A guy built a DIY, one-off electric car that’s fully powered by solar panels and can offer ‘unlimited range’ — and took the vehicle on the road
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
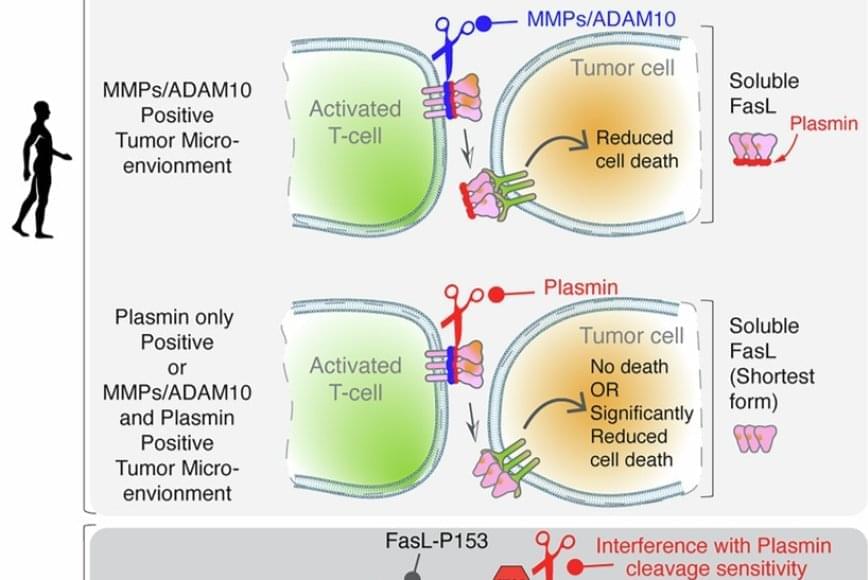
Role of plasmin in metastatic tumors
FasL is an immune cell membrane protein that triggers a programmed cell death called apoptosis. Activated immune cells, including CAR-T cells made from a patient’s immune system, use apoptosis to kill cancer cells.
The team discovered that in human genes, a single evolutionary amino acid change — serine instead of proline at position 153 — makes FasL more susceptible to being cut and inactivated by plasmin.
Plasmin is a protease enzyme that is often elevated in aggressive solid tumors like triple negative breast cancer, colon cancer and ovarian cancer.
This means that even when human immune cells are activated and ready to attack the tumor cells, one of their key death weapons — FasL — can be neutralized by the tumor environment, reducing the effectiveness of immunotherapies.
The findings may help explain why CAR-T and T-cell-based therapies can be effective in blood cancers but often fall short in solid tumors. Blood cancers often do not rely on plasmin to metastasize, whereas tumors like ovarian cancer rely heavily on plasmin to spread the cancer.
Significantly, the study also showed that blocking plasmin or shielding FasL from cleavage can restore its cancer-killing power. That finding may open new doors for improving cancer immunotherapy.

Scientists Confirm The Existence Of Element 117
The official Periodic Table of the Elements is one step closer to adding element 117 to its ranks. That’s thanks to an international team of scientists that was able to successfully create several atoms of element 117, which is currently known as Ununseptium until it’s given an official name.
The paper for this experiment has been published in Physical Review Letters.
Element 117 was first created in a joint collaboration between American and Russian scientists back in 2010. However, before an element can be officially added to the Periodic Table of Elements, its discovery must be independently confirmed.
