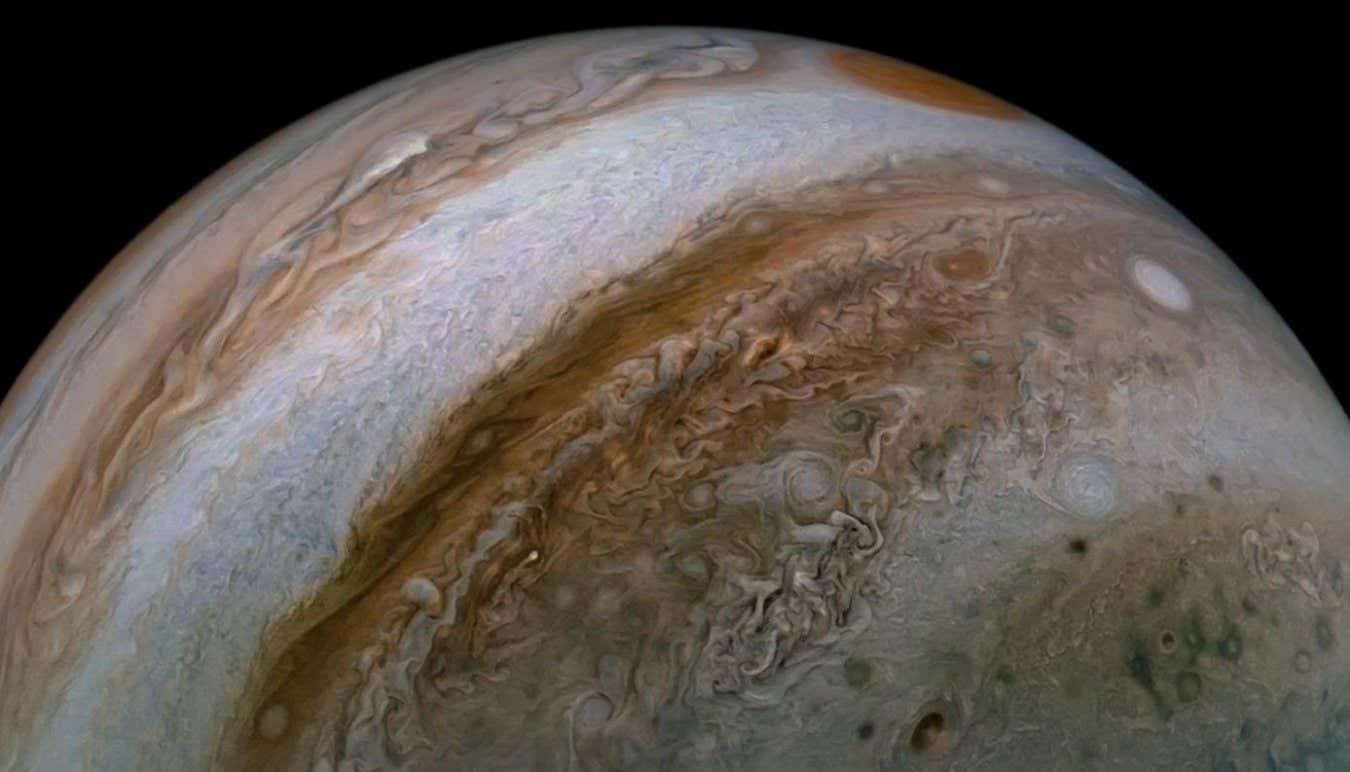
Observations from NASA’s Juno spacecraft reveal that Jupiter’s strong magnetic field and the unique properties of its plasma can produce a truly novel kind of extraterrestrial wave near its poles


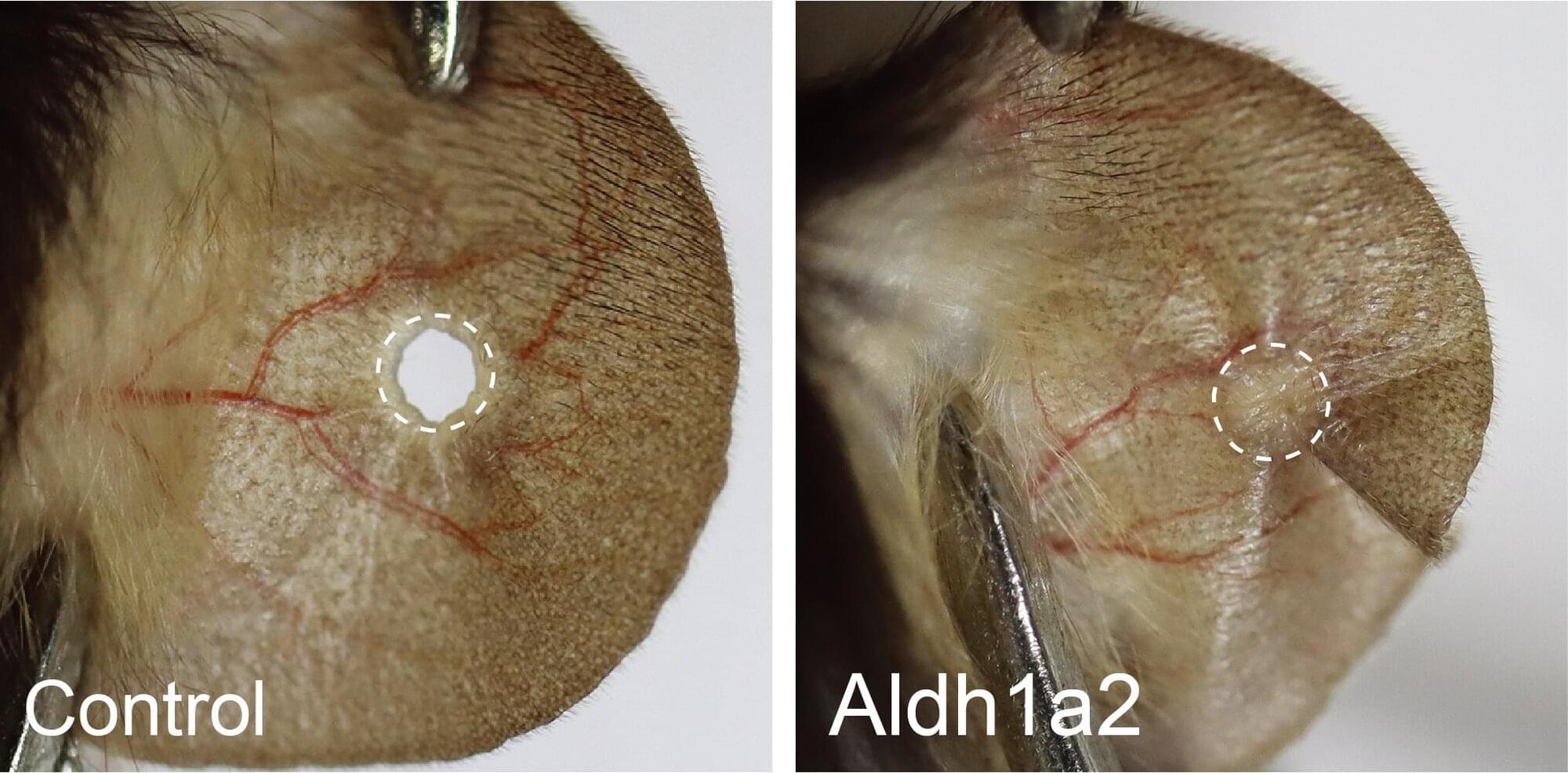
Research led by the National Institute of Biological Sciences in Beijing has discovered that switching on a single dormant gene enables mice to regenerate ear tissue.
Some vertebrates such as salamanders and fish can regenerate complex tissue structures with precision. A lost limb can be regrown, a damaged heart or eye can be repaired. Salamanders are so remarkable at reconstructing damaged tissues that even a spinal cord injury with severed neural motor connectivity can be restored.
Mammals occasionally showcase the ability to regenerate. Deer antlers and goat horns are examples of living tissue regeneration. Mice can