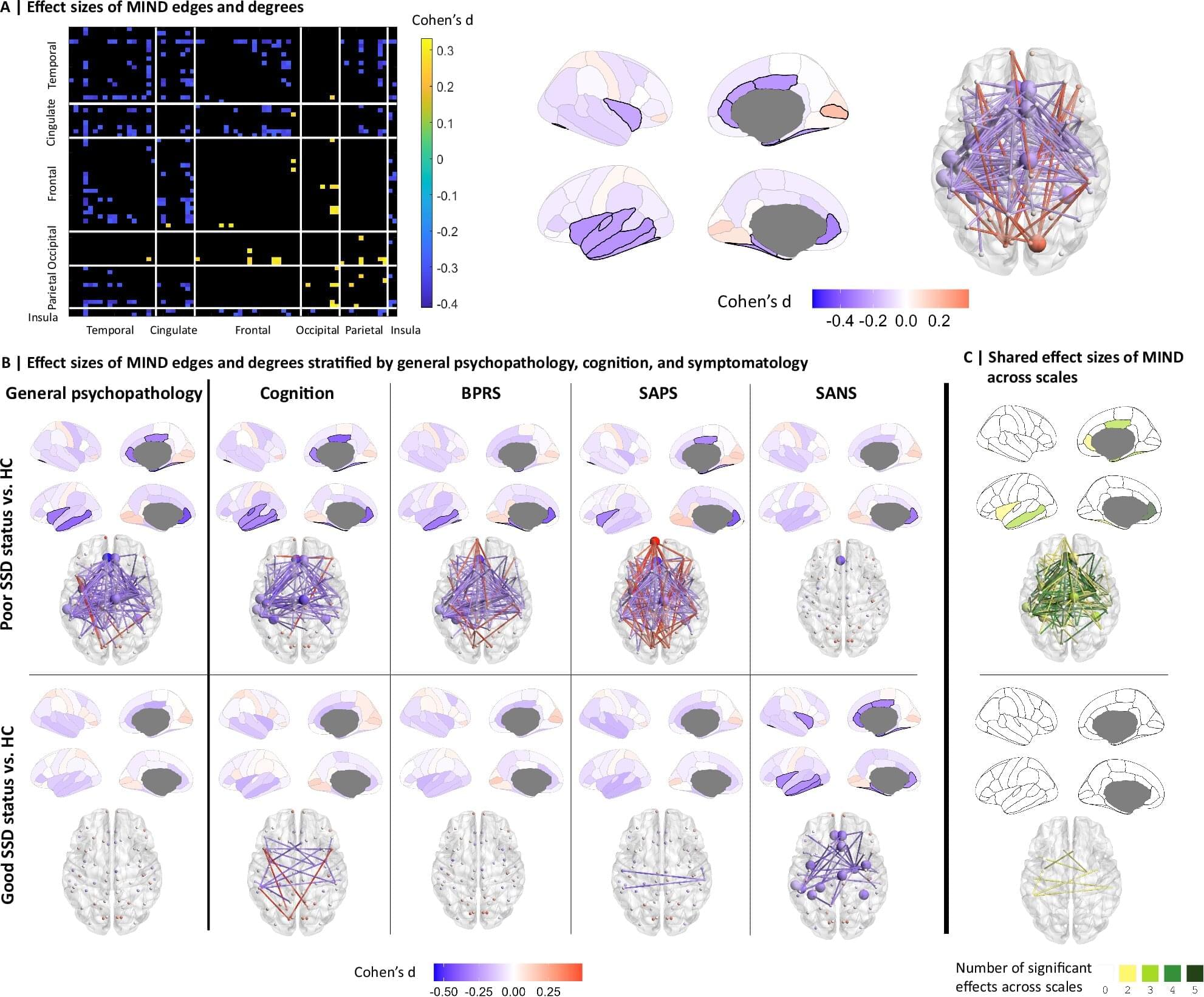
Researchers at the University of Seville have identified the possible origins of structural damage in the brains of patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders (SSDs). These are regions that show the greatest morphological alterations in the early stages of the disease compared to neurotypical people of the same sex and age. The study also found that people with SSD have significant reductions in structural similarity between different regions of the temporal, cingulate and insular lobes.
The research is published in the journal Nature Communications.