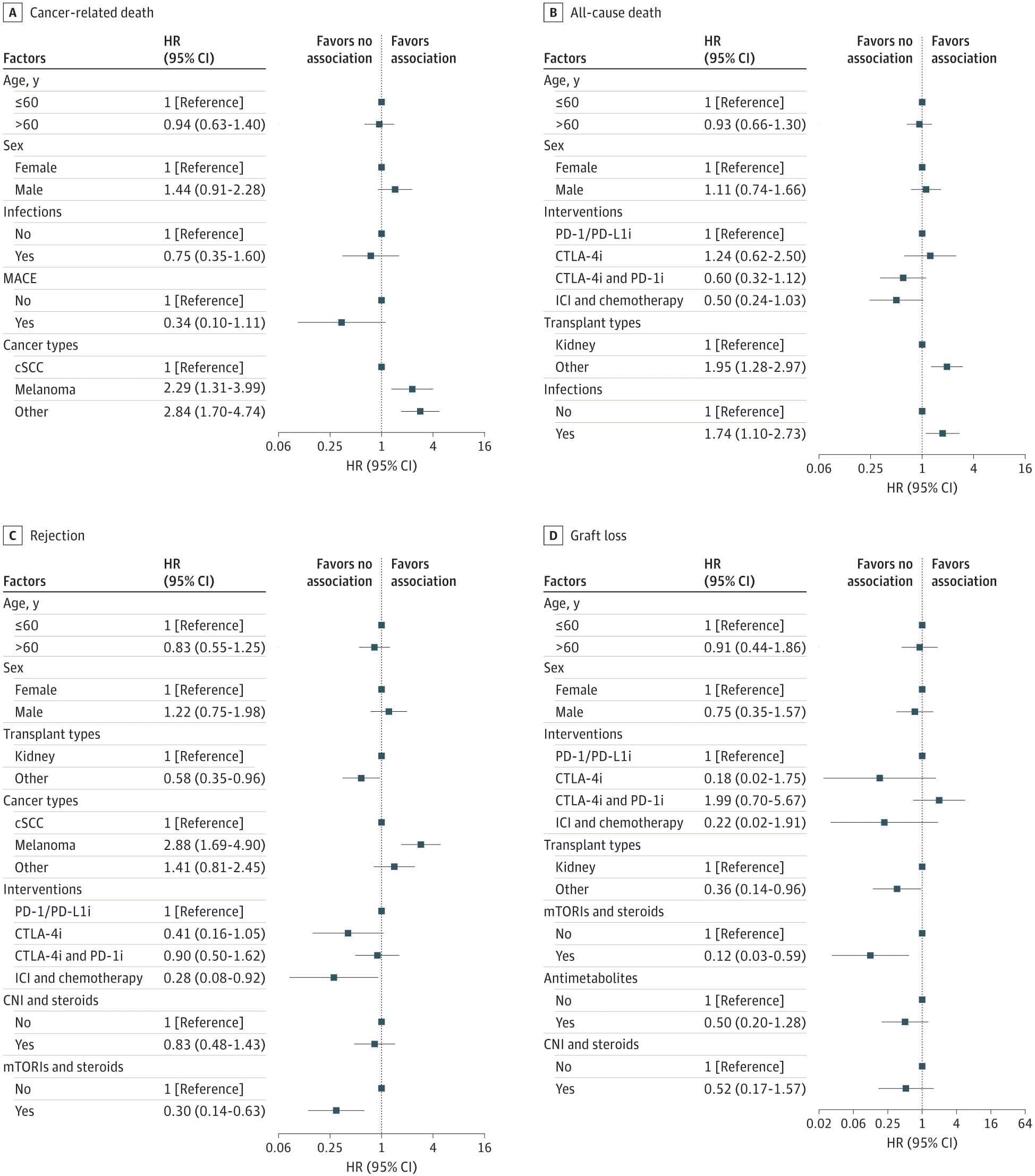
This systematic review and individual participant data met-analysis assesses the cancer-related and survival outcomes in solid organ transplant recipients with advanced-stage cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors.