regrow fingertips if they are lost. A healthy human liver can experience up to 70% loss of tissue and regrow to near full size within several weeks.
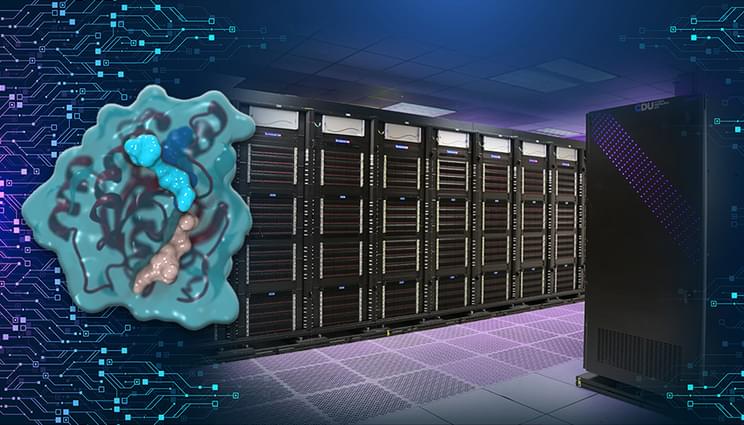




A new cancer drug candidate developed by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BBOT (BridgeBio Oncology Therapeutics) and the Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research (FNLCR) has demonstrated the ability to block tumor growth without triggering a common and debilitating side effect. In early clinical trials, the compound, known as BBO-10203, has shown promise in disrupting a key interaction between two cancer-driving proteins — RAS and PI3Kα — without causing hyperglycemia (high blood-sugar levels), which has historically hindered similar treatments. Published in Science

Matthew Berman
Can artificial intelligence (AI) potentially transform health care for the better?
