In 2021 Trend Micro predicts that cybercriminals will look to home networks as a critical launch pad to compromising corporate IT and IoT networks.





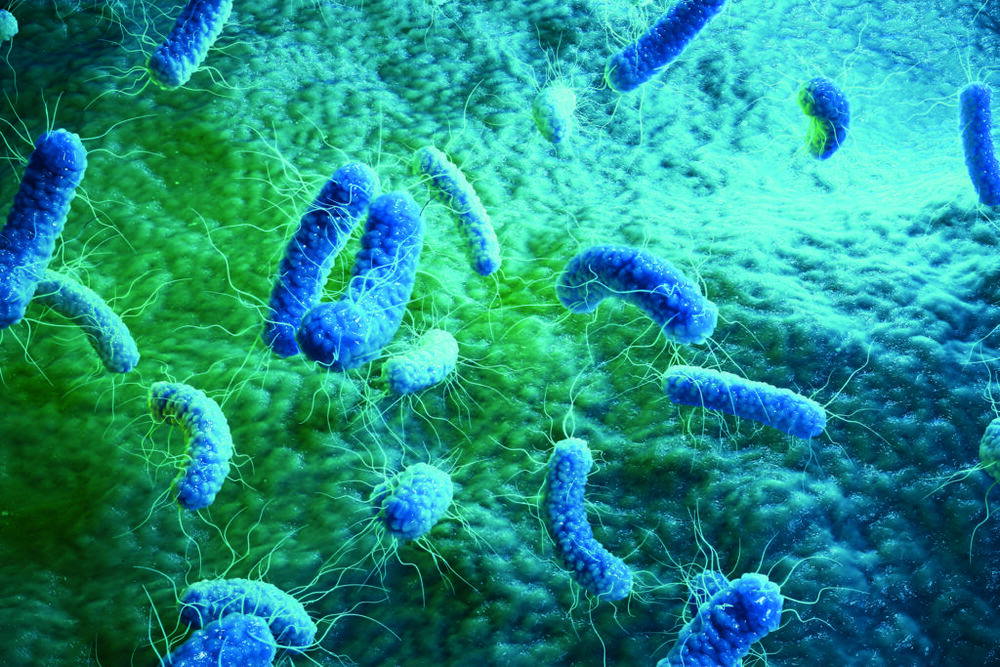
Wistar Institute scientists have designed a new class of antimicrobial compound, which, they claim, uniquely combines direct antibiotic killing of pan drug-resistant pathogenic bacteria, with a simultaneous rapid immune response for combating antimicrobial resistance (AMR). The team claims the dual-acting immuno-antibiotics (DAIA) strategy could represent a “landmark” in the fight against AMR.
“We took a creative, double-pronged strategy to develop new molecules that can kill difficult-to-treat infections while enhancing the natural host immune response,” said Farokh Dotiwala, MBBS, PhD, assistant professor in the Vaccine & Immunotherapy Center and lead author of the team’s work, which is reported in Nature, in a paper titled, “IspH inhibitors kill Gram-negative bacteria and mobilize immune clearance.”
The World Health Organization (WHO) has declared AMR to be one of the top 10 global public health threats against humanity, and it is estimated that by 2050, antibiotic-resistant infections could claim 10 million lives each year and impose a cumulative $100 trillion burden on the global economy. The list of bacteria that are becoming resistant to treatment with all available antibiotic options is growing and few new drugs are in the pipeline, creating a pressing need for new classes of antibiotics to prevent public health crises.


The Milky Way houses 8292 recently discovered stellar streams—all named Theia. But Theia 456 is special.
A stellar stream is a rare linear pattern—rather than a cluster—of stars. After combining multiple datasets captured by the Gaia space telescope, a team of astrophysicists found that all of Theia 456’s 468 stars were born at the same time and are traveling in the same direction across the sky.
“Most stellar clusters are formed together,” said Jeff Andrews, a Northwestern University astrophysicist and member of the team. “What’s exciting about Theia 456 is that it’s not a small clump of stars together. It’s long and stretched out. There are relatively few streams that are nearby, young and so widely dispersed.”
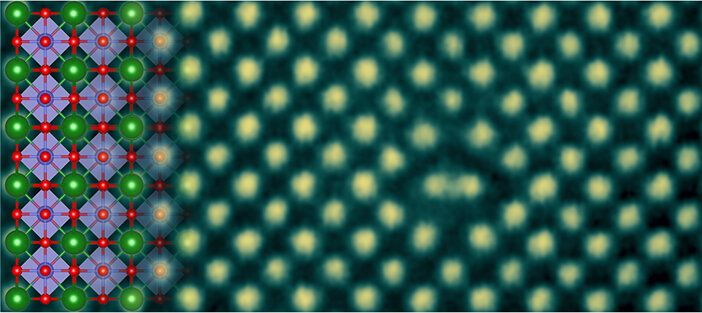
In groundbreaking materials research, a team led by University of Minnesota Professor K. Andre Mkhoyan has made a discovery that blends the best of two sought-after qualities for touchscreens and smart windows—transparency and conductivity.
