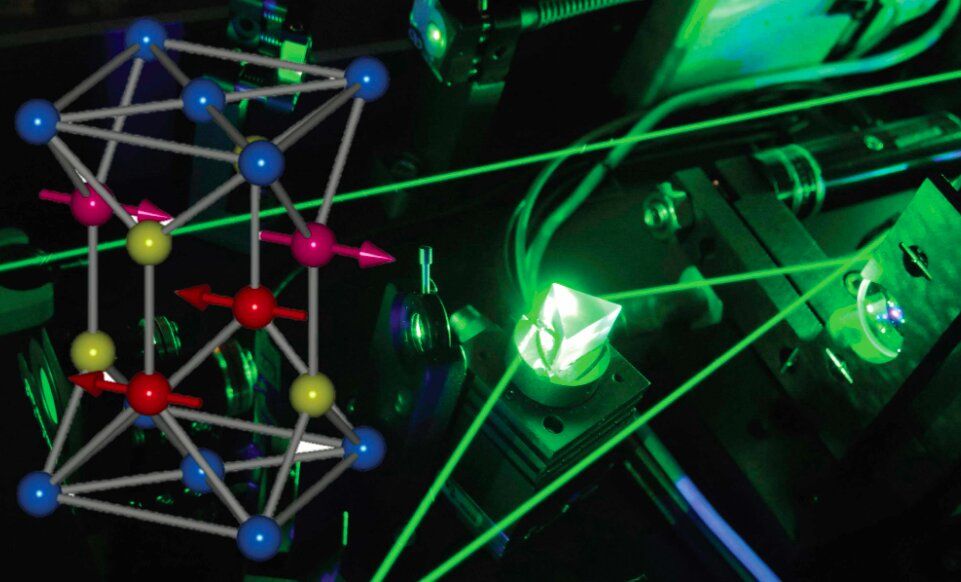
Antiferromagnetism is a type of magnetism in which parallel but opposing spins occur spontaneously within a material. Antiferromagnets, materials that exhibit antiferromagnetism, have advantageous characteristics that make them particularly promising for fabricating spintronic devices.
In contrast with conventional electronic devices, which use the electrical charge of electrons to encode information, spintronics process information leveraging the intrinsic angular momentum of electrons, a property known as “spin.” Due to their ultrafast nature, their insensitivity to external magnetic fields and their lack of magnetic stray fields, antiferromagnets could be particularly desirable for the development of spintronic devices.
Despite their advantages and their ability to store information, most simple antiferromagnets have weak readout magnetoresistivity signals. Moreover, so far physicists have been unable to change the magnetic order of antiferromagnets using optical techniques, which could ultimately allow device engineers to exploit these materials’ ultrafast nature.