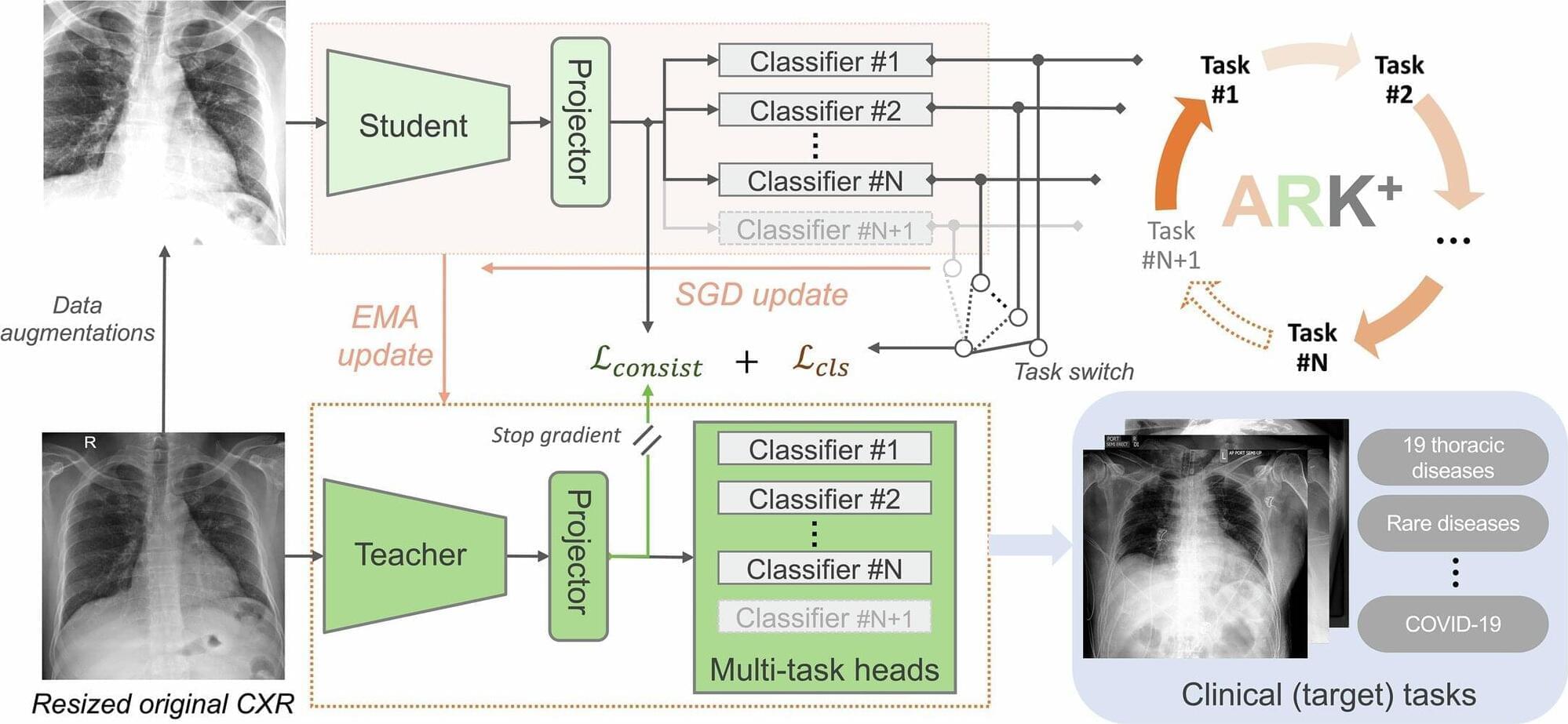
Now, rising to the challenge, an Arizona State University team of researchers has built a powerful new AI tool, called Ark+, to help doctors read chest X‑rays better and improve health care outcomes.
“Ark+ is designed to be an open, reliable and ultimately useful tool in real‑world health care systems,” said Jianming “Jimmy” Liang, an ASU professor from the College of Health Solutions, and lead author of the study recently published in Nature.