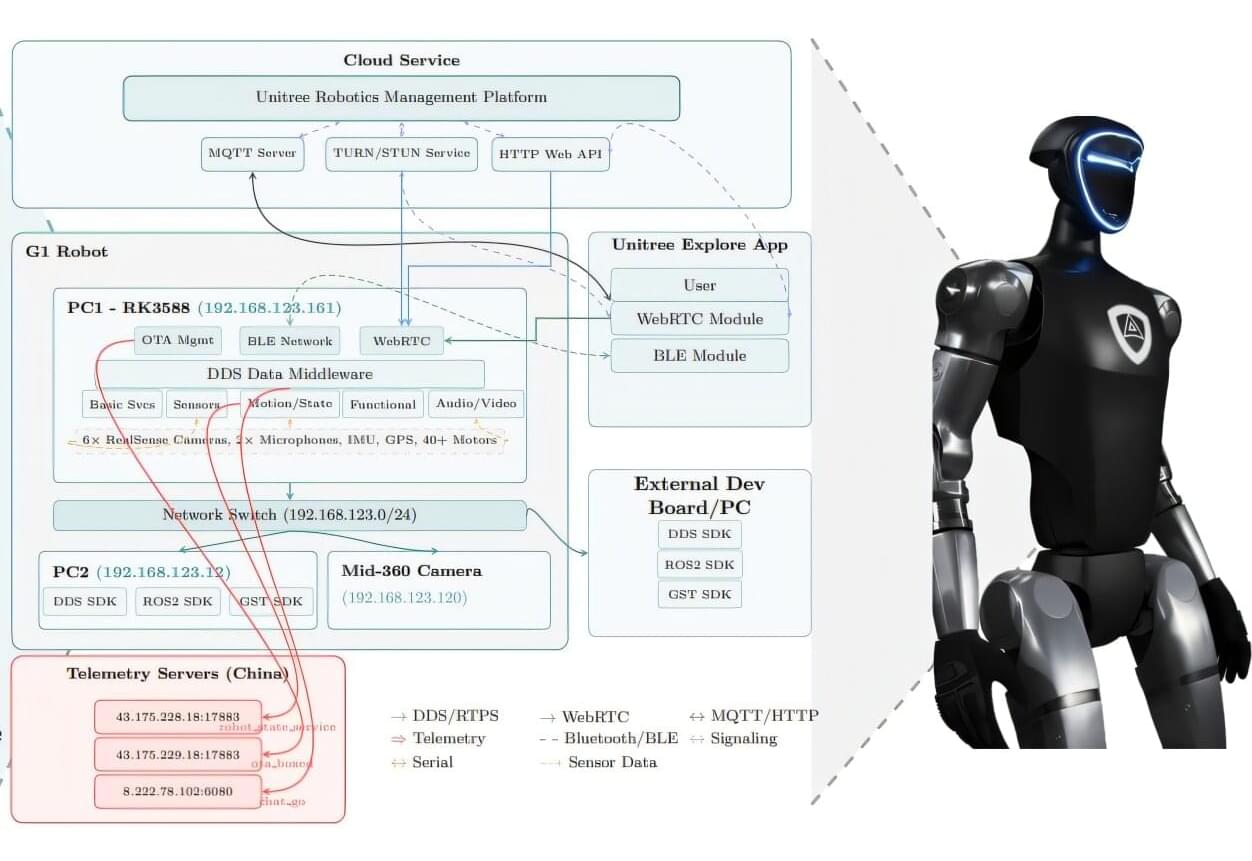
Researchers have uncovered serious security flaws with the Unitree G1 humanoid robot, a machine that is already being used in laboratories and some police departments. They discovered that G1 can be used for covert surveillance and could potentially launch a full-scale cyberattack on networks.
It sounds like the stuff of science fiction nightmares, robots that are secretly spying on you and could be controlled by remote hackers. However, the concern is real, as these types of robots are becoming increasingly common in homes, businesses, critical infrastructure and public spaces.