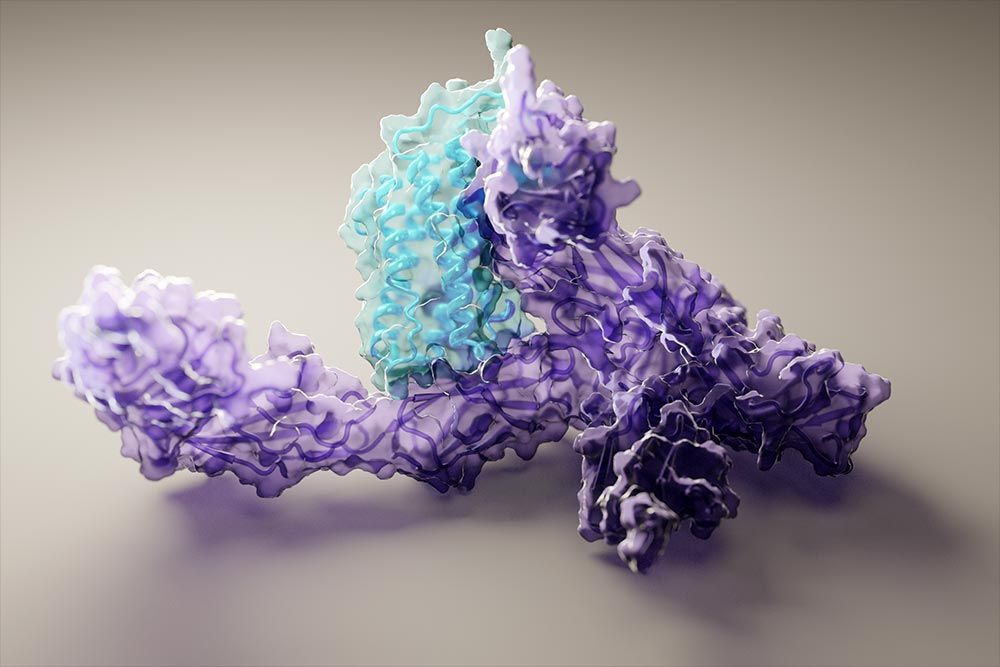
Unlike DeepMind, the UW Medicine team’s method, which they dubbed RoseTTAFold, is freely available. Scientists from around the world are now using it to build protein models to accelerate their own research. Since July, the program has been downloaded from GitHub by over 140 independent research teams.
Accurate protein structure prediction now accessible to all.
Scientists have waited months for access to highly accurate protein structure prediction since DeepMind presented remarkable progress in this area at the 2020 Critical Assessment of Structure Prediction, or CASP14, conference. The wait is now over.
Researchers at the Institute for Protein Design at the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle have largely recreated the performance achieved by DeepMind on this important task. These results were published online by the journal Science on July 15, 2021.