In 1912, astronomer Victor Hess discovered strange, high-energy particles known as “cosmic rays.” Since then, researchers have hunted for their birthplaces. Today, we know about some of the cosmic ray “launch pads”, ranging from the Sun and supernova explosions to black holes and distant active galactic nuclei. What astronomers are now searching for are sources of cosmic rays within the Milky Way Galaxy.
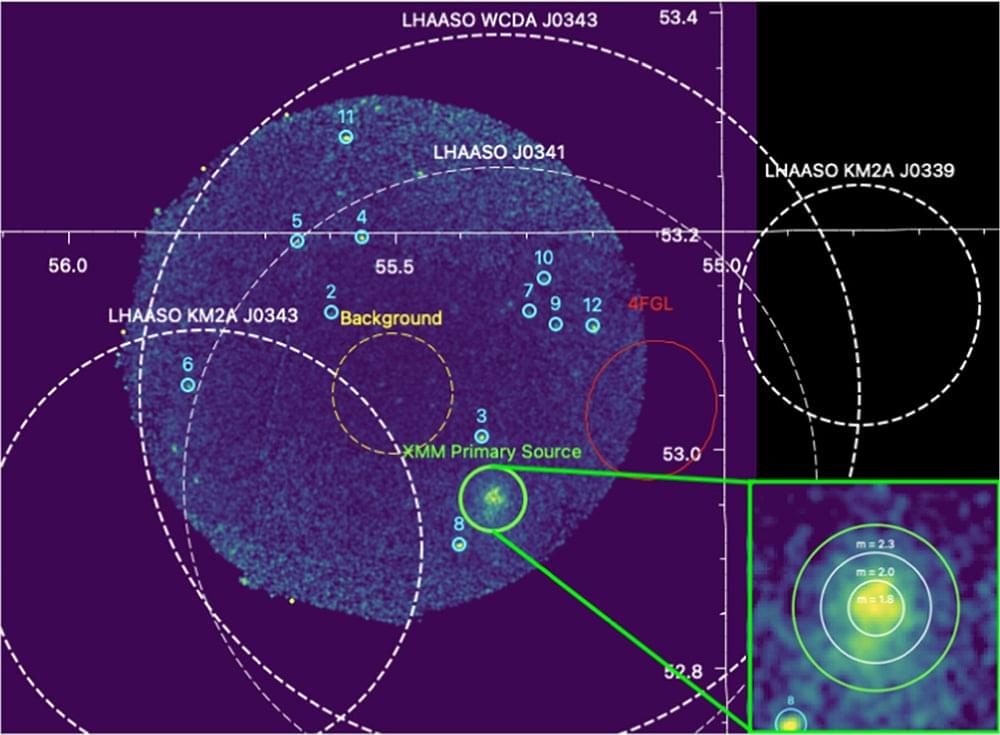
In a pair of presentations at the recent American Astronomical Society meeting, a team led by Michigan State University’s Zhuo Zhang, proposed an interesting place where cosmic rays originate: a pulsar wind nebula in our own Milky Way Galaxy. A pulsar is a rapidly rotating neutron star, formed as a result of a supernova explosion. High-energy particles and the neutron star’s strong magnetic field combine to interact with the nearby interstellar medium. The result is a pulsar wind nebula that can be detected across nearly the whole electromagnetic spectrum, particularly in X-rays. It makes sense that this object would be a source of cosmic rays. Pulsars are found throughout the Galaxy, which makes them a useful category in the search for cosmic ray engines in the Milky Way.
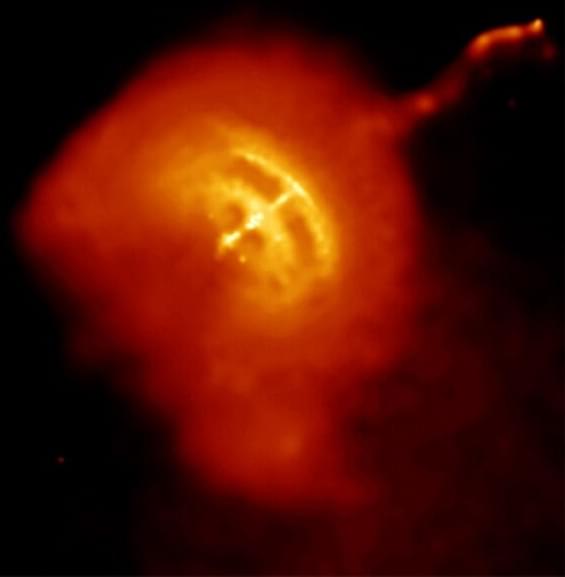

The Vela Pulsar is a good example of a pulsar wind nebula. The pulsar is at the center, and the surrounding cloudiness is the nebula. Courtesy NASA.