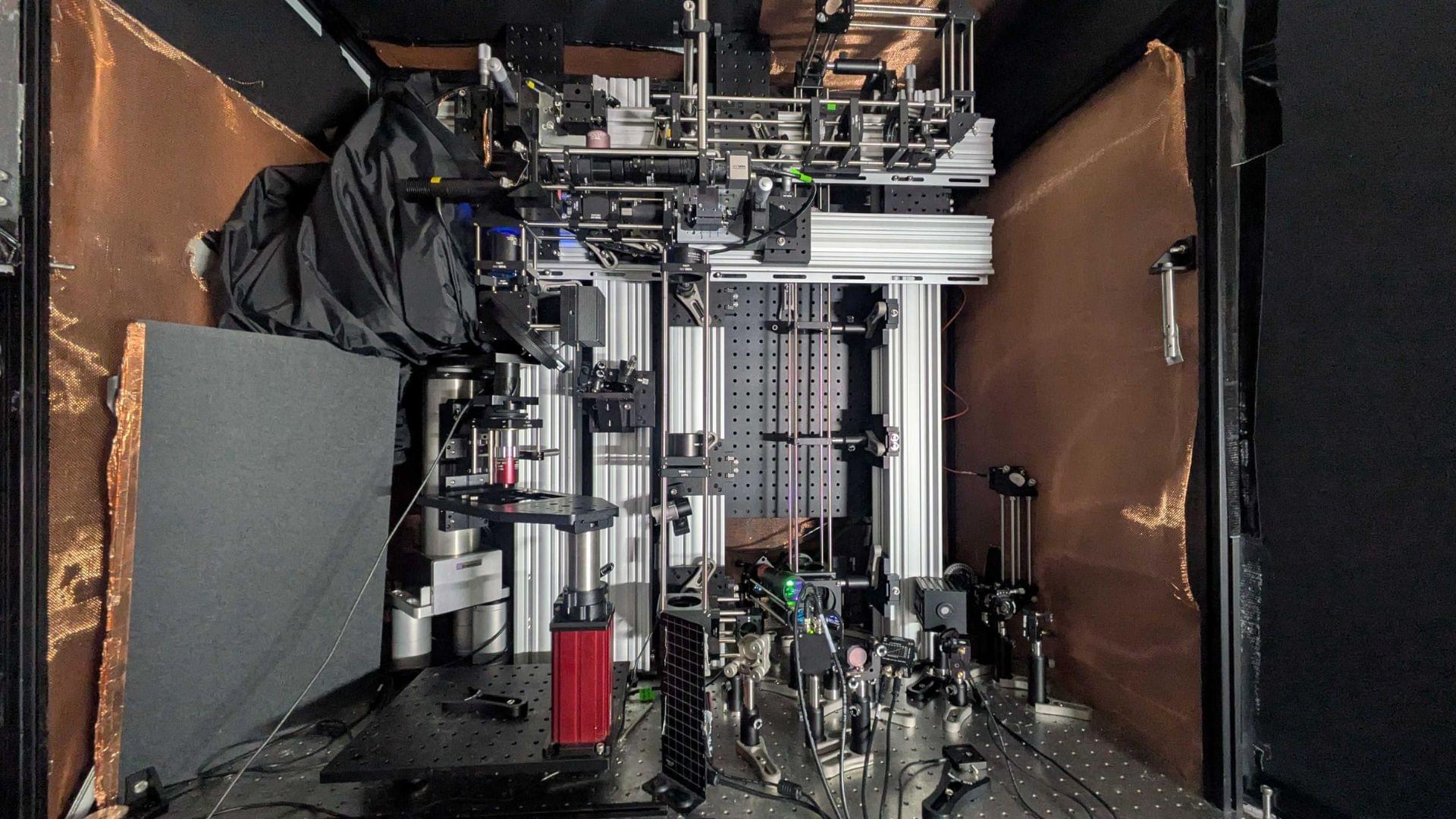
In a remarkable leap forward for machine navigation, researchers funded by the U.S. Army have developed a synthetic echolocation system inspired by the natural sonar abilities of bats and dolphins.
This cutting-edge technology enables drones, autonomous vehicles, and robots to detect and identify objects in complete darkness, relying not on traditional visual sensors like cameras or LIDAR, but on ultrasonic pulses processed by artificial intelligence (AI). The result is a system that promises to transform how machines operate in low-visibility environments, offering new possibilities for military operations and civilian applications alike. From navigating smoke-filled battlefields to aiding search and rescue missions in disaster zones, this bioinspired innovation could reshape the future of autonomous systems.
The U.S. Army’s investment in this research, supported by the Army Research Office and the DEVCOM Ground Vehicle Systems Center, reflects a growing need for machines that can function effectively where human senses or conventional technology falter. By drawing on the way bats and dolphins use sound to perceive their surroundings, this system provides a robust alternative to light-dependent sensors, which struggle in conditions such as darkness, fog, or dust. Its potential extends beyond defence, with researchers envisioning its use in fields as varied as medical imaging, industrial inspection, and underwater exploration. What makes this development particularly exciting is not just its versatility, but the clever way it was created—using simulated data to train AI, paving the way for a cost-effective and adaptable solution.