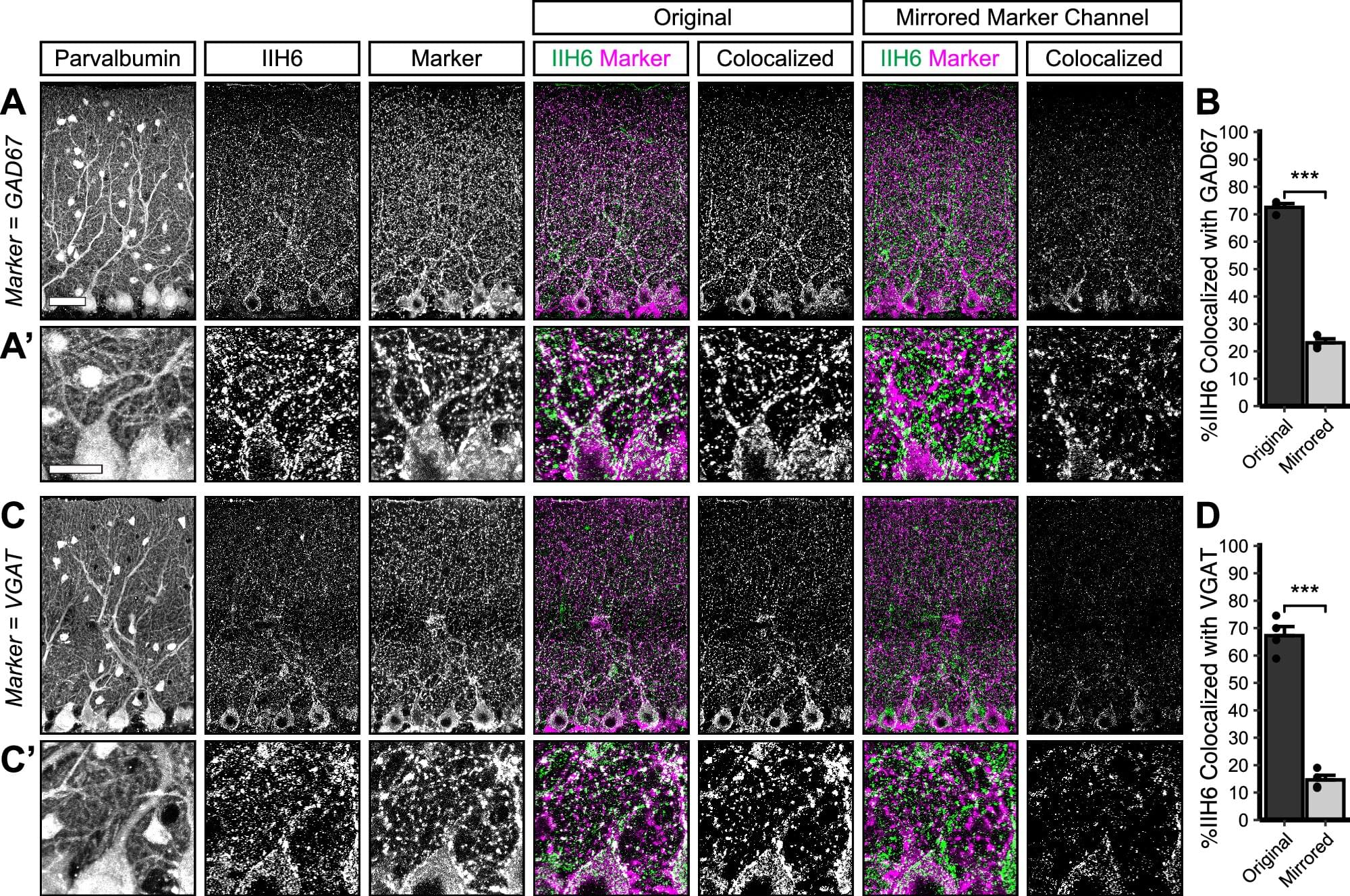
Scientists have uncovered how a protein helps build and maintain vital brain connections, providing insights into the neurological problems experienced by people with a rare form of muscular dystrophy known as dystroglycanopathy.
The research conducted at Oregon Health & Science University and published in Communications Biology reveals that the protein Dystroglycan plays a critical role in forming and maintaining connections between nerve cells in the cerebellum—the part of the brain responsible for movement coordination and motor learning.
In people with dystroglycanopathy, genetic mutations in the protein affect not only muscles but also the brain. The condition is a type of congenital muscular dystrophy, a group of inherited disorders that appear at birth or in early infancy.

Figuring out the ages of stars is fundamental to understanding many areas of astronomy—yet, it remains a challenge since stellar ages can’t be ascertained through observation alone. So, astronomers at the University of Toronto have turned to artificial intelligence for help.
Their new model, called ChronoFlow, uses a dataset of rotating stars in clusters and machine learning to determine how the speed at which a star rotates changes as it ages.
The approach, published recently in The Astrophysical Journal, predicts the ages of stars with an accuracy previously impossible to achieve with analytical models.

A history of Leibniz. Another Historic figure that did more then you or I ever will.