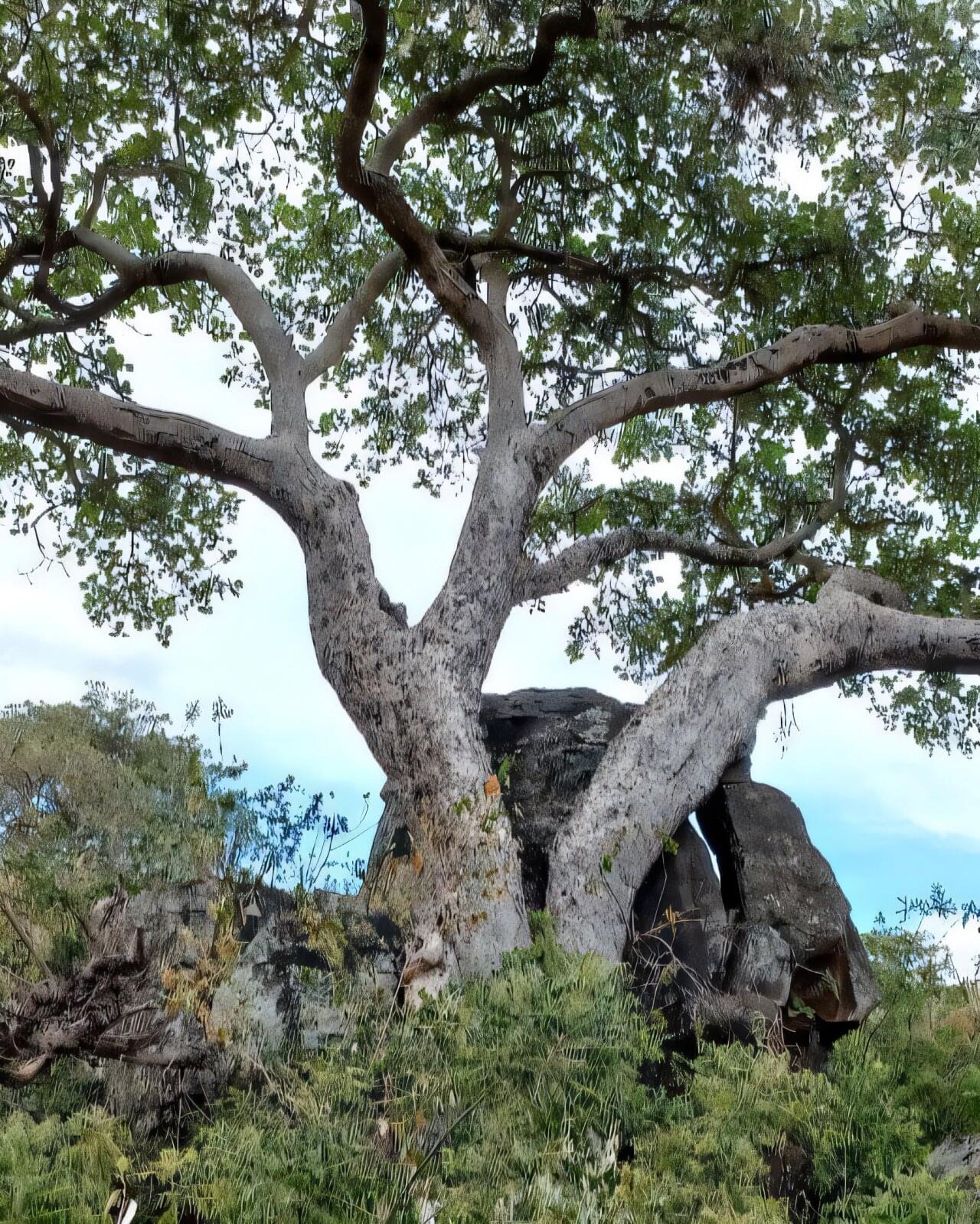

Fig trees convert atmospheric CO₂ to stone, research reveals
Some species of fig trees store calcium carbonate in their trunks—essentially turning themselves (partially) into stone, new research has found. The team of Kenyan, U.S., Austrian, and Swiss scientists found that the trees could draw carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and store it as calcium carbonate ‘rocks’ in the surrounding soil.
The research was presented at the Goldschmidt conference in Prague.
The trees —native to Kenya—are one of the first fruit trees shown to have this ability, known as the oxalate carbonate pathway.