Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
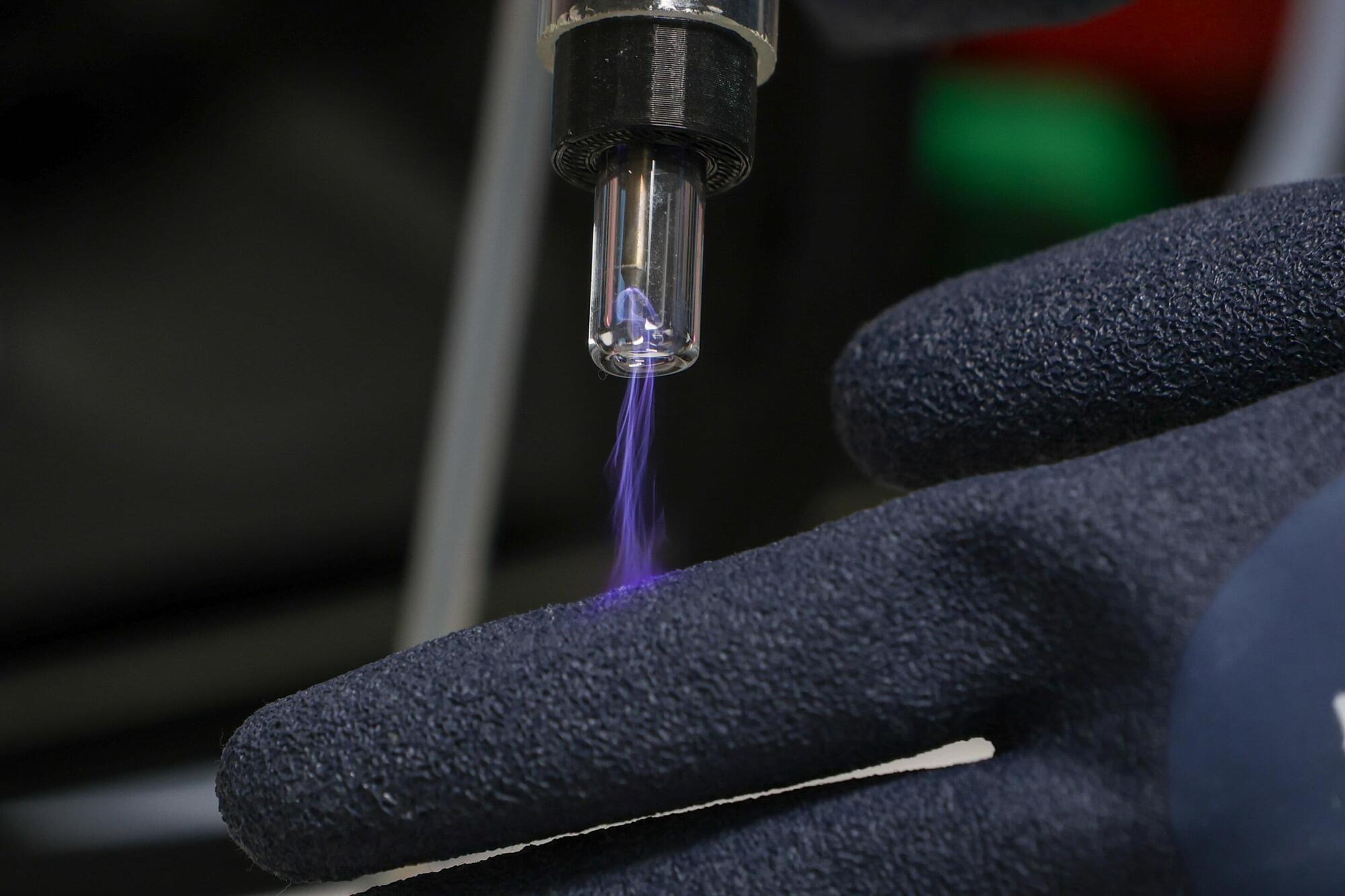

Peppermint oil plasma coating could cut catheter infections without releasing drugs
Australian researchers have developed a high‑performance coating made from peppermint essential oil that can be applied to the surfaces of many commonly used medical devices, offering a safer way to protect patients from infection and inflammation.
Matthew Flinders Professor and senior author of the new study, Professor Krasimir Vasilev, says the idea emerged after noticing that eating peppermint leaves from his drink significantly relieved his sore throat, inspiring him to explore whether its bioactivity could be converted into a durable coating using plasma technology—something he has been researching for more than two decades.
The team from Flinders’s Biomedical Nanoengineering Laboratory—including Professor Vasilev (Director), Associate Professor Vi‑Khanh Truong, Dr. Andrew Hayes, and Ph.D. candidates Trong Quan Luu and Tuyet Pham—created a nanoscale peppermint‑oil coating that protects against infection, inflammation and oxidative stress, while remaining compatible with human tissue and suitable for medical materials.
Salon with Stephen Wolfram × Joscha Bach_What if we had bigger brains
A CIMC salon at the internet archive in san francisco.
Joscha Bach presents “Machine Consciousness and Beyond” | dAGI Summit 2025
Bach reframes AI as the endpoint of a long philosophical project to “naturalize the mind,” arguing that modern machine learning operationalizes a lineage from Aristotle to Turing in which minds, worlds, and representations are computational state-transition systems. He claims computer science effectively re-discovers animism—software as self-organizing, energ†y-harvesting “spirits”—and that consciousness is a simple coherence-maximizing operator required for self-organizing agents rather than a metaphysical mystery. Current LLMs only simulate phenomenology using deepfaked human texts, but the universality of learning systems suggests that, when trained on the right structures, artificial models could converge toward the same internal causal patterns that give rise to consciousness. Bach proposes a biological-to-machine consciousness framework and a research program (CIMC) to formalize, test, and potentially reproduce such mechanisms, arguing that understanding consciousness is essential for culture, ethics, and future coexistence with artificial minds.
