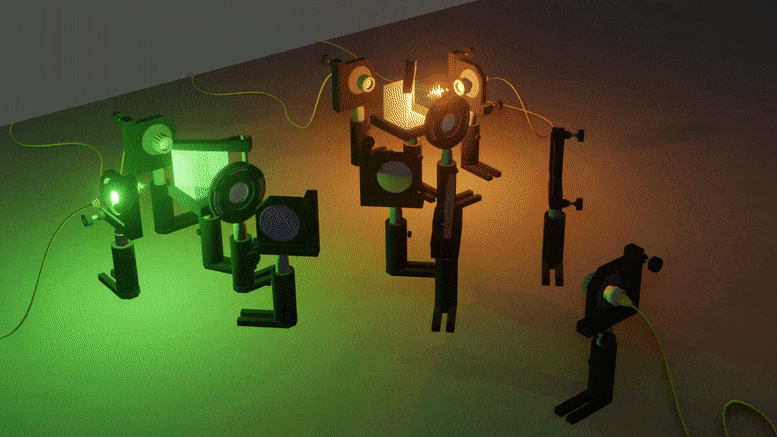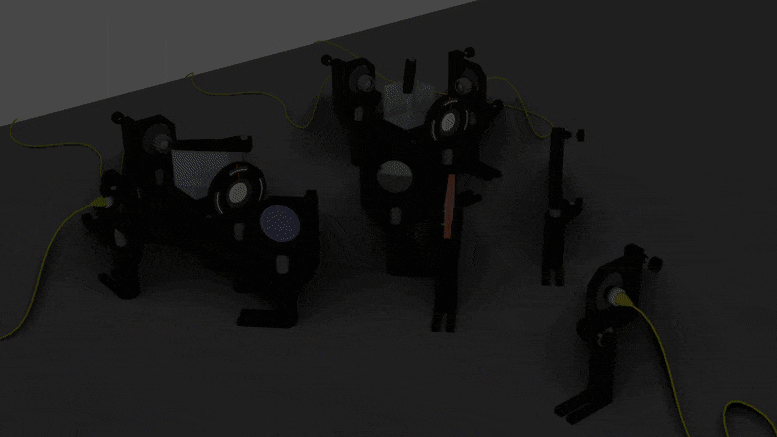
When Light and Atoms Share a Common Vibe
An especially counter-intuitive feature of quantum mechanics is that a single event can exist in a state of superposition — happening both here and there, or both today and tomorrow.
Such superpositions are hard to create, as they are destroyed if any kind of information about the place and time of the event leaks into the surrounding — and even if nobody actually records this information. But when superpositions do occur, they lead to observations that are very different from that of classical physics, questioning down to our very understanding of space and time.