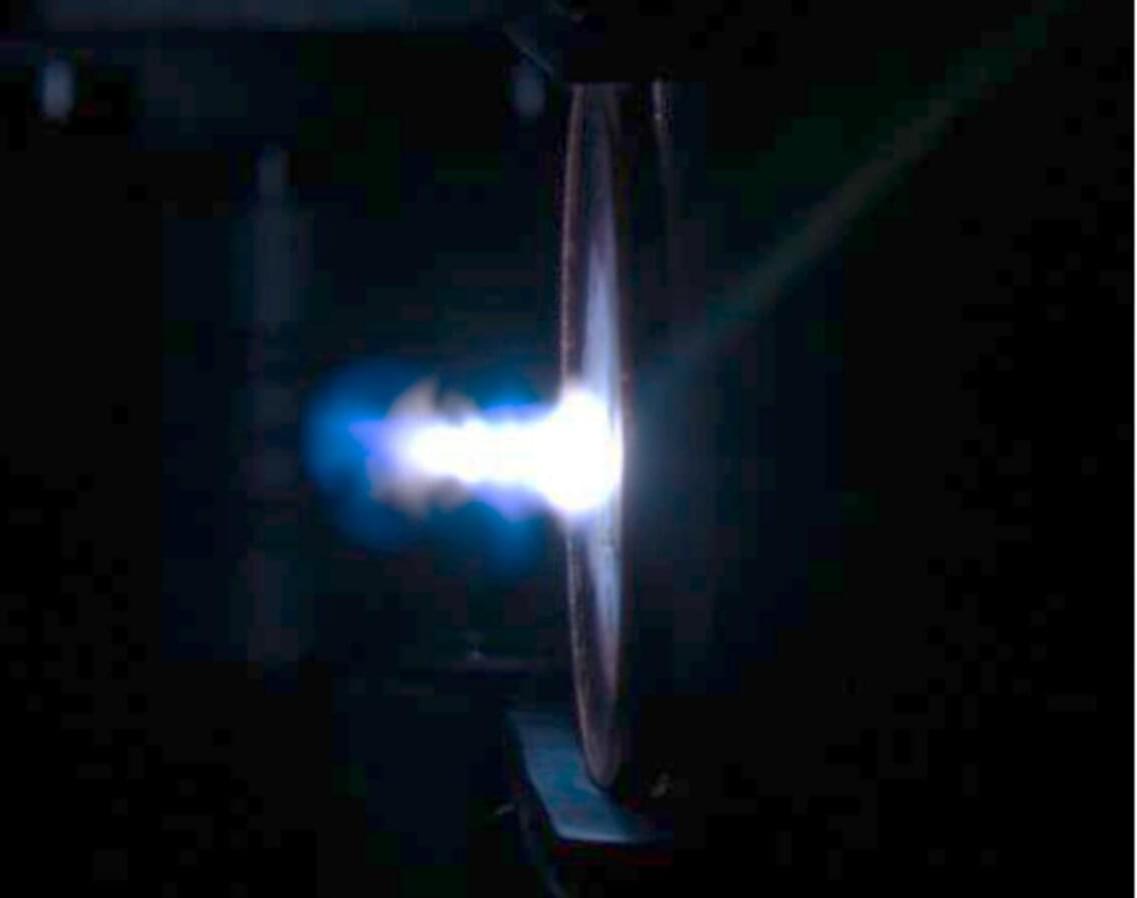
Researchers in the Oregon State University College of Engineering have developed new technology for uranium enrichment measurement and trace element detection, vital for nuclear nonproliferation and supporting the development and operation of next-generation nuclear reactors.
“The technology that we are developing can support nuclear safeguards as well as nuclear energy development,” said Haori Yang, associate professor of nuclear science and engineering. “It can enable on-site enrichment measurements with minimal or no sample preparation, which means a quick turnaround time. It can also be used to monitor fuel in Gen-IV nuclear reactors, such as liquid metal–cooled reactors.”
In its naturally occurring state, uranium contains less than 1% U-235, the isotope that can sustain a nuclear chain reaction; the rest is U-238, which is much less able to do so.