The researchers are the first to observe metallic lines in a perovskite crystal. Perovskites abound in the Earth’s center, and barium stannate (BaSnO3) is one such crystal. However, it has not been studied extensively for metallic properties because of the prevalence of more conductive materials on the planet like metals or semiconductors. The finding was made using advanced transmission electron microscopy (TEM), a technique that can form images with magnifications of up to 10 million.
The research is published in Science Advances.
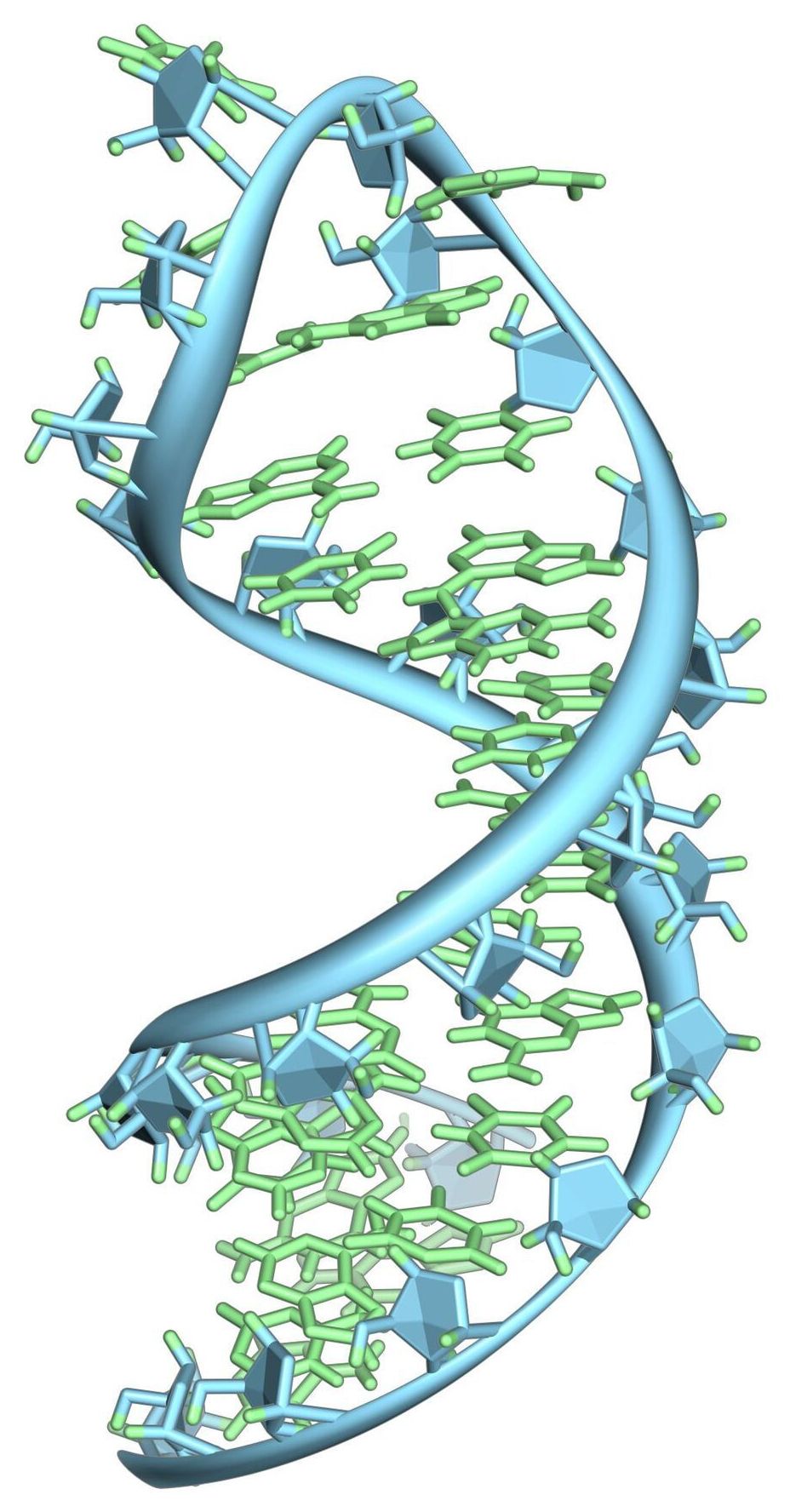
A new Northwestern University-led study is unfolding the mystery of how RNA molecules fold themselves to fit inside cells and perform specific functions. The findings could potentially break down a barrier to understanding and developing treatments for RNA-related diseases, including spinal muscular atrophy and perhaps even the novel coronavirus.
“RNA folding is a dynamic process that is fundamental for life,” said Northwestern’s Julius B. Lucks, who led the study. “RNA is a really important piece of diagnostic and therapeutic design. The more we know about RNA folding and complexities, the better we can design treatments.”
Using data from RNA-folding experiments, the researchers generated the first-ever data-driven movies of how RNA folds as it is made by cellular machinery. By watching their videos of this folding occur, the researchers discovered that RNA often folds in surprising, perhaps unintuitive ways, such as tying itself into knots—and then immediately untying itself to reach its final structure.