Key takeaways.
▸ Speaker & lens: Cognitive scientist and AI theorist aiming to unify philosophy of mind, computer science, and modern ML into a single computationalist worldview.
▸ AI as philosophical project: Modern AI fulfills the ancient ambition to map mind into mathematics; computation provides the only consistent language for modeling reality and experience.
▸ Computationalist functionalism: Objects = state-transition functions; representations = executable models; syntax = semantics in constructive systems.
▸ Cyber-animism: Software as “spirits”—self-organizing, adaptive control processes; living systems differ from dead ones by the software they run.
▸ Consciousness as function: A coherence-maximizing operator that integrates mental states; second-order perception that stabilizes working memory; emerges early in development as a prerequisite for learning.
▸ LLMs & phenomenology: Current models aren’t conscious; they simulate discourse about consciousness using data full of “deepfaked” phenomenology. A Turing test cannot detect consciousness because performance ≠ mechanism.
▸ Universality hypothesis: Different architectures optimized for the same task tend to converge on similar internal causal structures; suggests that consciousness-like organization could arise if it’s the simplest solution to coherence and control.
▸ Philosophical zombies: Behaviorally identical but non-conscious agents may be more complex than conscious ones; evolution chooses simplicity → consciousness may be the minimal solution for self-organized intelligence.
▸ Language vs embodiment: Language may contain enough statistical structure to reconstruct much of reality; embodiment may not be strictly necessary for convergent world models.
▸ Testing for machine consciousness: Requires specifying phenomenology, function, search space, and success criteria—not performance metrics.
▸ CIMC agenda: Build frameworks and experiments to recreate consciousness-like operators in machines; explore implications for ethics, interfaces, and coexistence with future minds.
Mars Base
To become an Interplanetary Species we need to colonize another planet, and Mars will be our first target. To establish a base there, and a future settlement, we need to get their first, so we will also examine the Aldrin Cycler, a type of spacecraft that may make traveling to other worlds far easier.
Visit our sponsor, Brilliant: https://brilliant.org/IsaacArthur/
National Space Society Roadmap:
https://space.nss.org/nss-roadmap-to–… this channel to get access to perks: / @isaacarthursfia Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur Support us on Patreon:
/ isaacarthur Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a… Facebook Group:
/ 1,583,992,725,237,264 Reddit:
/ isaacarthur Twitter:
/ isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content. SFIA Discord Server:
/ discord version:
/ mars-base-narration-only Credits: Becoming an Interplanetary Species: Mars Base Science & Futurism with Isaac Arthur Episode 261; October 22, 2020 Written, Produced & Narrated by Isaac Arthur Written by: Isaac Arthur Editors: Jerry Guern Keith Blockus Matthew Acker Cover Art: Jakub Grygier https://www.artstation.com/jakub_grygier Graphics: Jeremy Jozwik https://www.artstation.com/zeuxis_of_… Sam McNamara Sergio Botero https://www.artstation.com/sboterod?f… Tristan 3D Music Sergey Cheremisninov, “Sirius” https://www.s-cheremisinov.com Reign Pagaran, “Distant Voyager” Aerium, “Fifth Star of Aldebaran”
/ @officialaerium Denny Schneidemesser, “Across the Universe” & “Luminous Rays”
/ denny-schneidemesser.
Join this channel to get access to perks:
/ @isaacarthursfia.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a…
Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264
Reddit: / isaacarthur.
Twitter: / isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: / discord version: / mars-base-narration-only.
Credits:
Becoming an Interplanetary Species: Mars Base.
Science & Futurism with Isaac Arthur.
Episode 261; October 22, 2020
Written, Produced & Narrated by Isaac Arthur.
Written by:
Isaac Arthur.
Editors:
Sentience Beyond Biology — Debate w/Dmitry Volkov, Joscha Bach, Matthew MacDougall, Murray Shanahan
What happens when biology is no longer the foundation for sentience, agency, and consciousness?
This groundbreaking panel discussion brings together some of the world’s most brilliant minds in AI, neuroscience, and philosophy to tackle humanity’s most profound questions about the future of intelligence.
Chaired by neuroscientist Patrick House, the conversation explores the boundaries of machine agency, the possibility of AI emotion, and the future of human–machine interaction.
🎙 Featured Speakers:
- Joscha Bach – Cognitive Scientist, AI Researcher, Philosopher.
- Dmitry Volkov – Co-founder of the International Center for Consciousness Studies (ICCS), Philosopher, Entrepreneur, Founder of Social Discovery Group & EVA AI
- Matthew Macdougall – Head of Surgery at Neuralink, Pioneer in Brain–Computer Interfaces.
- Murray Shanahan – Professor of Cognitive Robotics at Imperial College London, Scientist at DeepMind.
Key Topics in This Debate:
- Whether giving machines “agency” is just a useful human shortcut (The Intentional Stance).
- If the deeper question is not “Is AI conscious?” but “Can it truly love?”
- How modern AI is erasing the Uncanny Valley.
- The challenge of true individuality and creativity in AI-generated art.
- How human biological hardware shapes consciousness — and what this means for building sentient machines.
00:00:00 — Introduction and Presentation of Participants.


Sri Newsletter — “We Speak For The Settlers!”
Space Renaissance International (SRI) is a Permanent Observer at the UN’s Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS). We are currently advocating for: Ownership of resources removed from in place (being considered by the COPUOS Working Group on the Legal Aspects of Space Resource Activity); Permanent advisory status for the private sector in Read More